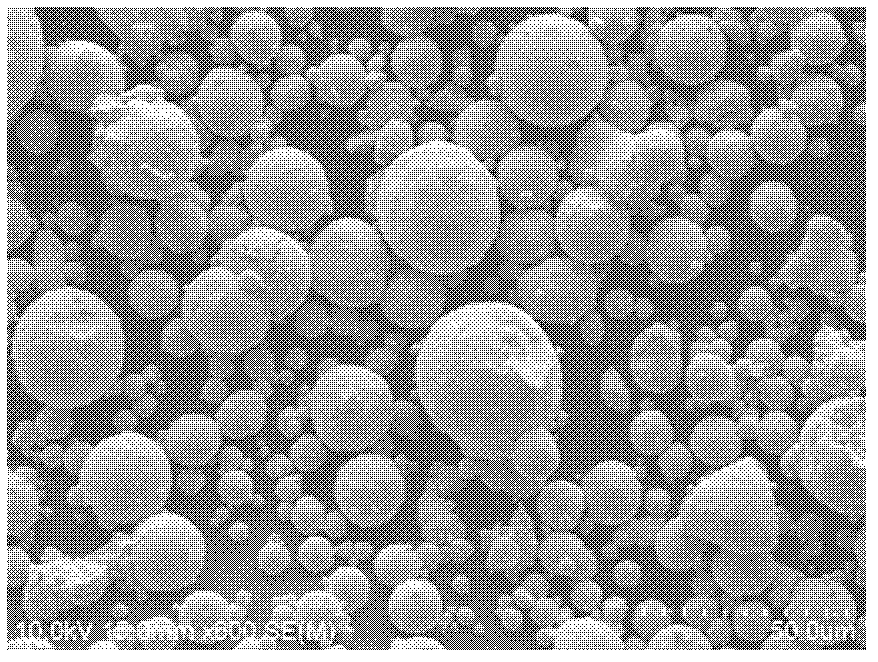
FeMnNi powder accelerant with low cost and preparation method and application
A low-cost, powder-based technology, used in chemical instruments and methods, metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc. The effect of enhancing the ability to dissolve carbon and increasing the nucleation rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The low-cost powder catalyst in this embodiment has an alloy composition of 35% Mn, 8% Ni, 1% Cr, 0.2% C, 0.06% Si, and the balance is Fe. The powder preparation method is as follows:
[0028] 1. Weigh Fe, Mn, Ni, Cr, C, and Si according to the proportion of the formula, and use an intermediate frequency induction furnace to melt and make ingots under the protection of inert gas. The melting temperature of the ingredients is about 1460-1480 ° C, considering the volatilization of Mn elements Mn should be added at the later stage of melting, after adding Mn and melting, keep it for about 5 minutes, and then cast it into an ingot.
[0029] 2. Remelt the alloy ingot at 1460-1650°C. During the melting process, pass through argon gas for protection. The ventilation time is about 10 minutes. Finally, use high-pressure nitrogen gas (pressure 3.0-4.5Mpa) to crush and atomize the metal liquid flow into powder .
[0030] The catalyst powder of the formula was prepared by the abo...
Embodiment 2
[0035]The preparation equipment and operating method of the powder catalyst are the same as in Example 1, except that, by mass percentage, the batching composition of the catalyst alloy is 40% Mn, 8% Ni, 1% Cr, 0.2% C, 0.06% Si, and the remaining The amount is Fe. The oxygen content of the catalyst powder was measured to be 263 ppm and the nitrogen content to be 145 ppm.
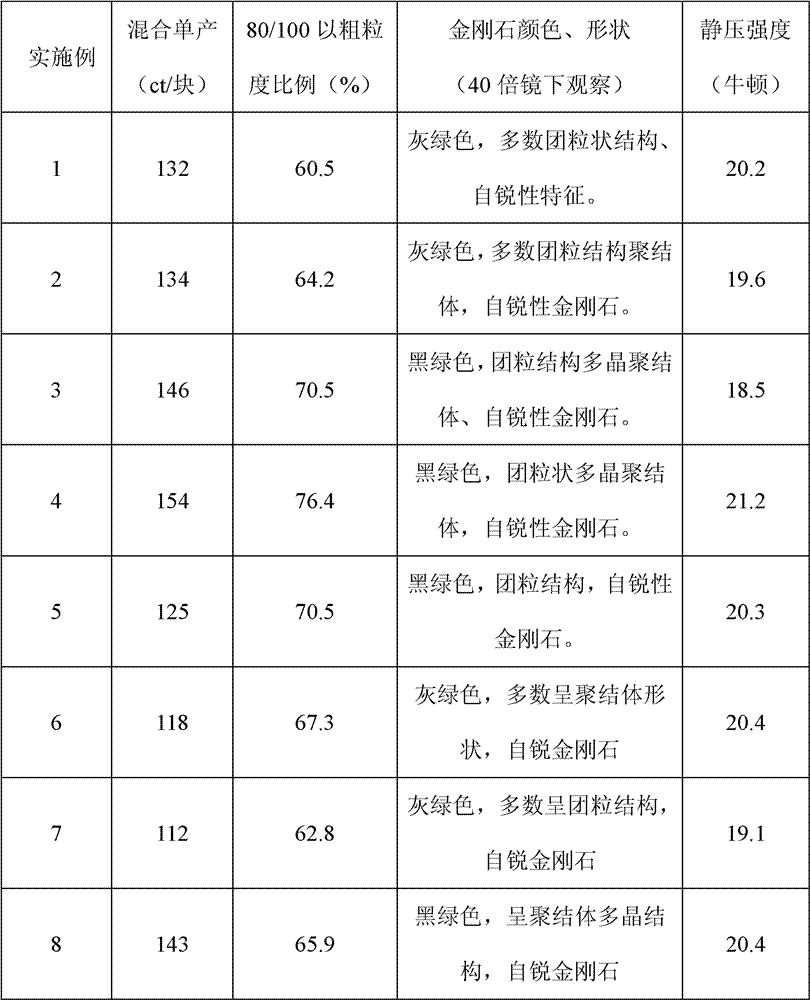
[0036] After sieving the alloy powder, take -325 mesh catalyst powder and graphite powder and mix uniformly at a ratio of 4:6 to prepare a synthetic rod. Also use a Φ40mm cavity at a pressure of about 5.4Gpa, a temperature above 1450°C, and a heating time of about 15 minutes Diamond synthesis was carried out under the following conditions, and the obtained diamond was subjected to particle size analysis, color, shape observation and static pressure strength test. The test results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0038] The preparation equipment and operating method of the powder catalyst are the same as in Example 1, but the difference is that, by mass percentage, the batching composition of the catalyst alloy is 45% Mn, 8% Ni, 1% Cr, 0.2% C, 0.06% Si, and the remaining The amount is Fe. The oxygen content of the catalyst powder was measured to be 280 ppm and the nitrogen content to be 168 ppm.
[0039] After sieving the alloy powder, take -325 mesh catalyst powder and graphite powder and mix uniformly at a ratio of 4:6 to prepare a synthetic rod. Also use a Φ40mm cavity at a pressure of about 5.4Gpa, a temperature above 1450°C, and a heating time of about 15 minutes Diamond synthesis was carried out under the following conditions, and the obtained diamond was subjected to particle size analysis, color, shape observation and static pressure strength test. The test results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com