Radio frequency low noise amplifier with high linearity
A low-noise amplifier and radio-frequency technology, which is applied to high-frequency amplifiers, improved amplifiers to reduce noise effects, and improved amplifiers to reduce nonlinear distortion. It can solve the problems that low-noise amplifiers are difficult to achieve low noise and high linearity at the same time. Achieve the effect of realizing monolithic integration, ensuring low noise performance, and maintaining noise performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
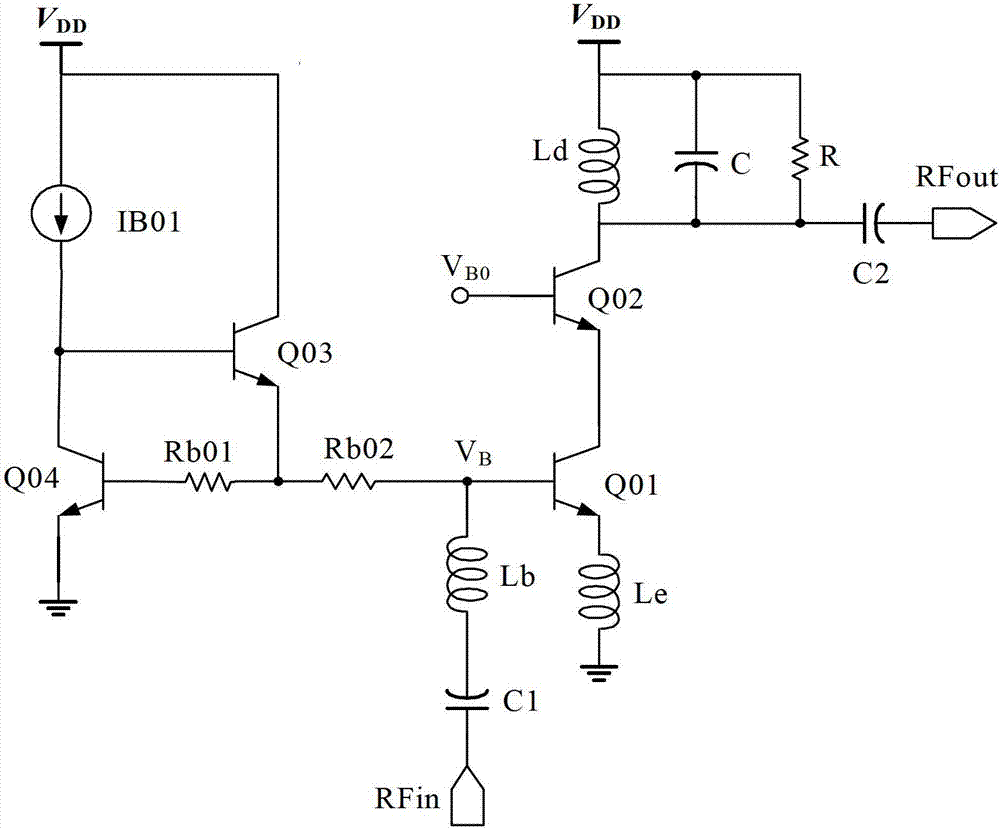
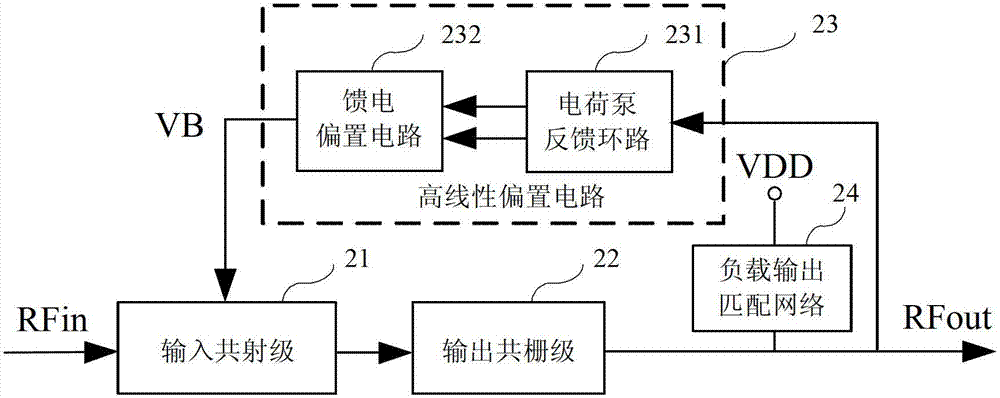
[0050] Figure 4a and Figure 4b The circuit diagrams of the high-linearity RF low-noise amplifiers of the first embodiment and the second embodiment of the present invention are given. As shown in FIG. 4 , the high linearity radio frequency low noise amplifier mainly includes four parts: an input cascode stage 41 , an output cascode stage 42 , a load output matching network 43 and a high linearity bias circuit 44 . The input common emitter stage 41 converts the radio frequency input voltage signal into a current signal while providing low noise performance; the output common gate stage 42 adds the current signal output by the input common emitter stage 41 to the load output matching network 43, while outputting impedance matching , the resonant load obtains high gain, and generates an output voltage signal amplified by low noise at the output terminal RFout. The high linearity bias circuit 44 provides a constant bias voltage V for the input tube of the input common emitter ...
no. 2 example
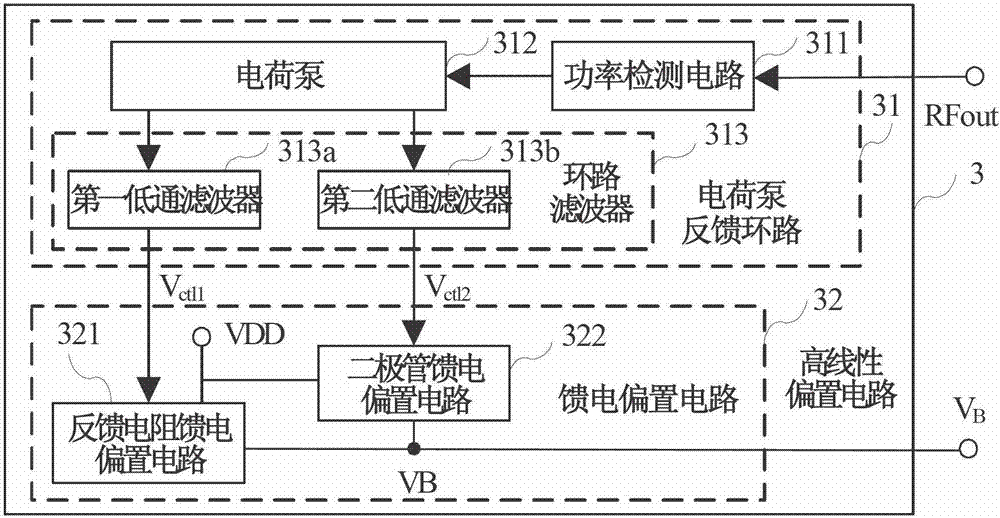
[0062] Figure 4b The second embodiment circuit shown with Figure 4a The circuit of the first embodiment shown is basically the same, the difference between the two embodiments is that the diode feed bias circuit is composed of the second current source IB2, the third MOS transistor M3, the fourth MOS transistor M4 and the fifth MOS transistor Composed of M5, the third MOS transistor M3, the fourth MOS transistor M4 and the fifth MOS transistor M5 are diode-connected structures, that is, their gates and drains are short-circuited. The source of the fourth MOS transistor M4 is connected in series with the drain of the fifth MOS transistor M5, and the source of the fifth MOS transistor M5 is grounded.
[0063] The output end of the second current source IB2 is connected to the drain of the third MOS transistor M3 and the drain of the fourth MOS transistor M4, and the source of the fifth MOS transistor M5 is grounded; the output end of the diode feed bias circuit 462 is the thi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com