Method for preparing neodymium-iron-boron material through main-auxiliary alloy method
A technology of neodymium iron boron and main alloy, which is applied in the direction of magnetic materials, magnetic objects, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of reducing Nd content and not involving Nd, DY, Tb, etc., so as to improve coercive force and reduce production cost Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] An inexpensive NdFeB material, formulated as follows:
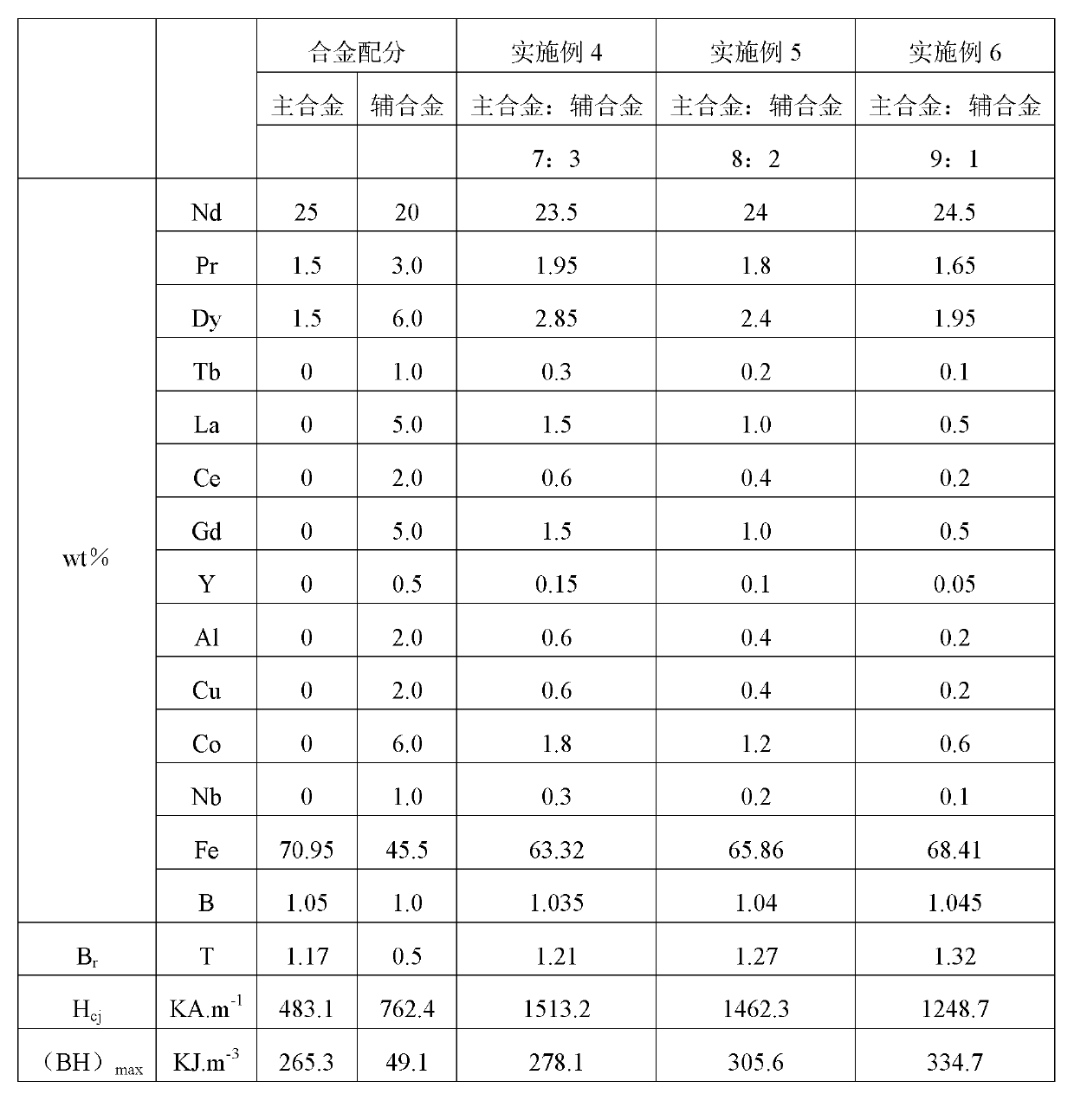
[0035] Main alloy composition in table 1 embodiment 1:
[0036] the element
Nd
Pr
Fe
B
Dy
Wt%
23.9
5.0
65.26
1.1
2.0
[0037] Auxiliary alloy composition in table 2 embodiment 1:
[0038] the element
Ce
Fe
Tb
co
Al
Cu
Ga
Nb
Wt%
58
34.9
1.5
3.0
1.1
0.8
1.0
1.2
[0039] Next, use the following steps to make NdFeB permanent magnet materials:
[0040] 1) Melting and casting The prepared main alloy and auxiliary alloy are respectively melted evenly in a vacuum induction quick-setting furnace, and then cast into ingots with a thickness of 20mm.
[0041] 2) Powder making Mix the smelted main and auxiliary alloy ingots at a ratio of 90:10, and grind them into powders with a particle size of 3-5 μm through hydrogen crushing, coarse grinding, intermediate crushing and jet mi...
Embodiment 2
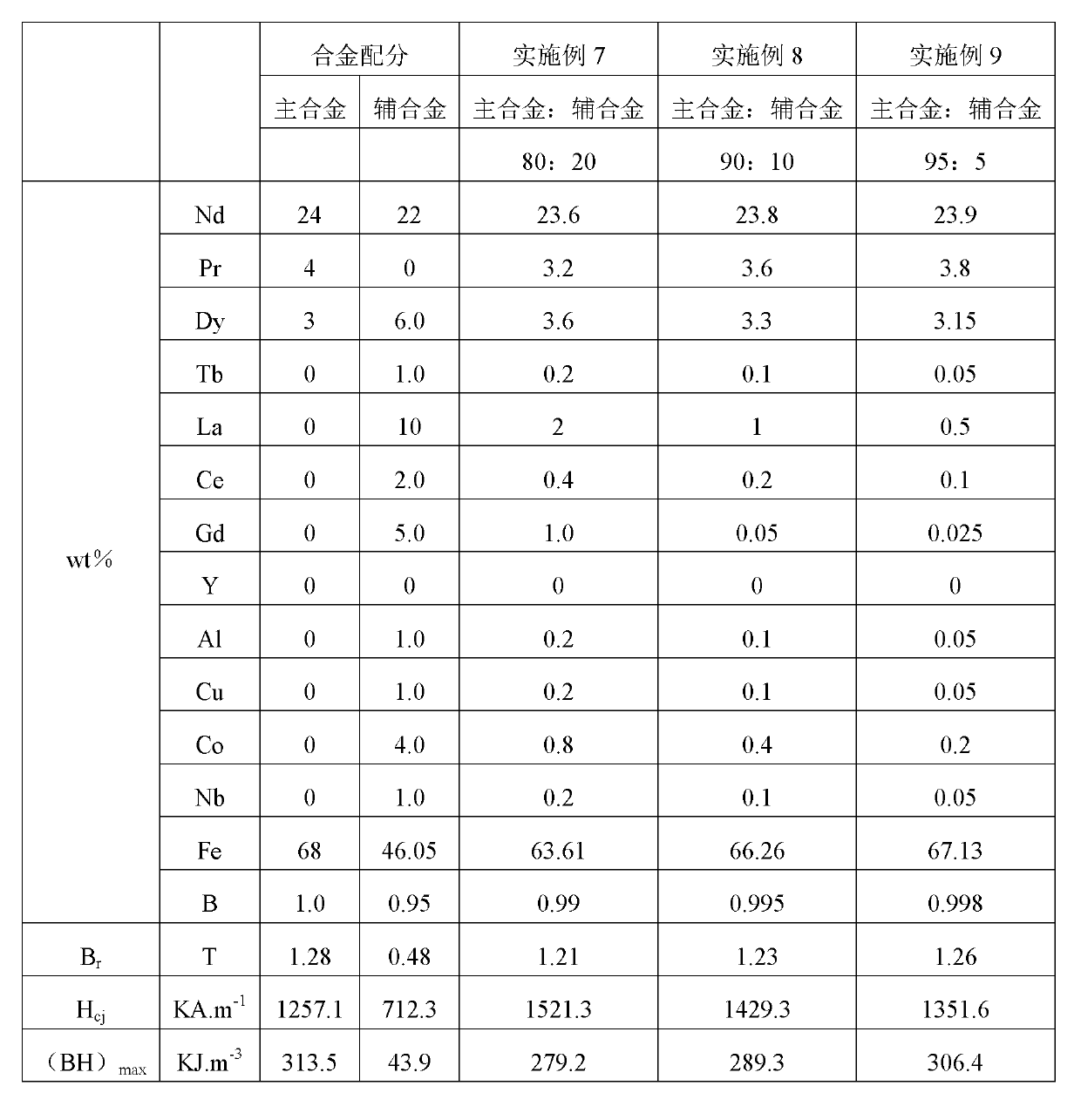
[0056] Table 5 Example 2 main alloy composition:
[0057] the element
[0058] Table 6 Example 2 Auxiliary Alloy Components:
[0059] the element
[0060] The main and auxiliary alloys are smelted in a vacuum quick-setting furnace; they are thrown into quick-setting thin strips with a thickness of about 0.2 mm, mixed at a ratio of 92:8, and then made into powders with an average particle size of 3-5 μm by hydrogen crushing, medium crushing and jet milling , Using rubber molding in a magnetic field to form a billet, after isostatic pressing, sinter in a vacuum sintering furnace at 1080°C for 2 hours, and then heat-treat at 900°C×0.5h+580°C×2h to make a billet.
Embodiment 3
[0069] Table 9 Example 3 main alloy composition:
[0070] the element
[0071] Table 10 Example 3 Auxiliary Alloy Components:
[0072] the element
[0073] The main alloy is smelted in a vacuum quick-setting furnace, and it is thrown into a quick-setting thin strip with a thickness of about 0.2mm. After hydrogen crushing, medium crushing and jet milling, it is made into a powder with an average particle size of 3-5μm. The auxiliary alloy is made in a vacuum electric arc furnace. It is smelted into an ingot, and then under the protection of an organic solvent, it is ground into a powder with an average particle size of 3-5 μm by disc milling and ball milling. The main alloy and the auxiliary alloy powder are mixed evenly at a ratio of 80:20, and pressed into a blank by molding in a magnetic field. After isostatic pressing, it is sintered in a vacuum sintering furnace at 1090°C for 3 hours, and then at 900°C×40min+580 ℃ × 2.5h heat treatment made into billet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com