Aspergillus oryzae strain and method for producing fungal alpha-amylase by liquid-state fermentation of aspergillus oryzae strain
A technology of liquid fermentation and Aspergillus oryzae, which is applied in the field of microbial fermentation, can solve the problems of expensive industrial production cost of fungal α-amylase, and achieve the effects of high yield, fast growth and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] The mutagenesis screening of embodiment 1 Aspergillus oryzae bacterial strain of the present invention
[0035] The mutagenesis screening steps are as follows:
[0036] (1) Treatment of monospore suspension: Take a fresh slant (plate) coated with the original strain (Aspergillus oryzae strain with preservation number CGMCC1.1923) and add 10ml of sterile saline, and use an inoculation needle to gently inoculate the Scrape off the spores, pour them into a sterile small Erlenmeyer flask with glass beads, oscillate to disperse the spores, filter them with absorbent cotton; count them with a microscope, and dilute the concentration of spores to n×10 6 a / ml;
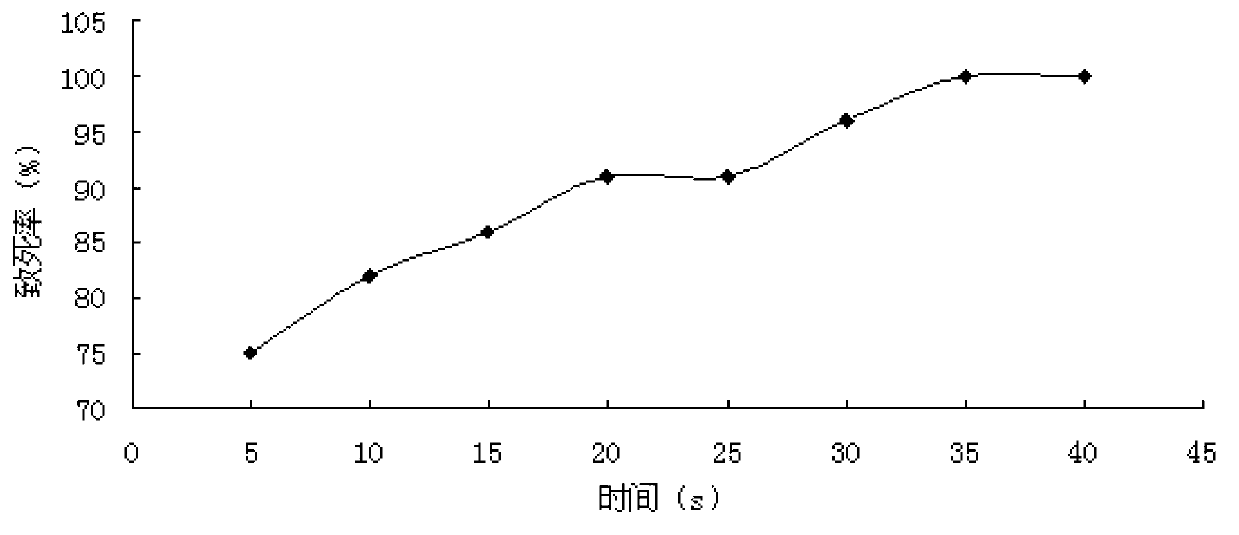
[0037] (2) Selection of mutagenic dose: Take 5 mL of dispersed spore suspension into a sterile plate, place it in an ultraviolet mutagenesis box, and set time doses of 5 s, 10 s, 15 s, 20 s, 25 s, and 30 s for mutagenesis. After the mutagenesis is completed, spread after multiple dilution, and use the diluted bacteria...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Embodiment 2 method of the present invention produces fungal α-amylase (50 liters of fermentation tanks)
[0042] 1. Medium [by weight and volume percentage (g / ml)]:
[0043] 1. Seed medium: 6% potato starch, 2% yeast powder, 0.3% dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.3% magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, the balance is water, and the pH is 6.5;
[0044] 2. Fermentation medium in a 50-liter tank: 6% potato starch, 2% yeast powder, 0.3% dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.3% magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 0.01% soybean oil, the balance is water, and the pH is 6.5.
[0045] 2. Pretreatment
[0046] Strain culture:
[0047] Take an appropriate amount of Aspergillus oryzae strains with the preservation number CGMCC No.6834, and put them into four 500mL Erlenmeyer flasks, each containing 100ml of seed medium; culture conditions: 30°C, 200rpm shaker, culture for 48 hours, until the bacteria The liquid is viscous; use a portable all-stainless steel pulverizer to disperse the myceli...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Embodiment 3 method of the present invention produces fungal α-amylase (10 tons of fermentation tanks)
[0057] 1. Medium [by weight and volume percentage (g / ml)]:
[0058] 1. Seed medium: 6% potato starch, 2% yeast powder, 0.3% dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.3% magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, the balance is water, and the pH is 6.5;
[0059] 2. Fermentation medium: 4% potato starch, 6% soybean flour, 1% ammonium sulfate, 0.3% dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.3% magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 0.03% soybean oil, the balance is water, pH 6.5
[0060] 2. Pretreatment
[0061] 1. Strain culture:
[0062] Take an appropriate amount of Aspergillus oryzae strains with a preservation number of CGMCC No.6834, and insert them into five 1000mL Erlenmeyer flasks, each of which contains 200ml of seed medium; culture conditions: 30°C, 200rpm shaker culture, culture for 48 hours, Until the bacterial liquid is thick; use a portable all-stainless steel pulverizer to break up the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com