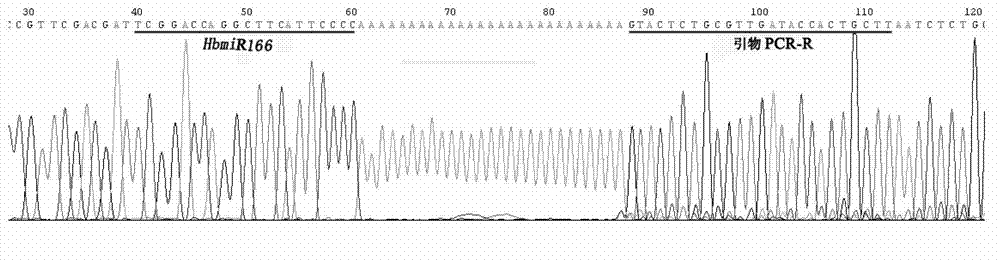
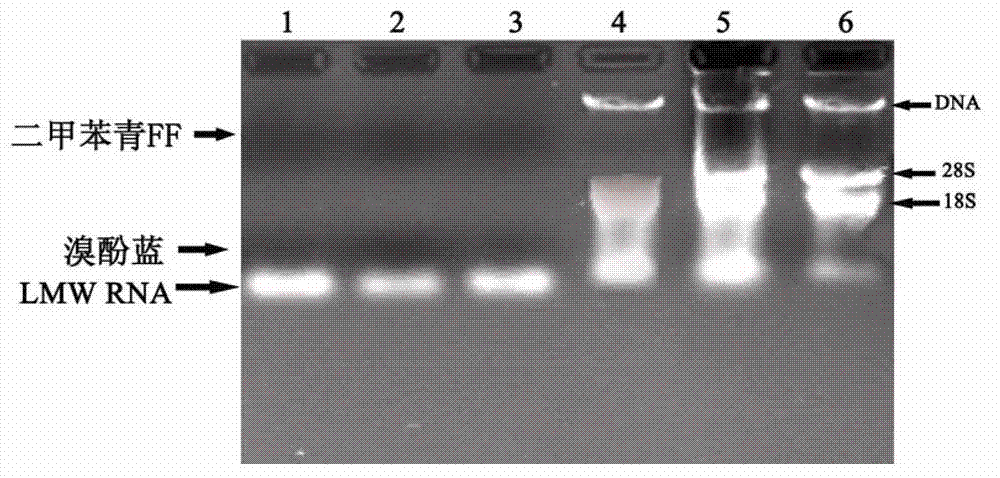
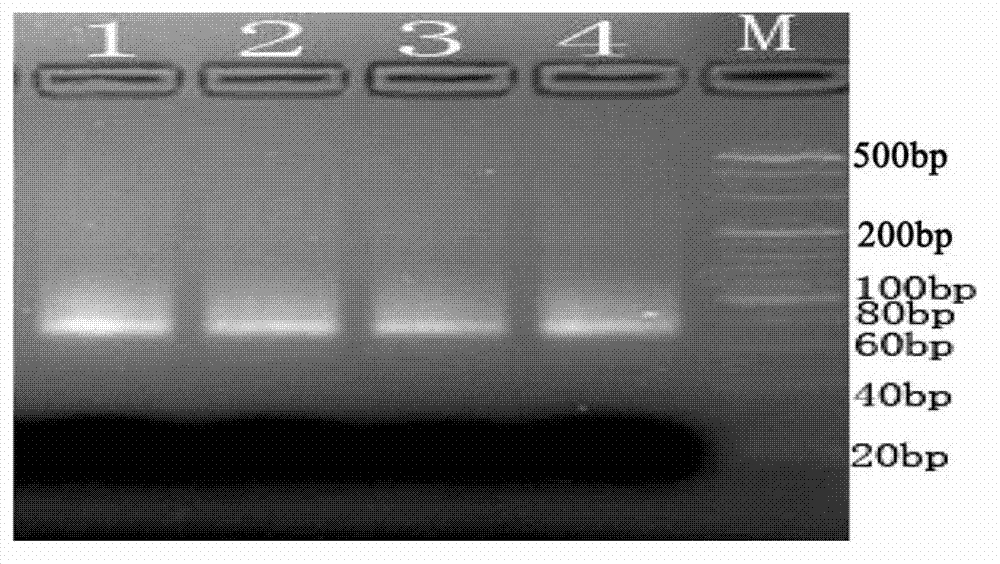
Method for separating low-molecular weight ribonucleic acid (RNA) of plant
A low-molecular-weight, high-molecular-weight technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems such as being unsuitable for large-scale extraction of small RNA, low yield of small RNA, expensive and other problems, achieving clear electrophoresis bands, low experimental cost, and easy operation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The following examples are used to illustrate the present invention, but are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
[0027] When implementing the present invention, available pawpaw, banana, the fresh blade of rubber tree. The implementation steps are:
[0028] (1) Weigh 0.5g leaves, grind them into powder with liquid nitrogen, quickly transfer the powder to a 15ml centrifuge tube, and add CTAB extraction buffer [2% hexadecane] preheated at 65°C to the centrifuge tube trimethylammonium bromide, 25mmol / L ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, 2mol / L sodium chloride, 3% polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP-40), 100mmol / L trishydroxymethylaminomethane (pH8.0), 0.5g / L spermidine] 5ml and β-mercaptoethanol 200μl, shake and mix; then add water-saturated phenol: chloroform: isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1) solution 5ml to the centrifuge tube, cover the centrifuge tube Tight, invert 50 times to mix evenly, and then centrifuge at 12000rpm for 20min at 4°C.
[0029] (2) Transfer t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com