Method and system of laser scanning phase-microscope imaging
A technology of laser scanning and microscopic imaging, which is applied in the field of optical imaging, can solve problems such as fusion, lack of sample phase information transformation, unfavorable fusion of laser scanning confocal microscopic technology, etc., to shield the impact of imaging quality and simplify the switching process Easy operation, high imaging contrast effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
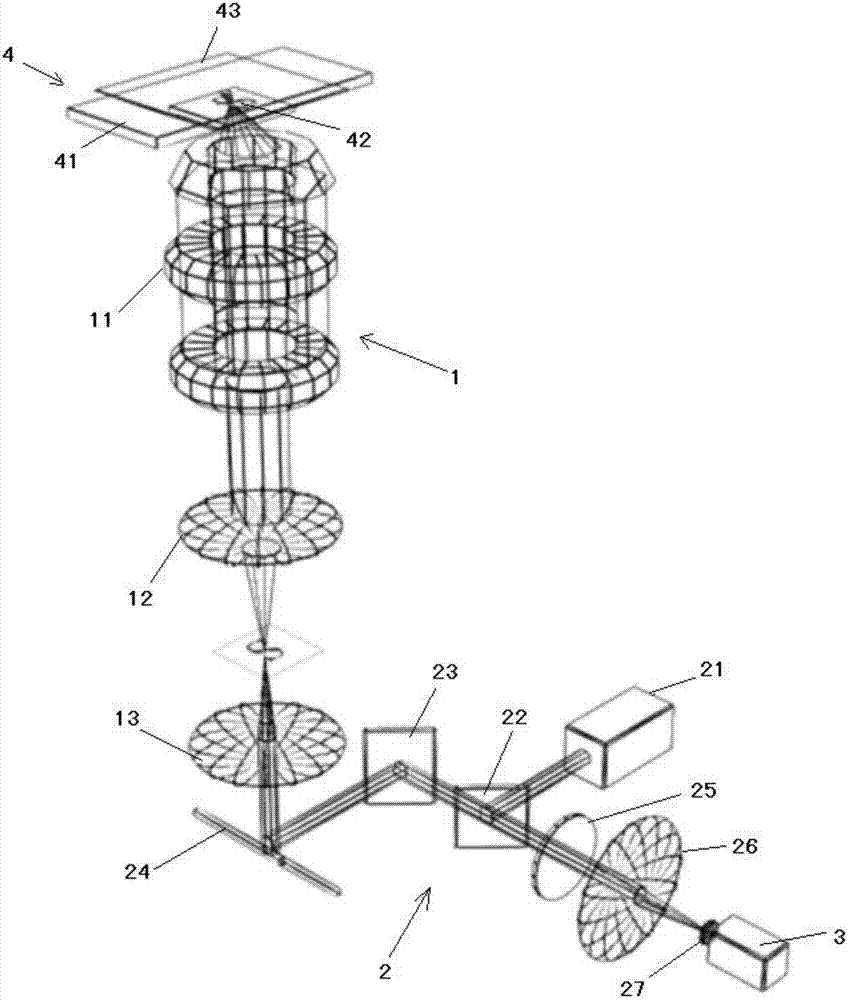
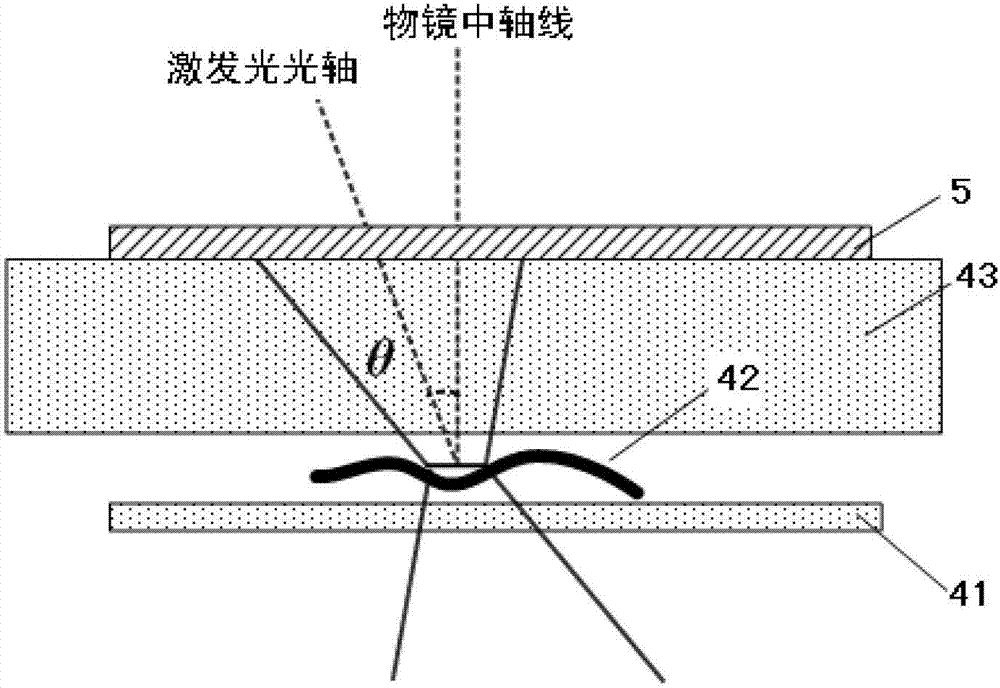
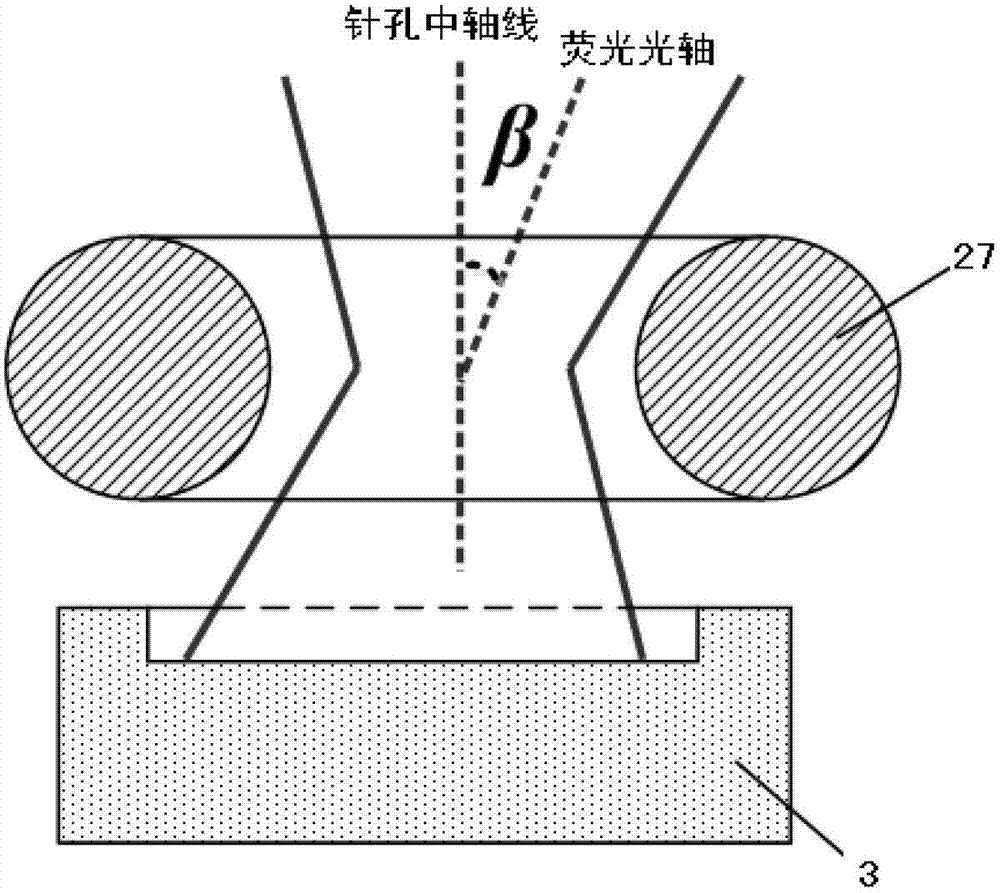
[0018] Such as figure 1As shown, the laser scanning phase microscopy imaging system of the present invention includes a fluorescence microscope 1, a laser confocal scanning system 2 and a photoelectric detection system 3; the fluorescence microscope 1 includes an objective lens 11, a tube mirror 12 and a scanning mirror 13; The focusing scanning system 2 includes a laser 21, a dichroic mirror 22, an X-direction scanning galvanometer 23, a Y-direction scanning galvanometer 24, a filter 25, a converging lens 26, and a pinhole 27; At the light entrance hole of the pinhole 27, the photodetection system 3 is located in the light exit direction of the pinhole 27, and is used to receive the fluorescence transmitted by the biological sample. The laser 21 emits excitation light to the dichroic mirror 22 for reflection or transmission (light splitting), and th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com