Method for quantification collecting heavy metal cations in water environment
A technology for quantitative collection and heavy metals, applied in the preparation of test samples, sampling devices, etc., can solve the problems of high detection limit, destroying solution balance, affecting the chemical form distribution of heavy metals, etc., and achieves a simple collection device and low detection limit. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] 1) Take a cellulose acetate membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 2000-12000 as a dialysis membrane, soak it in deionized water and boil to pretreat the cellulose acetate membrane, change the water every 20 minutes, and the cumulative boiling time is 2 hours;
[0040] 2) Use the cellulose acetate membrane pretreated in step 1) to make a dialysis bag, put the binder water-soluble polyaspartic acid into the dialysis bag, soak in deionized water for 72 hours for purification, and change the water every 12 hours;
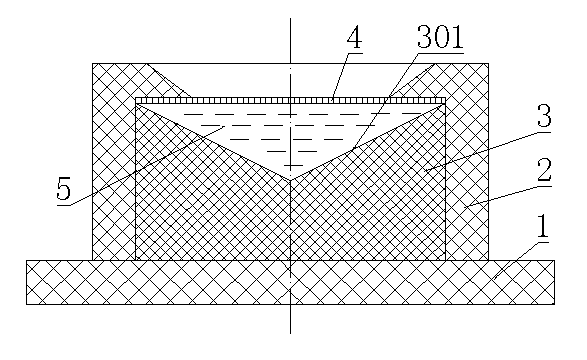
[0041] 3) Make the purified binder into a 0.005mol / L water-soluble polyaspartic acid solution, and take 3 collection devices made of polypropylene with a volume of 2mL, such as figure 1 As shown, the acquisition device includes a fixed plate 1, on which a shell 2 with an inner edge is provided, a support body 3 is arranged in the shell 2, and a The dialysis membrane 4 is provided with an inverted tapered groove 301 on the support body 3, and the groove 301 ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] 1) Take a cellulose acetate membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 2000-12000 as a dialysis membrane, soak it in deionized water and boil to pretreat the dialysis membrane, change the water every 20 minutes, and the cumulative boiling time is 1 hour;
[0044] 2) Use the cellulose acetate membrane pretreated in step 1) to make a dialysis bag, put the binder water-soluble polyaspartic acid into the dialysis bag, soak in deionized water for 168 hours for purification, and change the water every 24 hours;
[0045] 3) Make the purified binder into a 0.005mol / L water-soluble polyaspartic acid solution, and take 3 collection devices made of polypropylene with a volume of 2mL. The structure of the collection devices is the same as in Example 1; 2mL 0.005mol / L water-soluble polyaspartic acid solution, seal the device with the cellulose acetate membrane pretreated in step 1), put the device dialysis membrane down, hang it on the support and float on the surface containing Cu ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] 1) Take a cellulose acetate membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 2000-12000 as a dialysis membrane, soak it in deionized water and boil to pretreat the dialysis membrane, change the water every 30 minutes, and the cumulative boiling time is 3 hours;
[0048] 2) Use the cellulose acetate membrane pretreated in step 1) to make a dialysis bag, put the binder water-soluble polyaspartic acid into the dialysis bag, soak in deionized water for 108 hours for purification, and change the water every 18 hours;
[0049] 3) Make the purified binder into a 0.020mol / L water-soluble polyaspartic acid solution, and take 12 collection devices made of polypropylene with a volume of 2mL. The structure of the collection devices is the same as in Example 1; 2mL 0.020mol / L water-soluble polyaspartic acid solution, seal the device with the cellulose acetate membrane pretreated in step 1), put the device dialysis membrane down, hang it on the support and float on the 2+ In the water bod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com