Bacterial strain capable of secreting cellulase as well as cellulase extraction method and application thereof
A cellulase and high cellulose technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of low enzyme activity and yield, and achieve the effects of high cellulose degradation activity, wide industrial application prospects, and wide sources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1: Screening of bacterial strains
[0044]Trichoderma virens ZY-01 of the present invention (Trichoderma virens ZY-01, preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, the preservation number is CCTCC No: M 2012205, and the preservation date is June 5, 2012) is a strain belonging to fungi, The strain was isolated from soil and obtained by enrichment and screening from soil samples with the substrate carboxymethylcellulose sodium (CMC?Na) as the only carbon source.
[0045] The method for screening high-efficiency cellulase strains is:
[0046] (1) Weigh 10 g of soil sample (in this example, the soil is taken from the corn stalk crop field), add 90 mL of sterile water, and oscillate to form a suspension. Stand still to clarify the supernatant and set aside;
[0047] (2) Take 1 mL of the supernatant after standing still, inoculate it in Congo red selective medium under sterile conditions, and culture it at 30-40 ℃ for 3-5 days;
[0048] (3) After 3-5 ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: bacterial strain identification
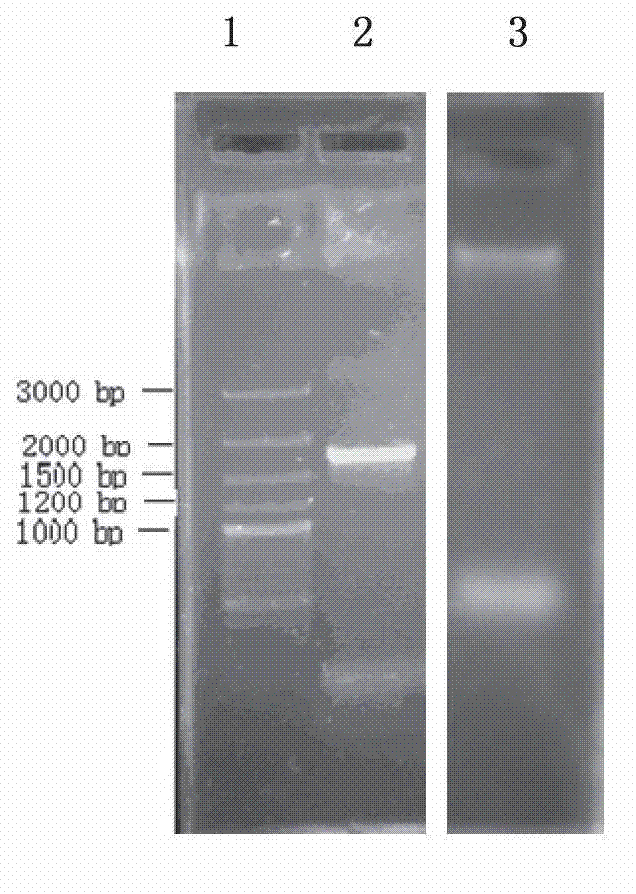
[0050] (1) The isolated bacterial strain in embodiment 1 adopts CTAB method to extract its genomic DNA:
[0051] Take 10 mL of bacterial liquid in a centrifuge tube at 4 °C and centrifuge at 10,000 r / min for 10 min to obtain mycelium; add 4 mL of CTAB and 0.8 mL of mercaptoethanol to the mycelia, mix evenly, and put in a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube for 30 min in a water bath ; Add an equal volume of phenol / chloroform isoamyl alcohol (the volume ratio of chloroform / isoamyl alcohol is 24:1), shake well, and centrifuge at 12000 r / min at 4 °C for 10 min; add 2 μL RNase to the supernatant, After mixing, keep in a 37°C water bath for 20-30 min; after the water bath, divide the mixture into 1.5 mL centrifuge tubes, about 400 μL per tube; add 2 times the volume of absolute ethanol and 1 / 10 volume of NaAC solution to precipitate; After the precipitation was complete, the supernatant was discarded by centrifugation, washed 2-3 times wit...
Embodiment 3-5
[0055] Embodiment 3-5: bacterial strain fermentation produces enzyme
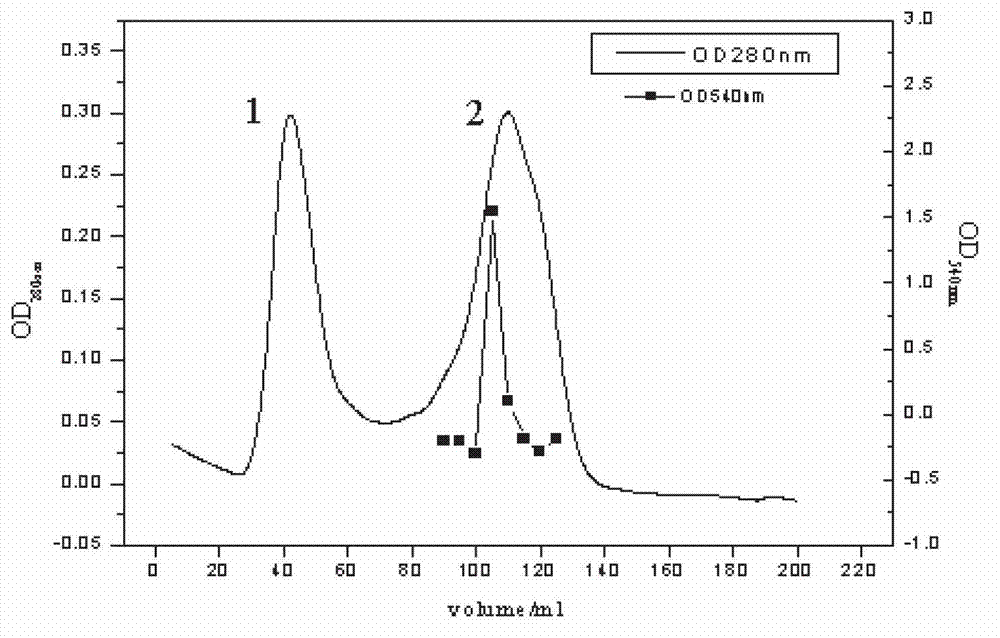
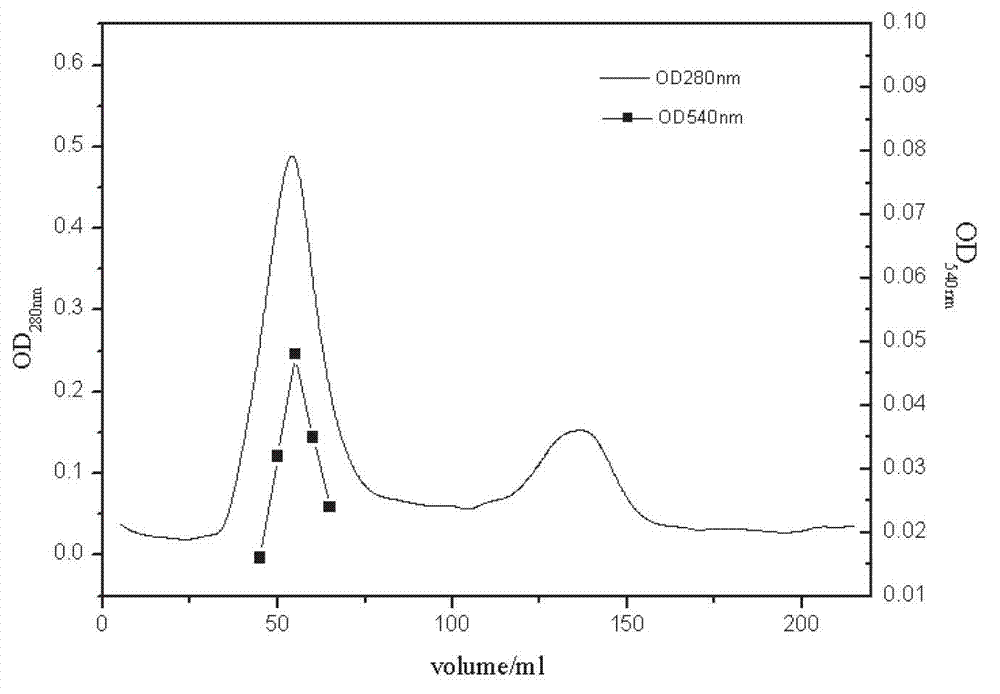
[0056] The bacterial strain obtained in Example 1 was transferred into a fermentation medium for fermentation to produce enzymes to obtain crude enzyme liquid. The fermentation medium components of the strains described in the examples mainly involve carbon sources, nitrogen sources, and inorganic salts. The carbon source in the fermentation medium is sodium carboxymethylcellulose (CMC?Na), the nitrogen source is yeast extract (OXOID, UK), and the inorganic salts are NaCl and MgSO 4 ?7H 2 O and K 2 HPO 4 . The specific steps are shown in Table 1:
[0057]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com