Nanofiber based flexible high performance thermoelectric material and preparation method thereof
A technology of nanofibers and thermoelectric materials, applied in the field of new energy thermoelectric conversion materials, can solve the problems of increasing the Seebeck coefficient, reducing the thermal conductivity of the lattice, and unable to solve the problem of thermal shock stress, which is easy to operate, repeat, and produce. Simple and convenient equipment, easy to promote and apply
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] In a 50ml Erlenmeyer flask, add 0.7g polyacrylonitrile (Mw=80,000) into 10ml N,N-dimethylformamide, stir at 60°C for 8h until the solution is completely clear, then cool to room temperature; 0.3g of silver nitrate was added to the above-mentioned polymer mixed solution, and stirred vigorously for 1h under the condition of avoiding light to make it evenly mixed.
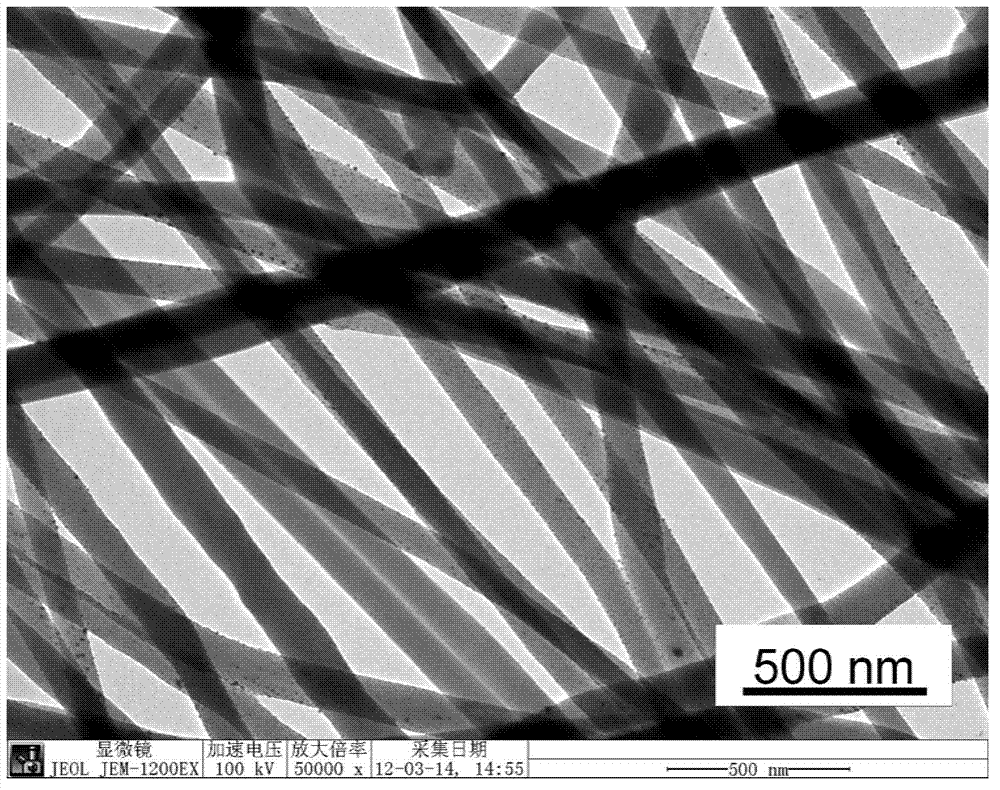
[0044] Put the mixed solution into the glass spinneret of the electrospinning equipment. The inner diameter of the tube head of the glass spinneret is 1mm, the aluminum sleeve is used as the anode, and the aluminum foil is used as the cathode plate to accept the product. The distance between the two poles is 20cm. A voltage of 20KV was applied between the two electrodes for electrospinning, so that a composite nanofiber membrane of polyacrylonitrile and silver nitrate was collected on the cathode.
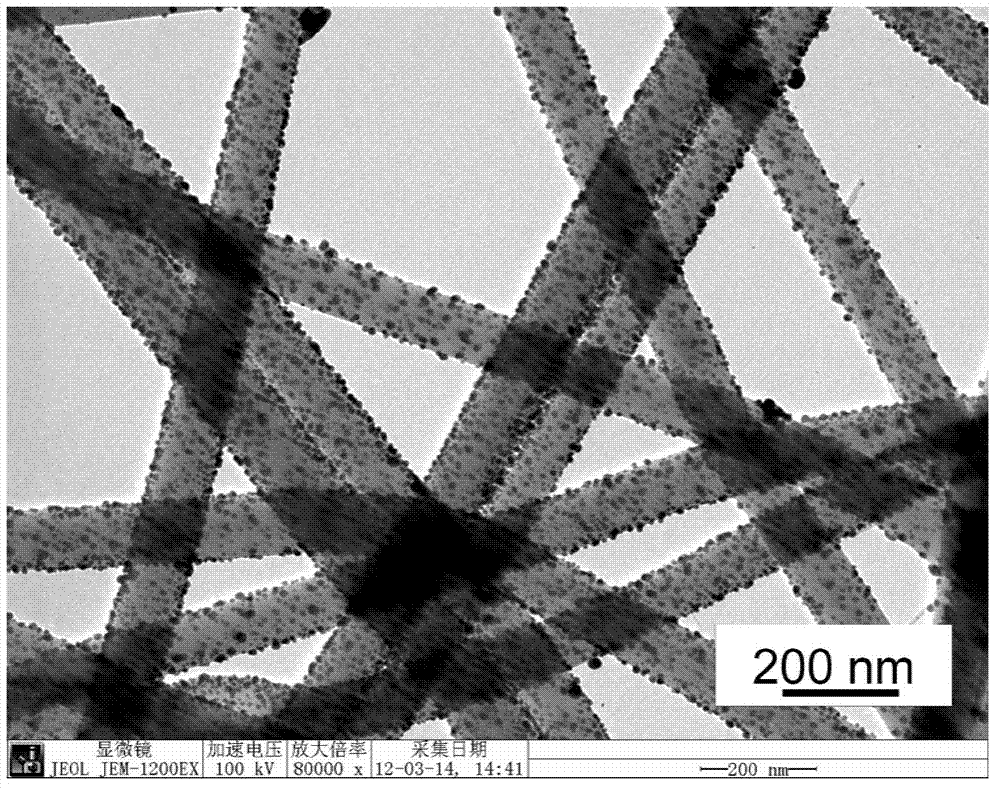
[0045] In a 50ml beaker, add 0.16g of sodium hydroxide and 20ml of ethylene glycol, stir well until the solution ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Solution preparation, spinning process and silver nitrate reduction are consistent with Example 1.
[0052] Dissolve 0.5 g of silver nitrate in 30 ml of deionized water, add ammonia water dropwise under rapid stirring until the solution becomes clear, and soak the nanofiber membrane in the solution. Another 30 ml of deionized water was taken to dissolve 3.0 g of potassium sodium tartrate, and the solution was transferred to the solution soaked with nanofiber membranes. After stirring at room temperature for 5 h, the nanofiber membranes were taken out, washed with deionized water and dried.
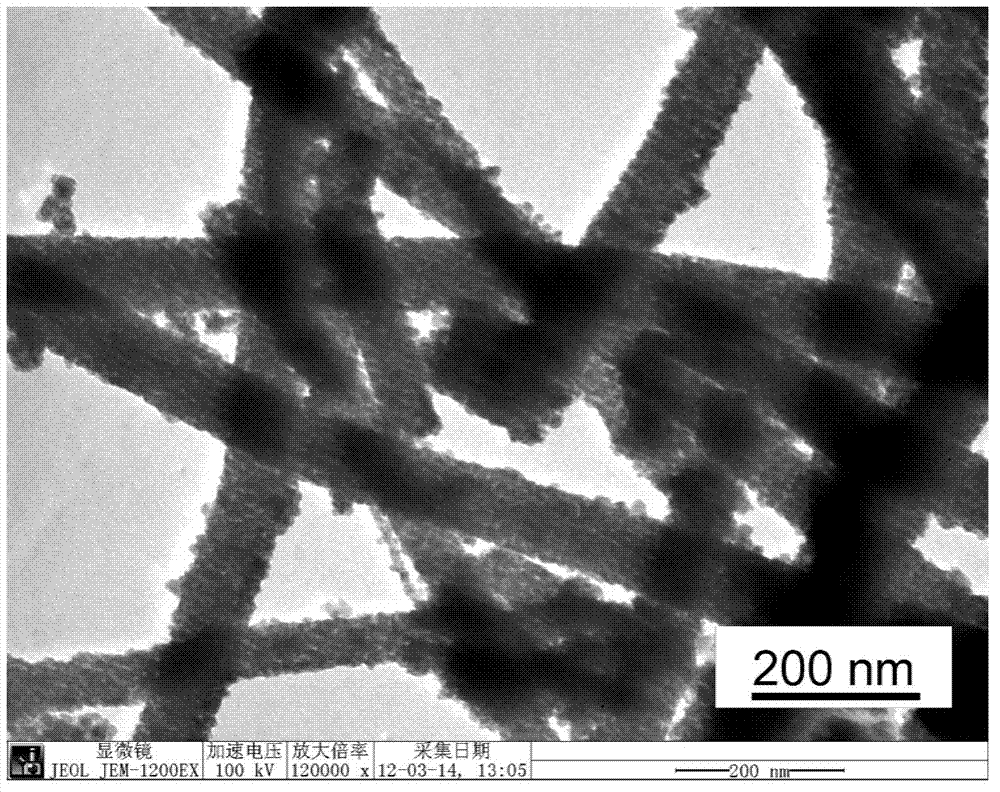
[0053] The in-situ redox and vulcanization process is consistent with that of Example 1.
[0054] At 340K, the Seebeck coefficient reaches a maximum of 1100μV / K, and the maximum value of ZT reaches about 0.66.
Embodiment 3
[0056] Solution preparation, spinning process and silver nitrate reduction are consistent with Example 1.
[0057] Dissolve 1.0 g of silver nitrate in 30 ml of deionized water, add ammonia water dropwise under rapid stirring until the solution becomes clear, and soak the nanofibrous membrane in the solution. Another 30 ml of deionized water was taken to dissolve 3.0 g of potassium sodium tartrate, and the solution was transferred to the solution soaked with nanofiber membranes. After stirring at room temperature for 1 h, the nanofiber membranes were taken out, washed with deionized water and dried.
[0058] Prepare 250ml of ferric chloride aqueous solution with a concentration of 0.003M, soak the nanofiber membrane in the solution and let it stand for 40min, take out the fiber membrane, wash it with deionized water and dry it.
[0059] Take a vacuum desiccator, add 30ml of concentrated sulfuric acid (mass fraction 98%) to the bottom, place the nanofiber membrane on the support...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Seebeck coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com