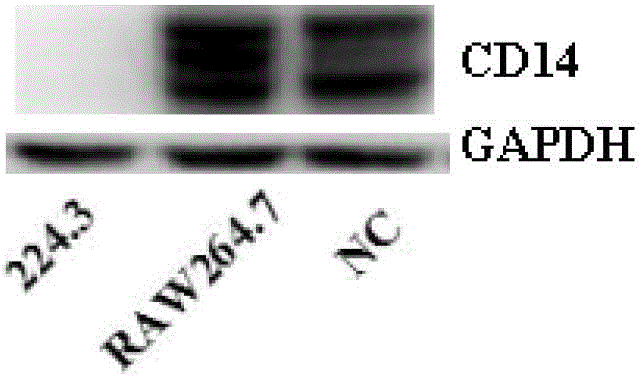Method for distinguishing smooth type lipopolysaccharide and rough type lipopolysaccharide
A technology of lipopolysaccharide and rough type, which is applied in the field of identifying smooth lipopolysaccharide and rough type lipopolysaccharide, can solve the problems of cumbersome steps and unsatisfactory accuracy of chemical identification methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] The present invention is a kind of method that can quickly distinguish smooth type lipopolysaccharide and rough type lipopolysaccharide, concrete implementation according to the following steps:
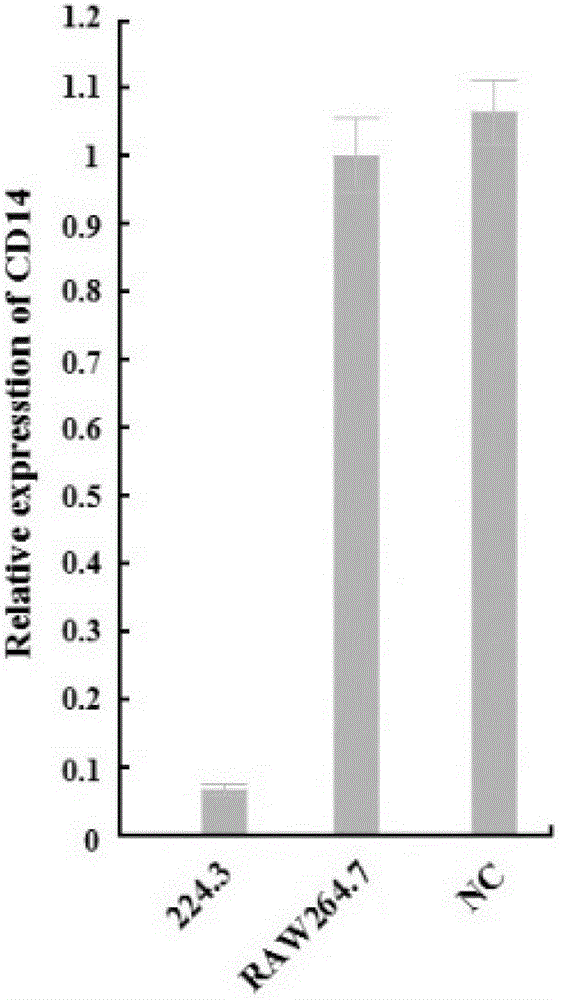
[0058] Step 1, according to the sequence of membrane-bound leukocyte differentiation antigen 14 (mCD14) gene, according to the basic principle of small interfering ribonucleic acid molecule (siRNA) design, synthesize a pair of small interfering ribose against membrane-bound leukocyte differentiation antigen 14 (mCD14) Nucleic acid molecule (siRNA-224.3), the siRNA sequence is shown in the sequence list 1 in the attachment, and you can choose to perform specific technical operations through Shanghai Gemma Technology Co., Ltd.;
[0059] Step 2, packing the synthesized siRNA-224.3 into a lentiviral vector
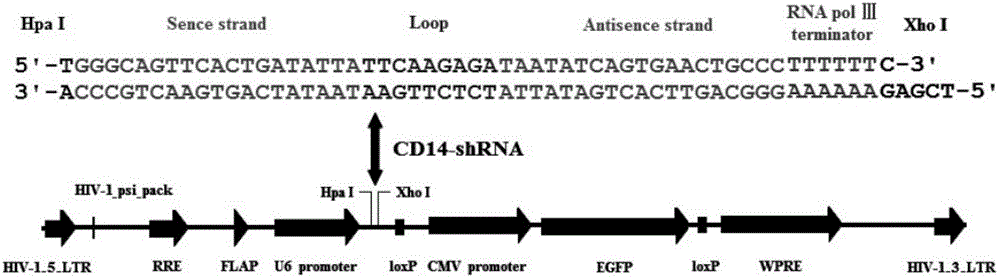
[0060] 2.1) Oligo Design (preparation of oligonucleotides): TTCAAGAGA is selected for the loop structure in the Lentivirus-shRNA template to avoid the formation of a terminati...
Embodiment 2
[0107] According to the step of embodiment 1, implement according to the following specific parameters:
[0108] Step 1. Synthesize a pair of small interfering ribonucleic acid molecule siRNA-224.3 directed at membrane-bound leukocyte differentiation antigen 14 according to the sequence of the membrane-bound leukocyte differentiation antigen 14 gene and according to the basic principles of small interfering RNA molecule design;
[0109] Step 2, packing the synthesized siRNA-224.3 into a lentiviral vector
[0110] 2.1) Prepare oligonucleotides: TTCAAGAGA is selected as the loop structure in the Lentivirus-shRNA template; T is added to the 5' end of the sense strand template to complement the sticky end formed after digestion with Hpa I; AGCT is added to the 'end, which is complementary to the sticky end formed after Xho I digestion; T4 ligase is ligated to form a recombinant vector;
[0111] 2.2) Anneal the Lentivirus-shDNA template, refer to Table 1 to configure the annealing...
Embodiment 3
[0144] According to the step of embodiment 1, adopt following concrete parameter to implement:
[0145] Step 1. Synthesize a pair of small interfering ribonucleic acid molecule siRNA-224.3 directed against membrane-bound leukocyte differentiation antigen 14 according to the sequence of the membrane-bound leukocyte differentiation antigen 14 gene and in accordance with the basic principle of small interfering RNA molecule design;
[0146] Step 2, packing the synthesized siRNA-224.3 into a lentiviral vector
[0147] 2.1) Prepare oligonucleotides: TTCAAGAGA is selected as the loop structure in the Lentivirus-shRNA template; T is added to the 5' end of the sense strand template to complement the sticky end formed after digestion with Hpa I; AGCT is added to the 'end, which is complementary to the sticky end formed after Xho I digestion; T4 ligase is ligated to form a recombinant vector;
[0148] 2.2) Anneal the Lentivirus-shDNA template, refer to Table 1 to configure the annealin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com