Flexible organic light emitting transistor display device
A technology of light-emitting transistors and transistors, which is applied in the manufacture of electric solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state devices, etc., can solve the problems of high device drive voltage, low device efficiency, and poor charge injection effect, and achieve lower operating voltage, The effect of improving work efficiency and improving working life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
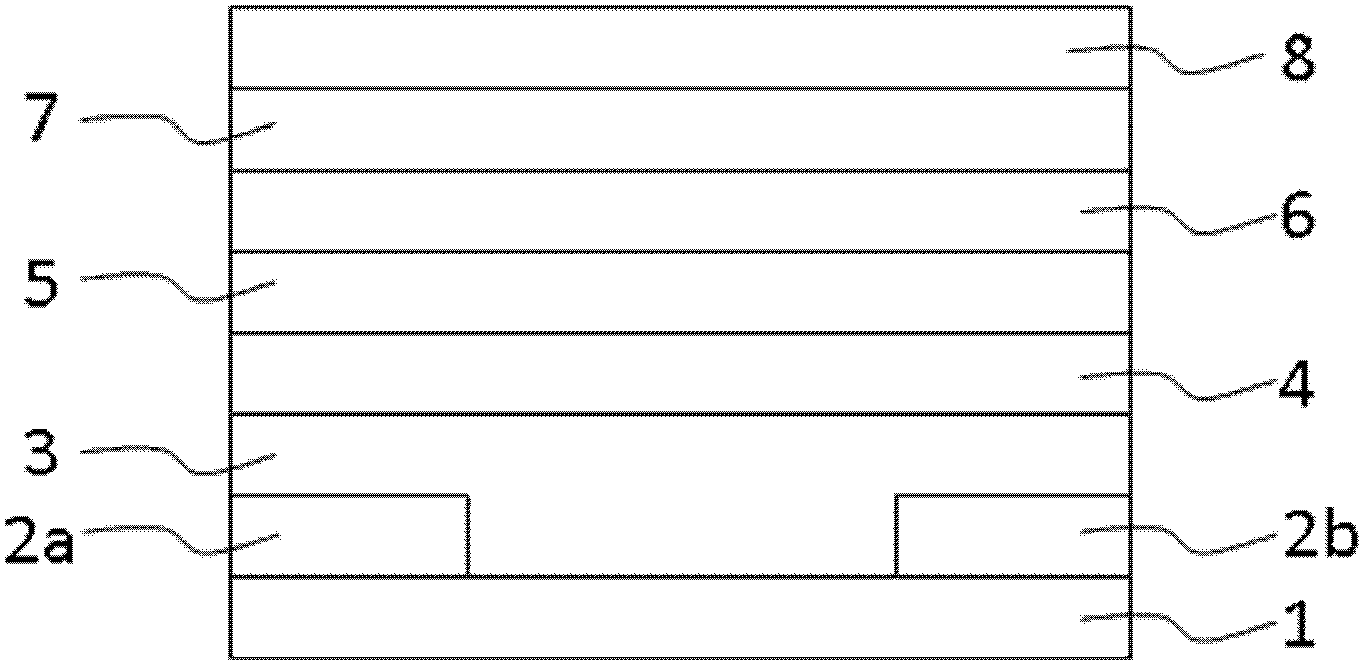
[0077] A flexible organic light-emitting transistor device structure includes: a substrate 1; source and drain electrode layers 2a and 2b; a charge injection layer 3; organic semiconductor layers 4, 5 and 6; a gate insulating layer 7; By using the novel charge injection layer 3, the charge injection capability can be improved, thereby improving the luminous efficiency of the device. Graphene is used as the source and drain electrodes, and as a bottom-emitting device, it has a very high aperture ratio. figure 1 It is a schematic cross-sectional structure diagram of the flexible organic light-emitting transistor device.
[0078] The fabrication process of the device mainly includes the following steps:
[0079] (1) The substrate 1 is cleaned.
[0080] (2) Use printing, spin coating, printing, transfer printing and other methods to prepare graphene on the surface of the flexible substrate as the source and drain electrode layer; at least ensure that some areas on the upper sur...
Embodiment 2
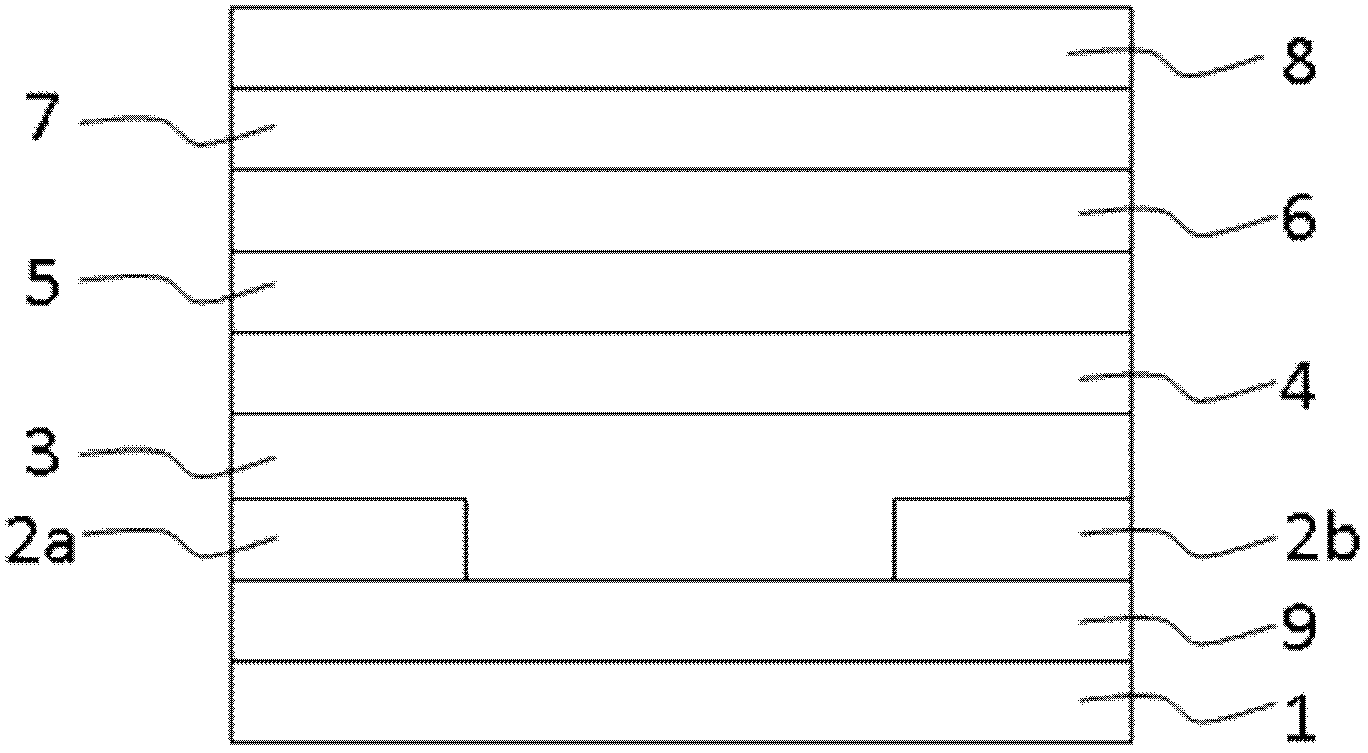
[0088] On the basis of the structure of the OLET provided in Example 1, an internal light extraction layer 9 is added. The extraction layer can be made of materials such as tantalum oxide, molybdenum oxide, tungsten oxide, vanadium oxide, etc., deposited on the substrate by sputtering, vacuum evaporation, etc. above the bottom. This layer structure can effectively extract the light emitted from the organic light-emitting layer to the inner surface of the substrate, so that more light can pass through the inner surface of the substrate and emit to the outer surface, thereby improving the working efficiency of the device, which is conducive to reducing the operating voltage of the device and improving the working efficiency of the device. Life-span, other each layer manufacturing method is identical with embodiment 1. figure 2 It is a schematic cross-sectional structure diagram of the flexible organic light-emitting transistor device described in Example 2.
[0089] It should ...
Embodiment 3
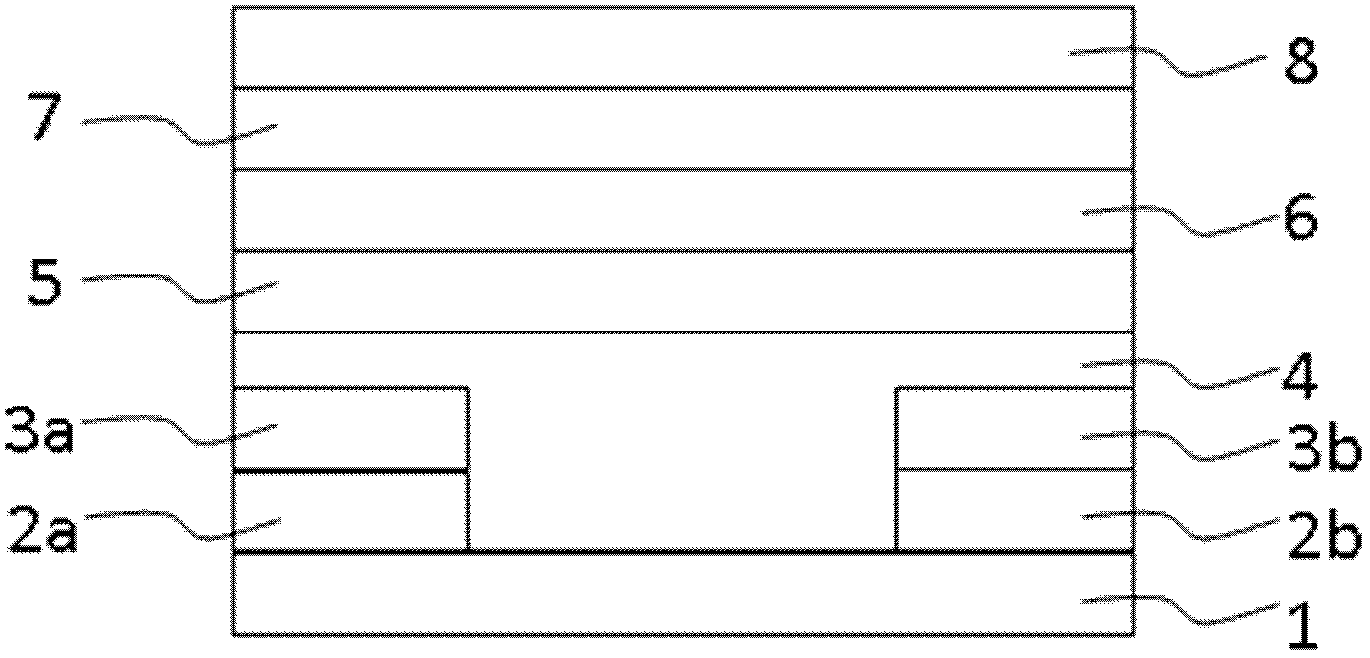
[0091] On the basis of the structure of the OLET provided in Example 1, corresponding independent electron and hole injection materials (injection layers) are respectively used. The charge injection layer uses two different types of charge injection materials 3a and 3b, which can achieve excellent electron injection and Hole injection, which greatly improves the working efficiency of the device, the hole injection layer can be molybdenum oxide, tungsten oxide, vanadium oxide, aluminum oxide, etc., and the material of the electron injection layer can be lithium fluoride, lithium oxide, zirconia, Titanium oxide, cesium carbonate etc., the preparation method of each layer is identical with embodiment 1. image 3 It is a schematic cross-sectional structure diagram of the flexible organic light-emitting transistor device described in Example 3.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com