Preparation method for graphene fiber
A graphene fiber and graphene solution technology, applied in the direction of graphene, nano-carbon, etc., can solve the problems of graphene fiber structure roughness, low fracture strength, complex preparation process, etc., achieve uniform appearance and internal structure, low cost, The effect of simple operation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] (1) Prepare 8 mg·mL by Hummers method (Xuejun Xie, etc. ACS Nano 4, 6050-6054 (2010)) -1 Graphene oxide solution.
[0032] (2) Inject the graphene oxide solution prepared in step (1) into a glass capillary with a diameter of 0.4 mm, and seal both ends.
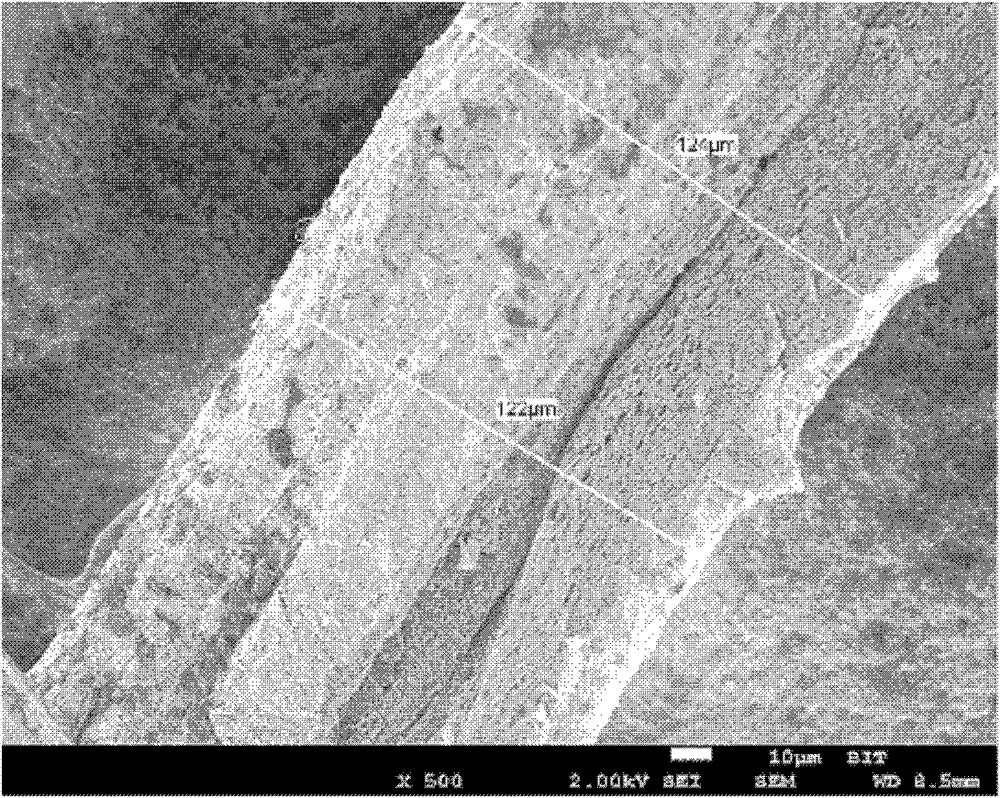
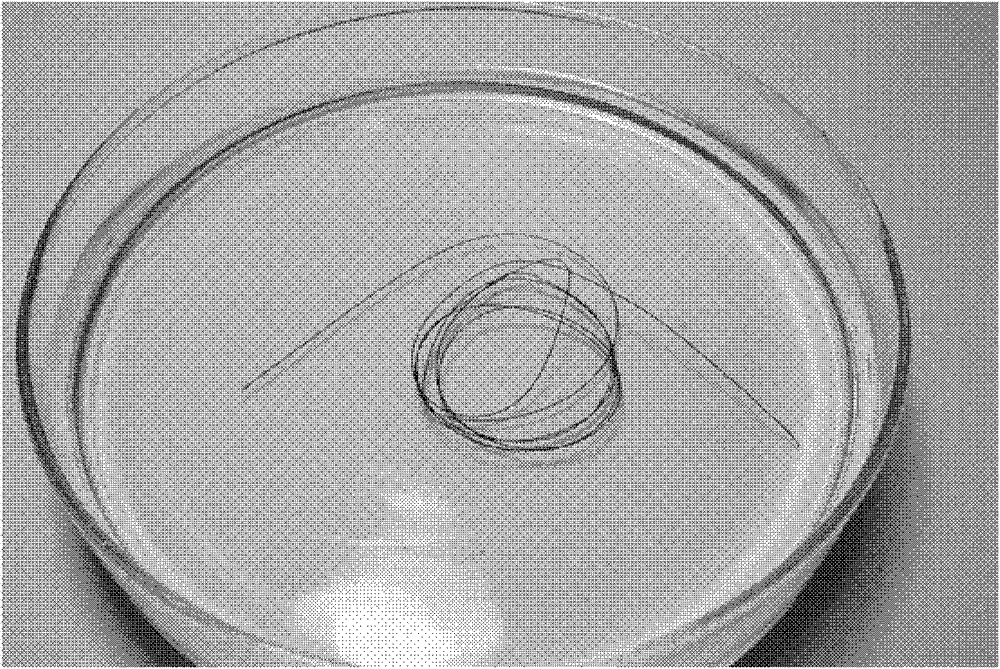
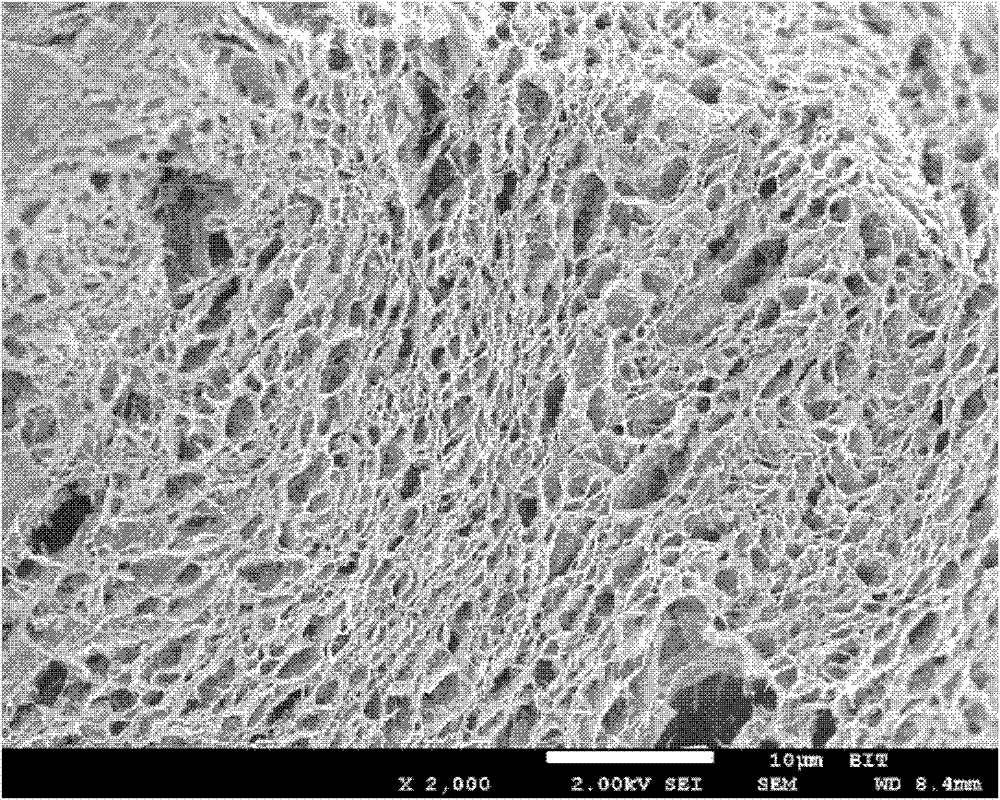
[0033] (3) Heat the sealed glass capillary at 230° C. for 2 h to form water-containing graphene fibers in the glass capillary. The appearance of hydrated graphene fibers is as figure 1 As shown, the fiber is continuous and uniform in diameter, and its diameter measured under an optical microscope is 150 μm; the hydrated graphene fiber is freeze-dried and cut longitudinally, and the fiber structure under a scanning electron microscope is as follows: figure 2 As shown, it can be seen that there are a large number of pore structures in the fiber, and the pores are uniform. Its section is partially enlarged as image 3 shown by image 3 It can be seen more clearly that the fiber has a large number of pore structures, ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] (1) Prepare 8 mg·mL by Hummers method (Xuejun Xie, etc. ACS Nano 4, 6050-6054 (2010)) -1 Graphene oxide solution
[0038] (2) Inject the graphene oxide solution prepared in step (1) into a glass capillary with a diameter of 0.2 mm, and seal both ends.
[0039] (3) Heat the sealed glass capillary at 230° C. for 2 h to form hydrated graphene fibers in the glass capillary, whose appearance is similar to that of the hydrated graphene fibers obtained in Example 1, that is, the fibers are continuous and uniform in diameter , the diameter measured under an optical microscope is 77 μm, and the scanning electron microscope after freeze-drying shows that there are a large number of pore structures in the fiber, and the pores are uniform. Compared with Example 1, it can be seen that the diameters of the glass capillaries are different, and the diameters of the obtained graphene fibers containing water are also different.
[0040] (4) On the workbench, dry the graphene fiber cont...
Embodiment 3
[0042](1) Prepare 4 mg·mL by Hummers method (Xuejun Xie, etc. ACS Nano 4, 6050-6054 (2010)) -1 Graphene oxide solution.
[0043] (2) Inject the graphene oxide solution prepared in step (1) into a glass capillary with a diameter of 0.4 mm, and seal both ends.
[0044] (3) Heat the sealed glass capillary at 230° C. for 2 h to form water-containing graphene fibers in the glass capillary. The appearance of the fiber shows that the fiber is continuous and has a uniform diameter. The diameter measured under an optical microscope is 105 μm. Scanning electron microscopy after freeze-drying showed that the fibers had a uniform pore structure and were more loose. Compared with Example 1, it can be seen that due to the reduction in the concentration of the graphene oxide solution prepared in step (1), the diameter of the obtained hydrated graphene fibers is also reduced, and the pore structure in the fibers is more loose.
[0045] (4) On the workbench, dry the graphene fiber containing...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electron mobility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com