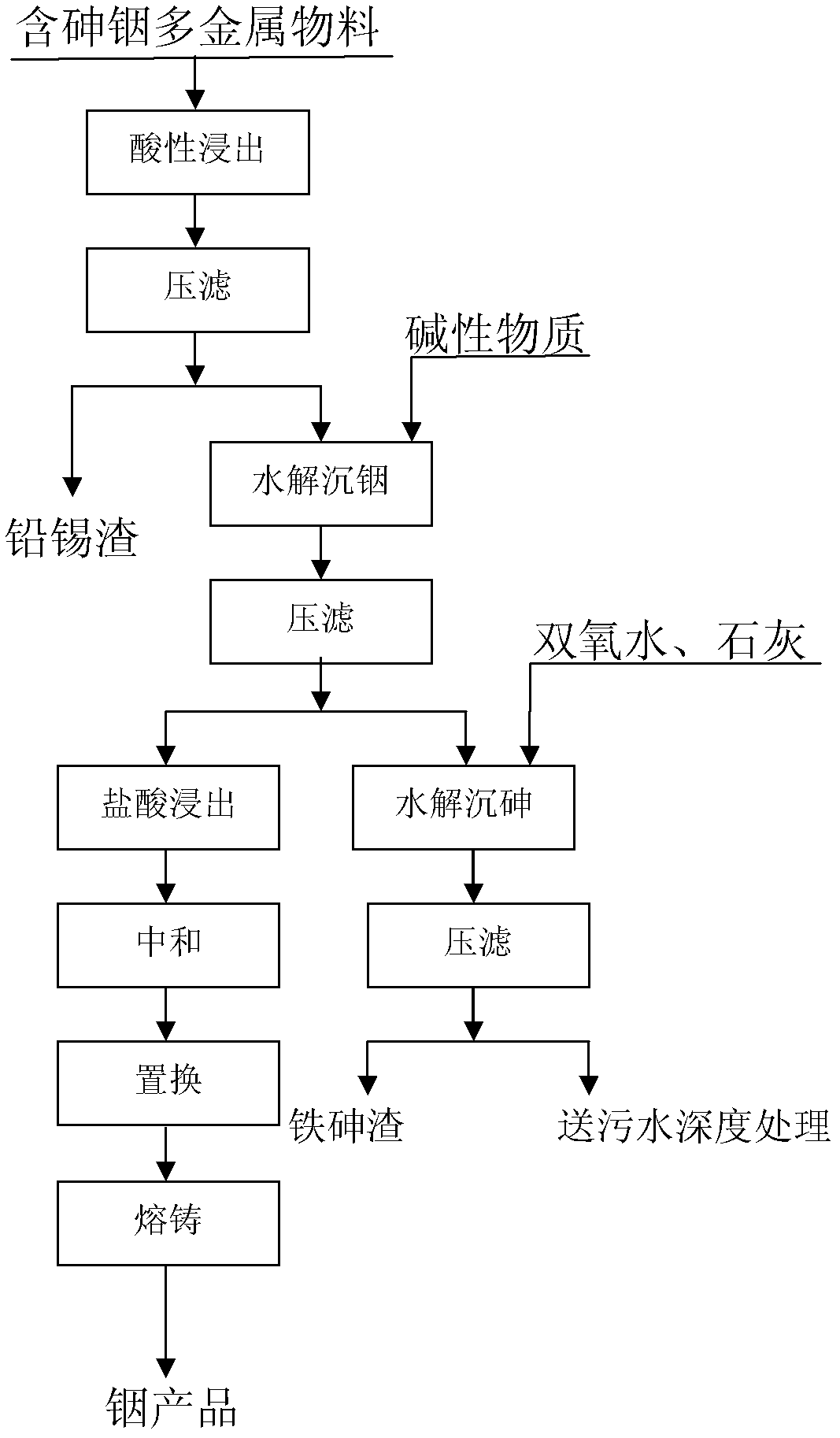
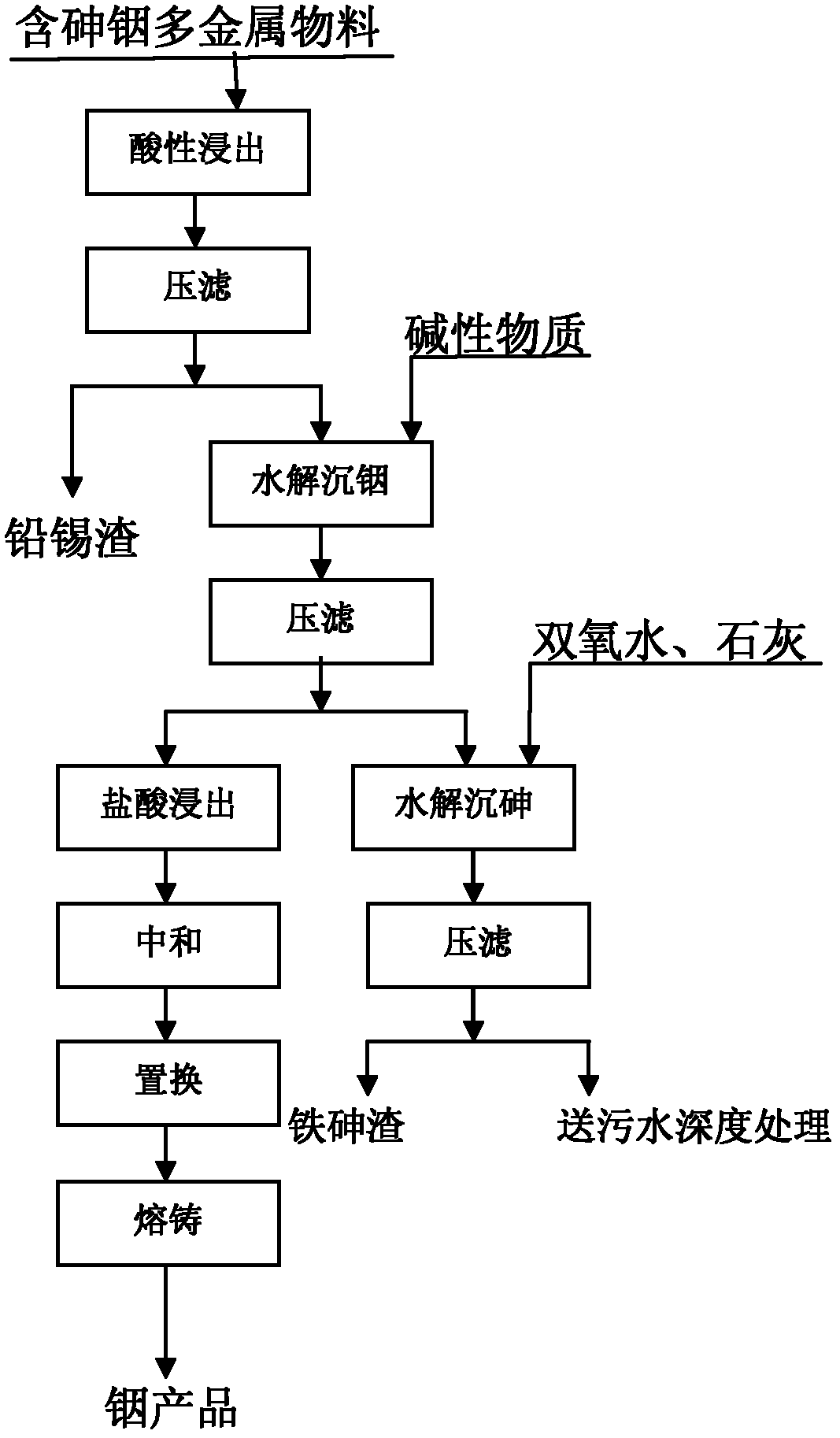
Method for utilization and harmless treatment of multi-metal material containing arsenic and indium
A harmless treatment, multi-metal technology, applied in photography technology, equipment, photography auxiliary technology, etc., can solve the problem that there is no comprehensive treatment method for multi-metal materials containing arsenic and indium, high sealing requirements for dust collection devices, and easy leakage of arsenic trioxide and other issues, to achieve the effect of comprehensive recycling and harmless, remarkable effect and good separation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Raw material: soot, the composition is as follows
[0029] soot element
Zn
In
sn
As
Pb
h 2 o
Content (%)
7.74
2962(g / t)
10.57
8.99
43.5
0.1
[0030] Acidic leaching: Weigh 200g of soot into a beaker, add 120ml of sulfuric acid to 1000ml of water, MnO 2 15g. When the temperature of the water bath rises to 95°C, place the beaker in the water bath and stir at constant temperature for 5 hours. Final acid: 90g / L, filtered, respectively sampling test:
[0031] Lead dross
Pb
sn
In
As
Zn
dry residue
Content (%)
44.46
10.7
451(g / t)
0.51
2.41
193.7
[0032] Filtrate result:
[0033] filtrate
Pb
sn
In
As
Zn
Volume ml
Content (g / L)
0.05
0.42
520(mg / L)
17.5
11.17
970
[0034] Hydrolysis of indium precipitation:
[0035] Add 70 grams of c...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Raw materials: 2000 kg of soot,
[0043] soot element
Zn
In
sn
As
Pb
h 2 o
Content (%)
3.34
2066g / t
0
18.58
31.47
0.68
[0044] Acid leaching: at 15m 3 Add 10m of clean water to the reaction tank 3 , add 1000 kg of sulfuric acid to make the initial acid reach 150g / l, MnO 2 200 kg, heat up and stir, when the temperature reaches 95°C, keep stirring for 5 hours, and the final acid is 56g / l. Compression, sampling test respectively: get solution 9.8m 3 , 2683 kg of slag.
[0045] Lead dross
Pb
sn
In
As
Zn
h 2 o
Content (%)
31.63
0
252g / t
1.32
0.34
26.56
[0046] Filtrate result:
[0047] filtrate
Pb
sn
In
As
Zn
volume
Content (g / L)
0.06
0
375mg / L
35.2
0.65
9.8m 3
[0048] Hydrolysis of indium precipitation:
[0049]Add 450 k...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com