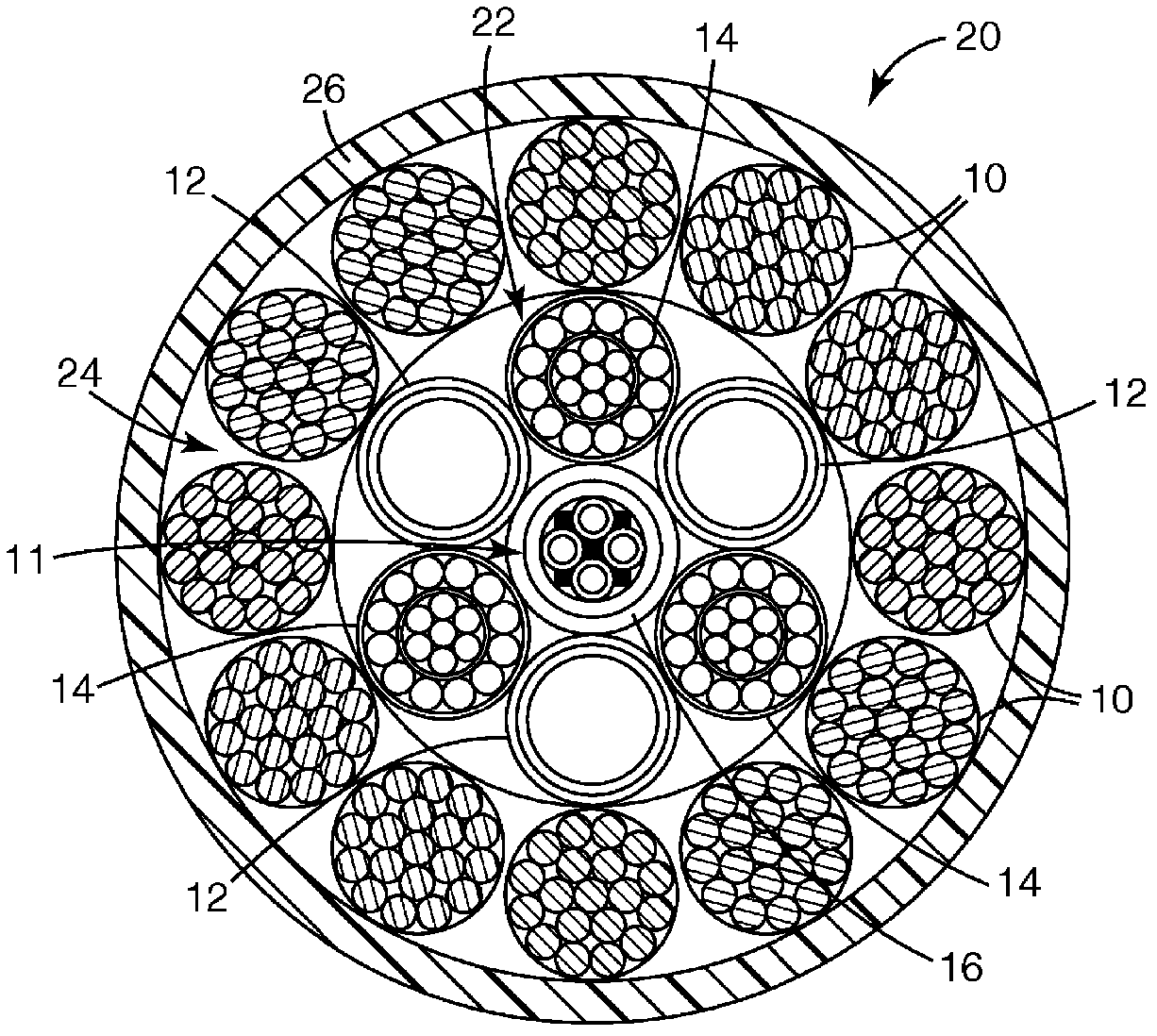
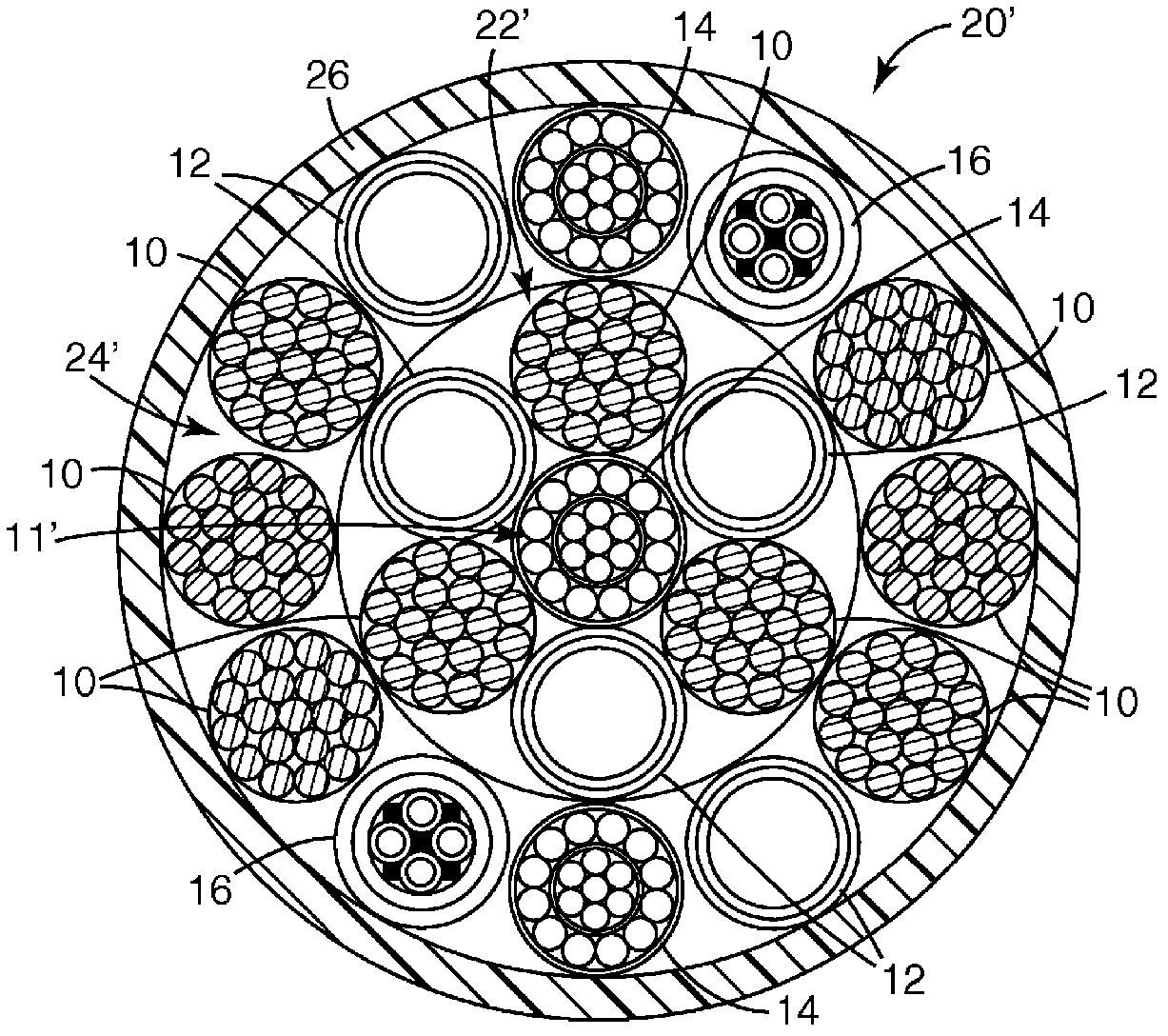
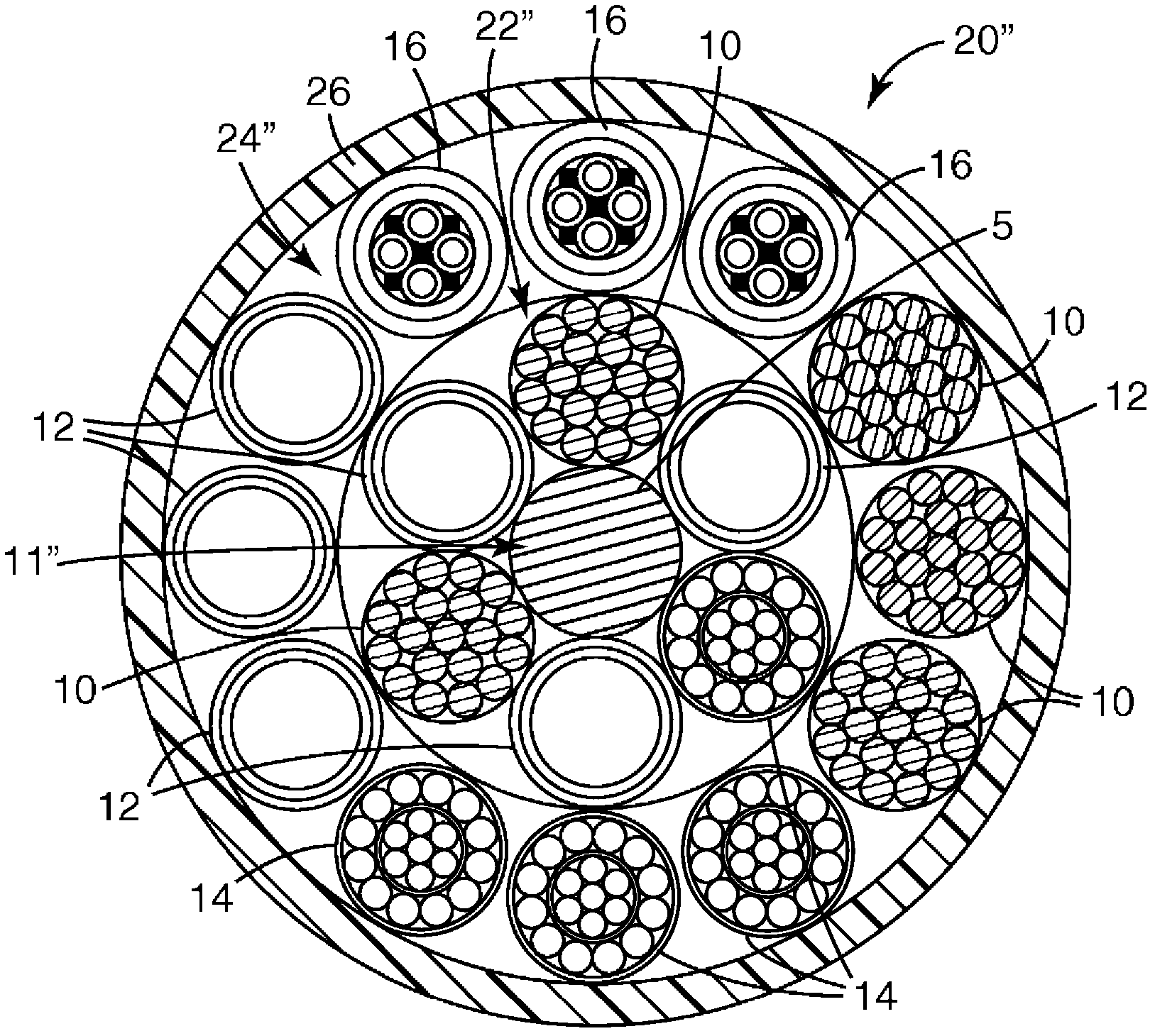
Submersible Composite Cable And Methods
A composite cable and composite wire technology, which is applied in the direction of cable, power cable, submarine cable, etc., can solve the problems of water depth limitation and poor load-bearing capacity of submersible transmission cables, and achieve easy laying, increased working depth, and light weight Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0165] The following materials were used in the comparative examples and examples below:
[0166] NEXTEL 610, alpha alumina ceramic fiber (3M Company, St. Paul, MN);
[0167] AMC30, an aluminum matrix composite wire comprising 30% by weight NEXTEL 610 fibers, and 70% by weight aluminum (3M Company, St. Paul, MN);
[0168] AMC50, an aluminum matrix composite wire comprising 50% by weight NEXTEL 610 fibers, and 70% by weight aluminum (3M Company, St. Paul, MN);
[0169] KEVLAR 49, poly(aramid) fiber (E.I. DuPont de Nemours, Inc., Wilmington, DE).
[0170] Figure 7 The superior properties of the exemplary composite conductor wires in terms of specific strength, specific modulus, and specific (electrical) conductivity compared to copper or steel conductor wires are shown. Various properties are expressed on a per unit weight basis. Figure 7 The values reported represent the specific property value of the composite conductor wire divided by the specific property value of co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com