Semiconductor refrigerating device
A refrigeration device and semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device parts, electric solid-state devices, etc., can solve the problems of inability to conduct heat, low thermal conductivity, discounted cooling effect, etc., and achieve convenient use and small size. , the effect of high work efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
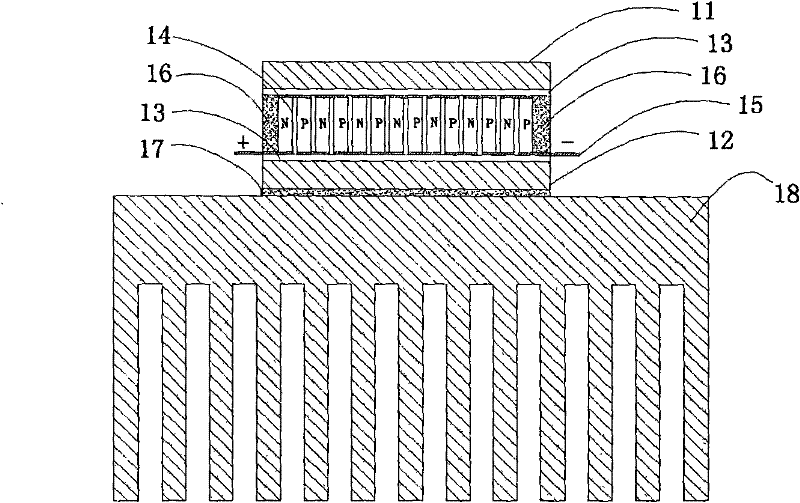
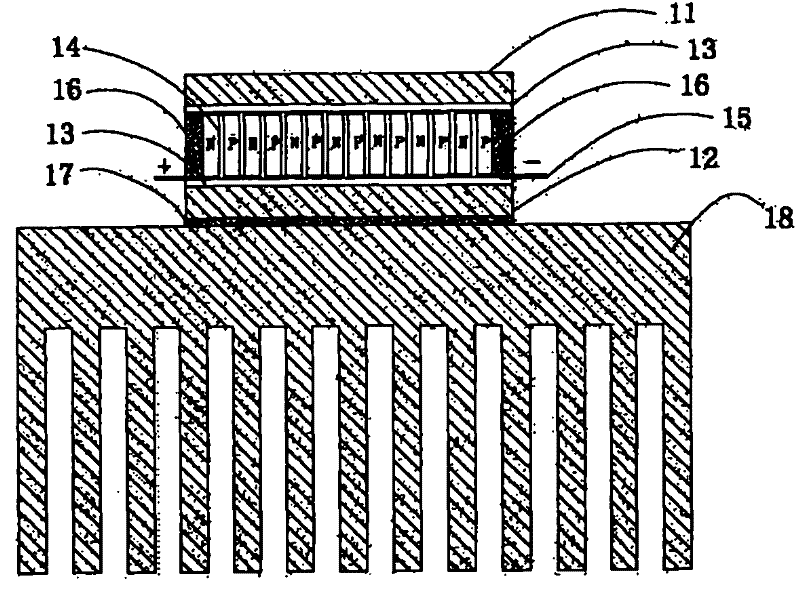
[0030] Such as figure 1 As shown, the semiconductor refrigeration device uses the cold end part 11 and the hot end part 12 of copper material with higher thermal conductivity and larger heat capacity, and the shape is a smooth and flat sheet, and the cold end part 11 and the heat One surface of the end part 12 is prepared by magnetron sputtering, chemical vapor deposition and other techniques to prepare a 50μm thick AlN thermally conductive insulating layer with high thermal conductivity; several p-type semiconductors 14 and n-type semiconductors 14 pass through the electrodes 15 are connected in series end to end, and the p-type semiconductor 14 and the n-type semiconductor 14 are spaced apart and arranged in parallel on the same plane; the cold end part 11 and the hot end part 12 are attached and connected to the p-type semiconductor 14 and the n-type semiconductor 14 ; Because AlN has a high thermal conductivity, up to 270W / mk, which can quickly conduct heat away, the AlN the...
Embodiment 2
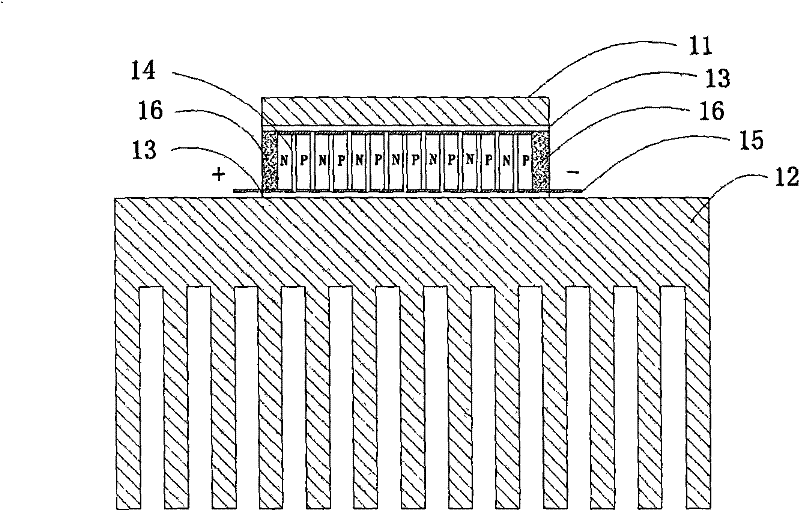
[0033] Such as figure 2 As shown, the structure of the semiconductor refrigeration device in this embodiment is similar to that of Embodiment 1, except that the hot end part 12 is made into a block with a fin tail, and at the same time, the heat sink 18 and thermally conductive silica gel are omitted. 17; Compared with Example 1, the heat sink 18 is omitted, which makes the heat dissipate faster and reduces the use of thermally conductive silicone grease, that is, reduces the thermal resistance in the thermal channel, and can better improve the heat dissipation rate ; At the same time, it saves production costs.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com