Method for producing low-substituted hydroxypropylcellulose
A hydroxypropyl cellulose, low-substituted technology, applied in the field of producing low-substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose, can solve difficult, expensive and other problems, and achieve the effect of avoiding explosions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
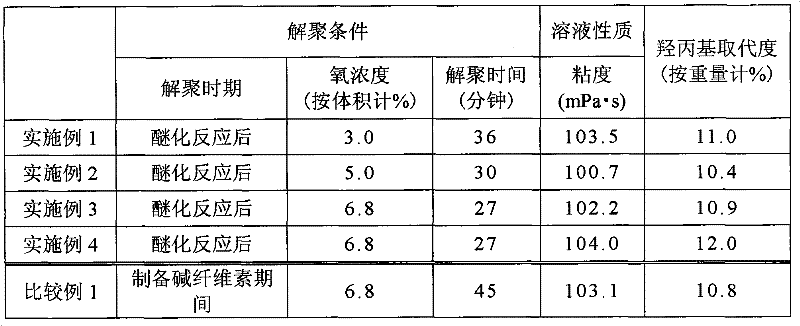
[0033] A reactor with a volume of 144 liters and equipped with an internal stirring structure was filled with 8 kg of powdery slurry. Under stirring, 6.32 kg of 25% by weight aqueous sodium hydroxide solution was added to the reactor for 6 minutes, followed by stirring for 14 minutes to prepare alkali cellulose.
[0034] The reactor was then purged with nitrogen. After purging with nitrogen, 1.48 kg of propylene oxide was added while maintaining the reactor at 60° C. and an etherification reaction was performed for 75 minutes.
[0035] After the etherification reaction, the measured pressure in the reactor dropped to -0.080 MPa under stirring conditions. Then, the pressure in the reactor was increased to -0.0145 MPa with nitrogen. Once the air supply valve was opened to increase the pressure to 0 MPa, the vacuum valve and the air supply valve of the reactor were closed. Through this operation, the oxygen concentration in the reactor was adjusted to 3.0% by volume and depoly...
Embodiment 2
[0039] A reactor with a volume of 144 liters and equipped with an internal stirring structure was filled with 8 kg of powdery slurry. Under stirring, 6.32 kg of 35% by weight aqueous sodium hydroxide solution was added to the reactor for 6 minutes, followed by stirring for 14 minutes to prepare alkali cellulose.
[0040] The reactor was then purged with nitrogen. After purging with nitrogen, 1.48 kg of propylene oxide was added while maintaining the reactor at 60° C. and an etherification reaction was performed for 75 minutes.
[0041] After the etherification reaction, the measured pressure in the reactor dropped to -0.080 MPa under stirring conditions. Then, the pressure in the reactor was increased to -0.024 MPa with nitrogen. Once the air supply valve was opened to increase the pressure to 0 MPa, the vacuum valve and the air supply valve of the reactor were closed. Through this operation, the oxygen concentration in the reactor was adjusted to 5.0% by volume and depolym...
Embodiment 3
[0044] A reactor with a volume of 144 liters and equipped with an internal stirring structure was filled with 8 kg of powdery slurry. Under stirring, 6.32 kg of 35% by weight aqueous sodium hydroxide solution was added for 6 minutes, followed by stirring for 14 minutes to prepare alkali cellulose.
[0045] The reactor was then purged with nitrogen. After purging with nitrogen, 1.48 kg of propylene oxide was added while maintaining the reactor at 60° C. and an etherification reaction was performed for 75 minutes.
[0046] After the etherification reaction, the measured pressure in the reactor dropped to -0.080 MPa under stirring conditions. Then, the pressure in the reactor was increased to -0.0336 MPa with nitrogen. Once the air supply valve was opened to increase the pressure to 0 MPa, the vacuum valve and the air supply valve of the reactor were closed. Through this operation, the oxygen concentration in the reactor was adjusted to 6.8% by volume and depolymerization of t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com