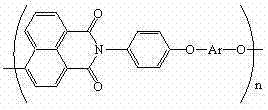
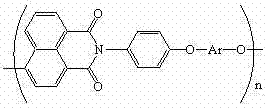
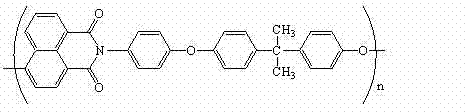
Polyarylether light-emitting material with main chain containing naphthalimide and synthesis method thereof
A technology of naphthalimide and luminescent material, which is applied in the field of polyarylene ether luminescent material containing naphthalimide in the main chain and its synthesis, can solve the problem of low glass transition temperature of conjugated polymer, influence on device stability, The problems of increasing synthesis steps, etc., achieve the effects of excellent solubility, reliable thermal stability, and overcoming easy crystallization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] (1) Synthesis of phenol sodium salt: Add 2.28 g of bisphenol A and 0.8 g of sodium hydroxide into a 50 mL single-necked bottle filled with 20 mL of methanol, pass through the nitrogen protection, react at room temperature for 3 h, and then raise the temperature to 60 ℃, remove the solvent methanol under reduced pressure; put the bottles together in a vacuum drying oven at 80 ℃ to dry to remove water, rinse the resulting solid with a small amount of methanol to remove residual reactants, and dry to obtain the product sodium phenolate.
[0026] (2) Synthesis of bishalogenated naphthalimide monomer: Add 3.048 g of 4-bromo-1,8-naphthalene dicarboxylic anhydride (recrystallized from chlorobenzene), 1.72 g of p-bromoaniline into a 50 mL three-necked flask, 20 mL of dimethylacetamide (DMAc), 5 mL of toluene, 0.5 mL of pyridine, and nitrogen protection at the same time. Stir at room temperature for 2 h, then raise the temperature to 140°C for 6 h with toluene and water, and the...
Embodiment 2
[0032] (1) Synthesis of phenol sodium salt: Add 2.28 g of bisphenol A and 0.8 g of sodium hydroxide into a 50 mL single-necked bottle filled with 20 mL of methanol, pass through the nitrogen protection, react at room temperature for 3 h, and then raise the temperature to 60 ℃, remove the solvent methanol under reduced pressure; put the bottles together in a vacuum drying oven at 80 ℃ to dry to remove water, rinse the resulting solid with a small amount of methanol to remove residual reactants, and dry to obtain the product sodium phenolate.
[0033](2) Synthesis of bishalogenated naphthalimide monomer: Add 2.909 g of 4-bromo-1,8-naphthalene dicarboxylic anhydride (recrystallized from chlorobenzene), 1.72 g of p-bromoaniline into a 50 mL three-necked flask, 20 mL of dimethylacetamide (DMAc), 5 mL of toluene, 0.5 mL of pyridine, and nitrogen protection at the same time. Stir at room temperature for 2 h, then raise the temperature to 140°C for 6 h with toluene and water, and then...
Embodiment 3
[0039] (1) Synthesis of phenol sodium salt: Add 2.28 g of bisphenol A and 0.8 g of sodium hydroxide into a 50 mL single-necked bottle filled with 20 mL of methanol, pass through the nitrogen protection, react at room temperature for 3 h, and then raise the temperature to 60 ℃, remove the solvent methanol under reduced pressure; put the bottles together in a vacuum drying oven at 80 ℃ to dry to remove water, rinse the resulting solid with a small amount of methanol to remove residual reactants, and dry to obtain the product sodium phenolate.
[0040] (2) Synthesis of bishalogenated naphthalimide monomer: Add 3.047 g of 4-bromo-1,8-naphthalene dicarboxylic anhydride (recrystallized from chlorobenzene), 1.72 g of p-bromoaniline into a 50 mL three-necked flask, 20 mL of dimethylacetamide (DMAc), 5 mL of toluene, 0.5 mL of pyridine, and nitrogen protection at the same time. Stir at room temperature for 2 h, then raise the temperature to 140°C for 6 h with toluene and water, and the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com