Method for controlling desertification by adopting novel biological material gamma-polyglutamic acid (PGA)
A technology of polyglutamic acid and biological materials, applied in soil conditioning materials, chemical instruments and methods, organic fertilizers, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in success, and achieve the effect of reducing transpiration and infiltration, and high physical strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0025] After planting Salix salix in the desert, spray the ground surface of Salix salix roots with gamma-polyglutamic acid aqueous solution for 5 times; 3% and 3%;
[0026] The use interval of the gamma-polyglutamic acid aqueous solution is once every 3 days;
[0027] The gamma-polyglutamic acid consumption is 175g / m 2 ;
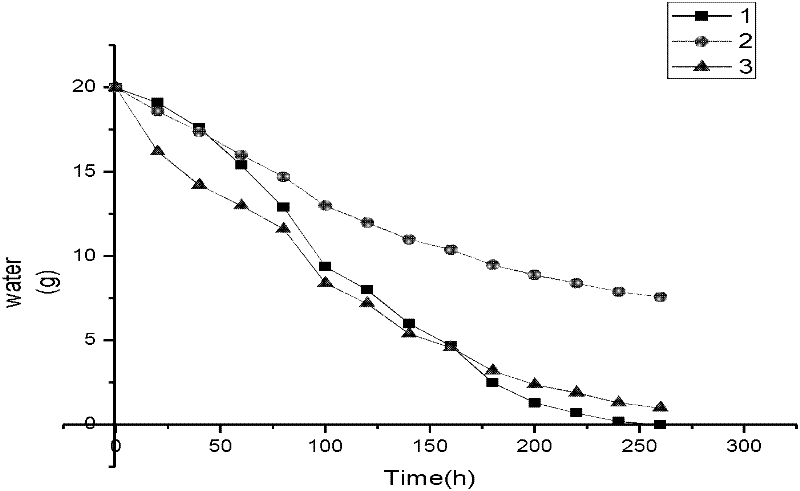
[0028] The salix salix treated by the method of the invention has a survival rate of 91 percent, the film on the root of the plant still exists within one year, and has good water absorption and water retention effects. Due to the presence of γ-polyglutamic acid film on the surface of Salix salix, it is not necessary to continue watering 30 days after planting Salix salix.
[0029] Compared with the Salix salix irrigated with the control water, the Salix salix treated by the method of the invention reduces the amount of irrigation water by 30%, and the survival rate is increased by 50%.
example 2
[0031] After planting Hippophae rhamnoides on the desert, spray the root surface of Salix salix 10 times with γ-polyglutamic acid aqueous solution;
[0032] The concentration of the polyglutamic acid aqueous solution used each time is 3%;
[0033] The use interval of the gamma-polyglutamic acid aqueous solution is once every 2 days;
[0034] The gamma-polyglutamic acid consumption is 75g / m 2 ;
[0035] The survival rate of the seabuckthorn treated by the method of the invention reaches 75%, and the film at the root of the seabuckthorn still exists within 6 months, and has good water absorption and water retention effects. Due to the presence of γ-polyglutamic acid film on the surface of seabuckthorn, Salix salix does not need to be watered 20 days after planting.
[0036] Compared with the seabuckthorn irrigated with the control water, the seabuckthorn treated by the method of the invention reduces the water consumption by 30%, and the survival rate increases by 24%.
example 3
[0038] After planting camel thorns on the desert, spray the γ-polyglutamic acid aqueous solution onto the ground surface of Salix salix roots for 3 times; the concentration of the polyglutamic acid aqueous solution used for the three times is 8%, 5%, and 2% successively;
[0039] The use interval of the gamma-polyglutamic acid aqueous solution is once every 4 days;
[0040] The γ-polyglutamine consumption is 260g / m 2 ;
[0041] The survival rate of the camel thorn treated by the method of the invention reaches 95%, the film at the root of the camel thorn still exists within one year, and has good water absorption and water retention effects. Due to the existence of the γ-polyglutamic acid film on the surface of the camel thorn, the camel thorn does not need to continue watering after 20 days of planting.
[0042] Compared with the camel thorns irrigated with contrasting water, the camel thorns treated by the method of the invention reduce the water consumption by 30%, and th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com