Digger teeth of ballast digger chain and manufacturing method thereof
A technology for excavating teeth and excavating chains, which is applied to the field of ballast excavating chain excavating teeth and its preparation, can solve the problems of restricting the service life of the excavating teeth, difficulty in melting the brazing material, weak bonding, etc., so as to improve the brazing connection strength and reduce the The difficulty of brazing process and the effect of prolonging the life of the digging teeth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
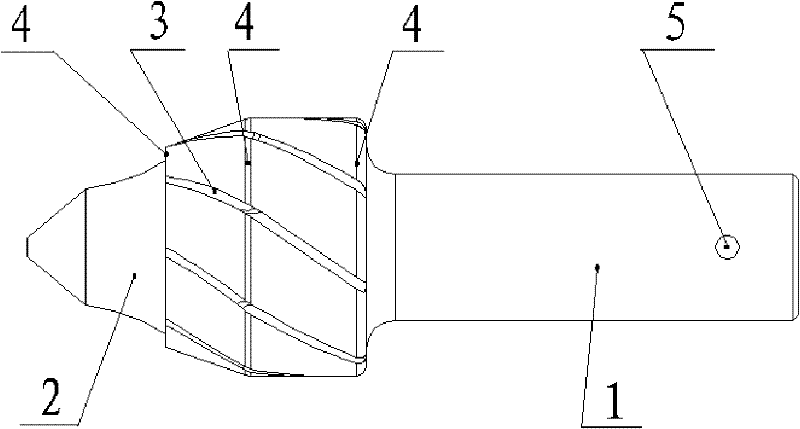
[0034] The excavating tooth of the ballast excavating chain disclosed in this embodiment comprises an excavating tooth shank and an alloy head embedded in one end of the excavating tooth shank,
[0035] The end of the digging shank close to the alloy head is provided with grooves along the direction of the helix, and the distance between two grooves is not limited; the grooves are provided with a thermal spraying and cladding groove wear-resistant layer; the digging shank is along the circumferential direction. An annular wear-resistant layer clad by thermal spraying is provided. The wear-resistant layer of the groove can be made of wear-resistant materials containing iron, carbon, silicon, boron and other metals. This embodiment solves the problem that the alloy head is easy to fall off, reduces the difficulty of the brazing process, and improves the wear resistance of the digging tooth handle. Applying this embodiment to a roadbed processing vehicle can improve its working ...
Embodiment 2
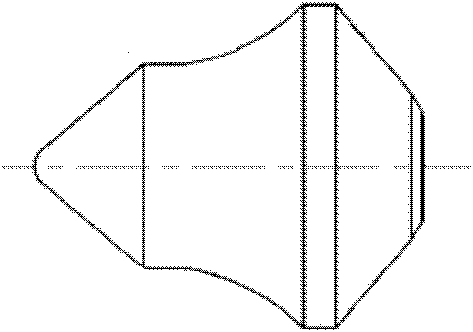
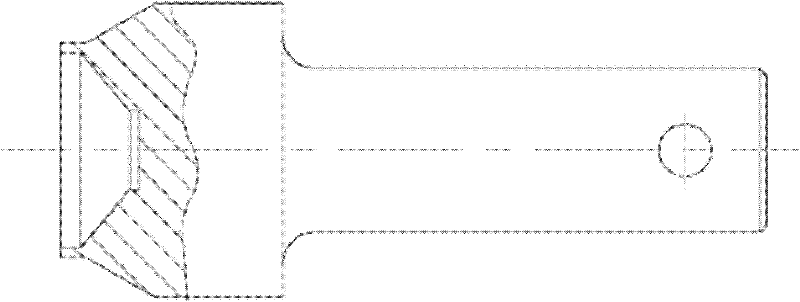
[0037] figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of the alloy head of the present invention; figure 2 It is a structural schematic diagram of the excavating tooth shank of the present invention; image 3 It is a structural schematic diagram of the excavating teeth of the ballast excavating chain of the present invention.
[0038] Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that the alloy head has a conical structure, and the material of the alloy head is YG13.
[0039] Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that the excavating tooth shank includes a frustum section and a cylindrical section with variable diameter, and the frustum section of the excavating tooth shank is provided with a central hole for embedding the alloy head; the radius of the end of the cylindrical section with variable diameter close to the embedded alloy head Larger than the end away from the alloy head, the radius of the cylindrical section away from the alloy head is reduced for installation and can also eff...
Embodiment 3
[0047] The preparation method of the excavation teeth of the ballast excavation chain described in embodiment 2, the steps are as follows:
[0048] First, process grooves along the direction of the helix at the end of the digging shank close to the alloy head (precision casting can be used to save costs);
[0049] The alloy head is embedded on the digging tooth handle, and the embedding is brazed;
[0050] Laser cladding is carried out in the groove to form a groove wear-resistant layer, the thickness of the groove wear-resistant layer is not limited, and it is preferably flush with the notch of the groove;
[0051] Finally, a ring-shaped wear-resistant layer is laser clad on the wearable part of the excavation tooth shank along the circumferential direction, and multiple ring-shaped wear-resistant layers can be set according to actual needs.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com