New method for producing bacterial cellulose
A technology for bacterial cellulose and seeds, applied in the field of fermentation engineering, can solve the problems of inability to produce bacterial cellulose on a large scale, increase the shear force of the bacteria, and reduce the shear force, so as to achieve a small footprint, improve yield and production. Efficiency, the effect of short production cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
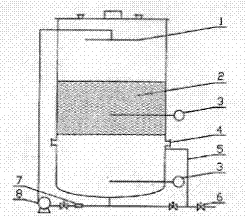
[0027] Example 1: After mixing the saccharified liquid with a total sugar content of 171.28g / L and the alcoholic fermented mash with an ethanol content of 8.24% v / v at a ratio of 3:5 (v:v), accurately measure 8L of the above mixed liquid and add it to boiling water Sterilize the bottom of the pouring fermentation tower for 30 minutes, transfer 7.5 kg of corncobs and 5 kg of rice husks sterilized at 121°C to the packing layer above the false bottom of the pouring fermentation tower while hot (the corncobs are stacked naturally, and the rice hulls are placed on the corn husks). The bottom and top of the core are laid flat in two layers), and after the top cover is covered, the jacket is forced to cool by cooling water. When the temperature in the tower drops to 35°C, it is further cooled to 30°C naturally, and then inoculated with 10% (v / v) wood Acetobacter and 3% acetic acid bacteria seed liquid, after 12 hours of static culture, poured once every 4 hours, each time for 1 minute...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: The total sugar content of 171.28g / L saccharification liquid and alcoholic fermentation mash with ethanol content of 8.24% (v / v) were accurately measured at 3:5 (v:v), and 8L of the above mixed solution was added and sterilized by boiling water for 30 minutes At the bottom of the pouring fermentation tower, 7.5kg of corncobs and 5kg of rice husks sterilized at 121°C were transferred to the packing layer above the bottom of the pouring fermentation tower while hot (wherein the corncobs were stacked naturally, and the rice hulls were placed on the bottom of the corncobs and The top part is tiled in two layers), and after the top cover is covered, the jacket is forced to cool with cooling water. When the temperature in the tower drops to 35°C, it is further cooled to 30°C naturally, and then inoculated with 8.2% (v / v) Acetobacter xylinum, 1.9% (v / v) acetic acid bacteria, 2.1% (v / v) yeast seed liquid, with 12h as a control cycle, no oxygen limitation in the first ...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3: The total sugar content of 165g / L saccharification liquid and alcoholic fermentation mash with ethanol content of 7.2% (v / v) were 3:5 (v:v), and 8L of the above mixed solution was accurately measured and added to the sterilized by boiling water for 30 minutes. In the pouring fermentation tower, 7.5 kg of corncobs and 5 kg of rice husks sterilized at 121°C were transferred to the false bottom of the pouring fermentation tower while hot (the corncobs were stacked naturally, and the rice hulls were placed on the bottom and top of the corncobs). After the top cover is covered, the jacket is forced to cool with cooling water. When the temperature in the tower drops to 35°C, it is further naturally cooled to 30°C, and then inoculated with 11% v / v Acetobacter xylinum, taking 12 hours as a control cycle, the first cycle does not limit oxygen, and from the second cycle, the frequency of pouring is 2 times / 12h (of which oxygen is limited for 4h), and each time is poured...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com