Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain suitable for thick mash fermentation and application thereof
A fermentation technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains and thick mash, which is applied in the direction of fermentation, fungi, and microorganism-based methods, etc., and can solve the lack of screening methods for by-metabolites of strains, the slowdown of fermentation speed of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and the tolerance of strain growth ability to improve the fermentation performance of thick mash, reduce energy consumption, and improve tolerance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1: Construction of genetically engineered ZΔGPD2
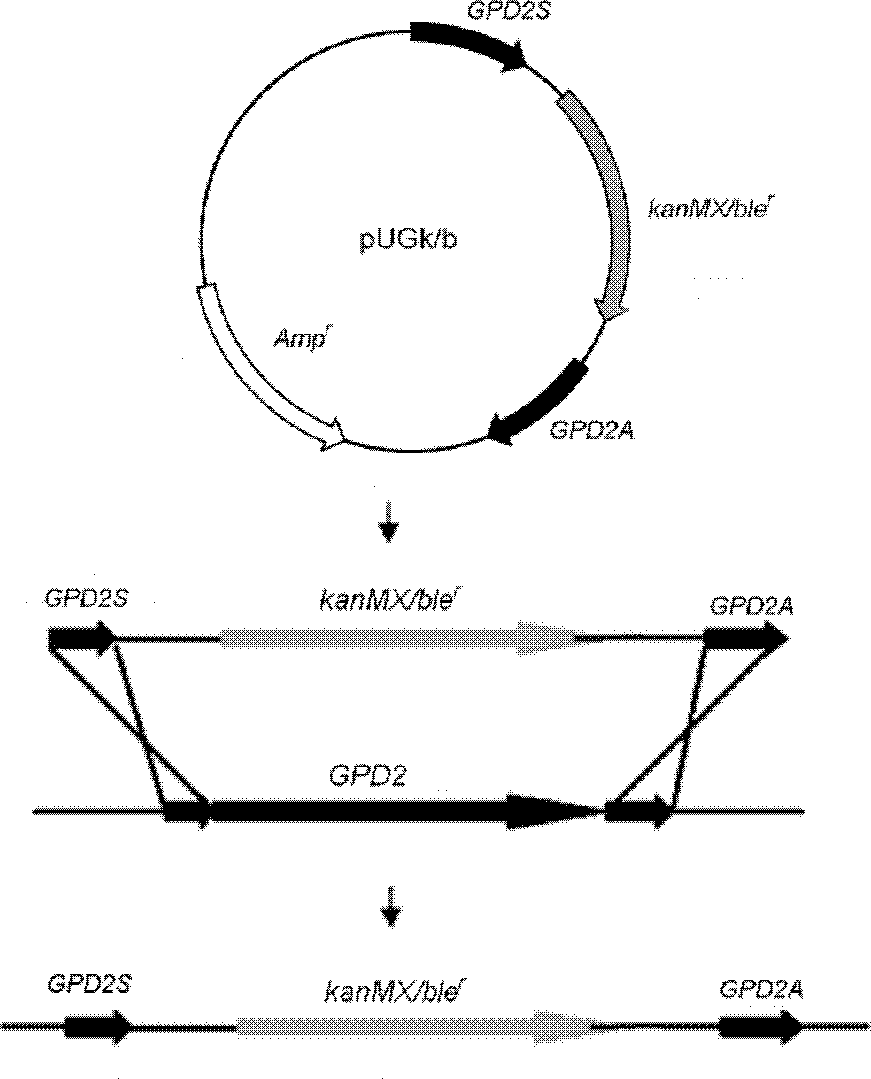
[0031]According to the reported Saccharomyces cerevisiae GPD2 gene and flanking sequence (Genebank number: NC 001147.6) as a template, primers (GPD5S and GPD5A) and primers (GPD3S and GPD3A) were designed to amplify the 5' and 3' ends of the GPD2 gene, respectively. The segment sequence was connected into Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene engineering operation conventional plasmids pUGk and pUGb with G418 and Zeocin resistance genes respectively to construct two kinds of GPD2 knockout cassettes ( figure 1 ). Using primers (GPD5S and GPD3A) to amplify the knockout cassette, transform Saccharomyces cerevisiae ZT12, and use it to perform homologous recombination with the GPD2 site on the genome to knock out the GPD2 gene. Two pairs of primers (VkS and VkA) and primers (VbS and VbA) were used to verify whether the two knockout cassettes were accurately integrated into the expected sites. Finally, the engineering strai...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: Whole Genome Rearrangement to Obtain Stable Recombinant ZTS3
[0042] Taking ZΔGPD2 as the starting strain, it was cultured in sporulation medium (10g / L NaAc, 2g / L yeast extract, 1g / L glucose and 2g / L KCl, pH 6.0) for 5 days to induce sporulation. Collect ascospores by centrifugation, add 700 μL Tris-HCl (pH 8.0, 0.01 mol / L), 200 μL 100 mg / mL helicase solution and 100 μL 0.1 mol / L mercaptoethanol, and incubate at 30°C for 16 hours at 120 r / min to rupture the ascus wall and release spores , vegetative cells were killed by high temperature treatment at 58°C for 15 minutes. All spores were mixed and randomly crossed in YPD medium to obtain recombinants. The recombinant was diluted to 10 with sterile water 3 The cells / mL were spread on a YPD plate with 20% glucose and 15% ethanol, and 50 fast-growing colonies were picked to determine the fermentation level. Then select 10 strains with excellent fermentation performance and repeat the above process for the seco...
Embodiment 3
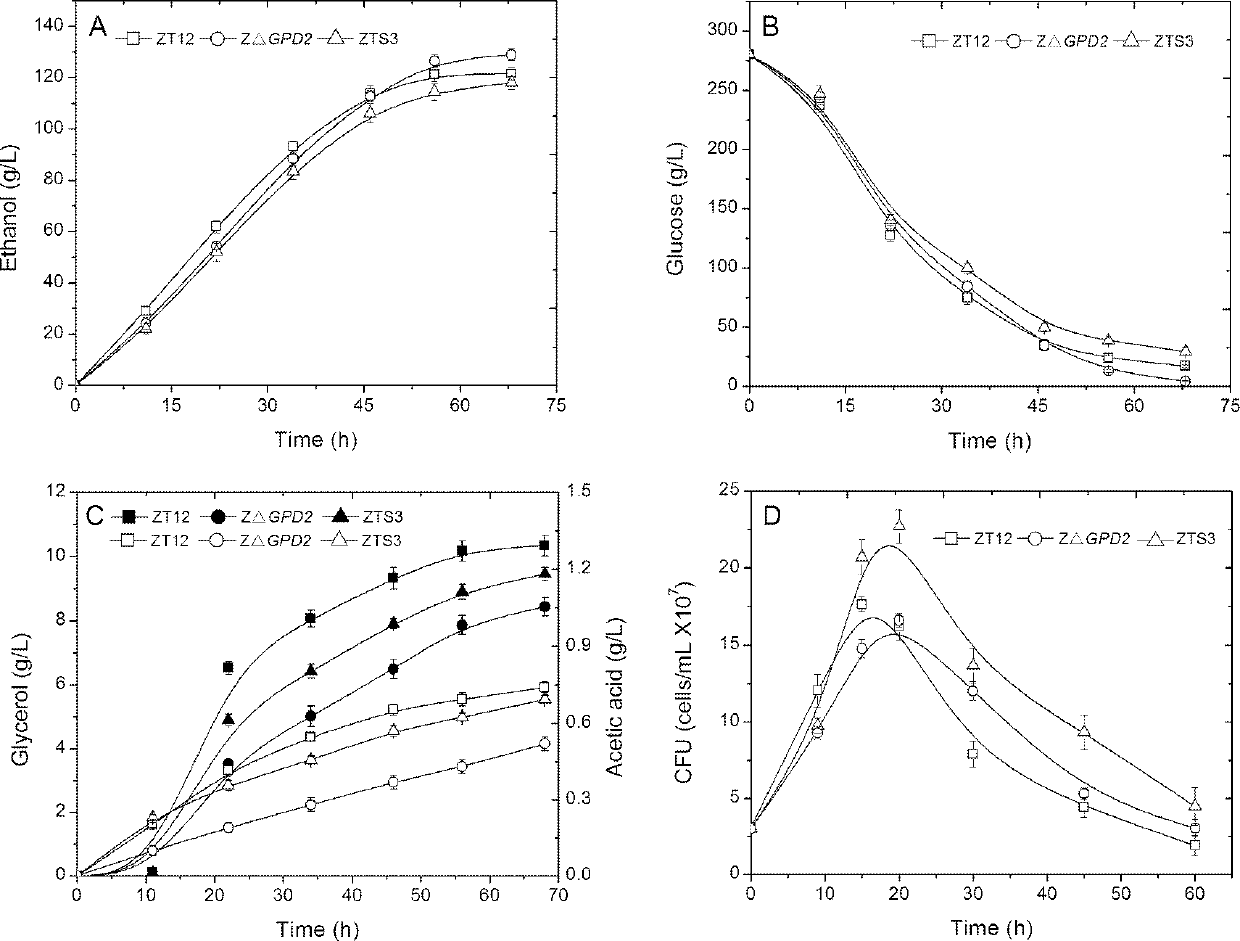
[0043] Embodiment 3: the fermenting level comparison of thick mash of bacterial strain
[0044] The fermented seed liquid was cultured in 50mL YPD for 20h until the cell concentration was about 12OD to collect the strains.
[0045] The fermentation medium is obtained by double-enzyme treatment of corn flour. The specific method is as follows: Weigh a certain amount of corn flour according to the mass ratio of material to water 1:1.9, add water and stir evenly, add liquefying enzyme (Henan Tianguan Enterprise Group Co., Ltd.) at 6 U / g starch, and heat up to about 90 ° C for 1 hour. When the liquid mash is cooled to 55°C, 200 U / g starch is added with glucoamylase (Henan Tianguan Enterprise Group Co., Ltd.), and 0.2% nitrogen source urea is added after saccharification for 0.5 h to obtain the fermentation medium.
[0046] After the fermentation medium was cooled to 34°C, the inoculation amount was 5% (v / v), and the seed solution was added, and the fermentation volume was 0.5L. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com