Experimental apparatus and method for researching response characteristic of natural gas hydrate stratum to drilling fluid intrusion
A technology of drilling fluid invasion and response characteristics, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, material inspection products, suspension and porous material analysis, and can solve problems such as ignoring the impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
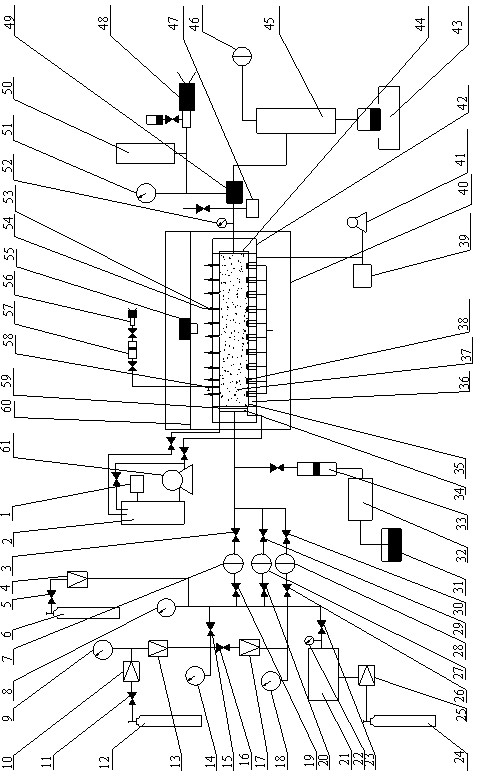
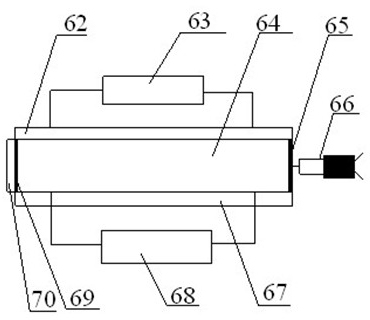
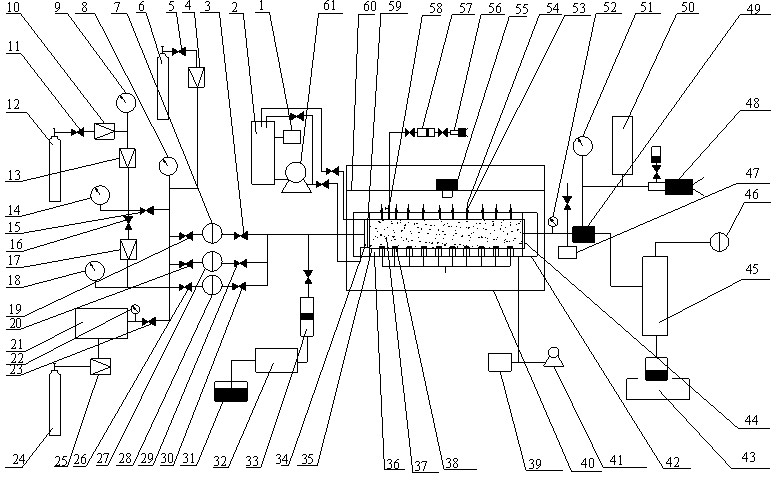
[0054] Embodiment 1: An experimental device for studying the response characteristics of natural gas hydrate formations to drilling fluid invasion according to the present invention, its structure is as follows figure 1 . Including drilling fluid circulation mechanism, test box, core transfer mechanism, gas permeability measurement mechanism, water / gas injection mechanism, ring pressure tracking mechanism, back pressure mechanism, testing mechanism, export metering mechanism, sampling mechanism and industrial computer.
[0055] The drilling fluid circulation mechanism includes a temperature controller 1, a drilling fluid storage tank 2, a drilling fluid circulation pump 61 and a wellhead annular cavity 59 of the physical model mechanism 42, wherein the drilling fluid storage tank 2 has a volume of 1000mL, and the temperature is between room temperature and It is controllable and adjustable between -50°C, the maximum injection pressure of the drilling fluid circulation pump 61 ...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Embodiment 2: The present invention proposes a set of experimental methods for studying the response characteristics of natural gas hydrate formations to drilling fluid invasion based on the application of the experimental device of the above-mentioned embodiment 1. The experimental method for testing the gas permeability of hydrate deposits is divided into It is an experimental method for testing the permeability of hydrate sediments with three different permeability: low, medium and high. The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0068] (1) The steps of the experimental method for permeability testing of low-permeability hydrate sediments:
[0069] a. Water injection: the liquid water in the liquid water storage container 31 is injected into the test rock core 37 in the rock core holder 35 through the advection pump 32 through the piston container A33; the test rock core material adopts a natural rock core with a length of 500mm. The length of 700mm uses a hollow...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Example 3: An experimental method for studying the response characteristics of natural gas hydrate formations to drilling fluid invasion based on the application of the experimental device in Example 1 above, wherein the drilling fluid invades hydrate deposits and the dynamics of hydrate deposits during the invasion process The experimental method steps of response characteristic monitoring are as follows:
[0085] (1) Synthesis of hydrate deposits: the length of the core holder 35 is 1200 mm, and the sand filling model is prepared in advance and placed in the core holder 35 to fill the core holder, using the low permeability of Example 2 Steps a and b in the experimental method for the permeability test of hydrate deposits synthesize hydrate deposits;
[0086] (2) Intrusion of drilling fluid into hydrate deposits: After the drilling fluid in the drilling fluid storage tank 2 is adjusted to 30°C by the temperature controller 1, it enters the wellhead annular cavity 59 o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com