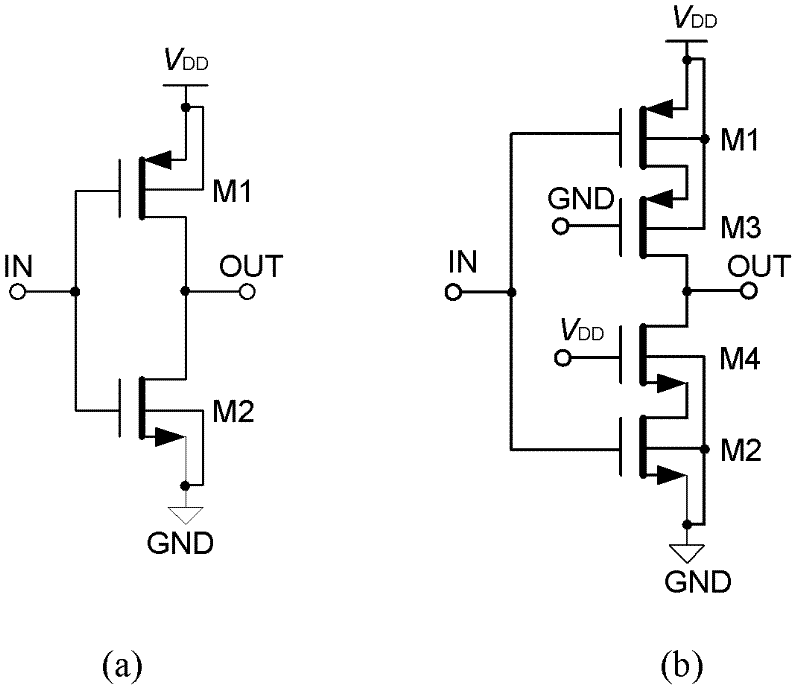
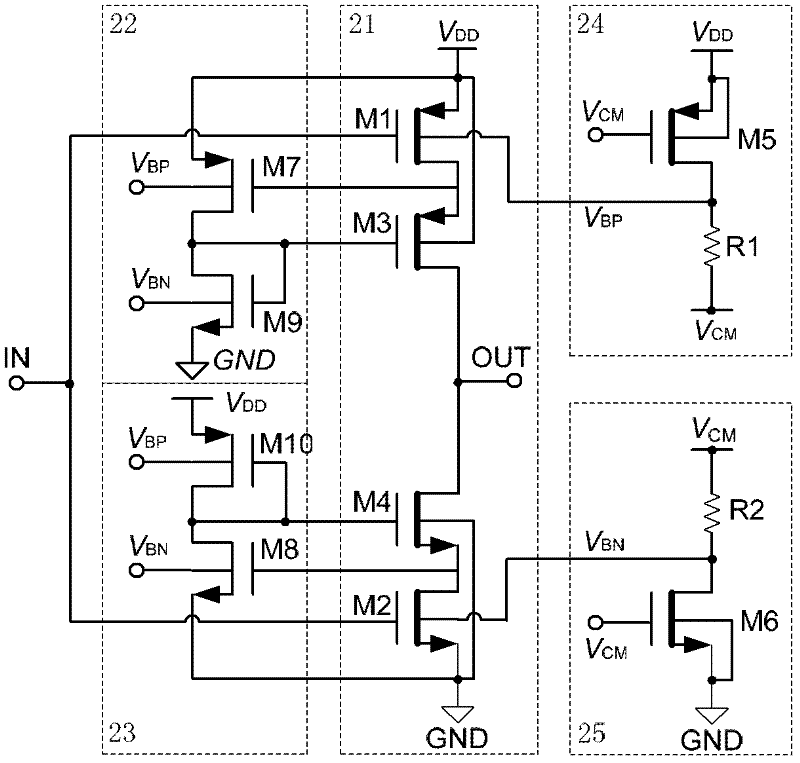
Dynamic Body Bias Type C Inverter and Its Application
A type of inverter and body bias technology, which is applied in the direction of pulse generation, electrical components, components of electric pulse circuit, etc., can solve the problems of large size and high static power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
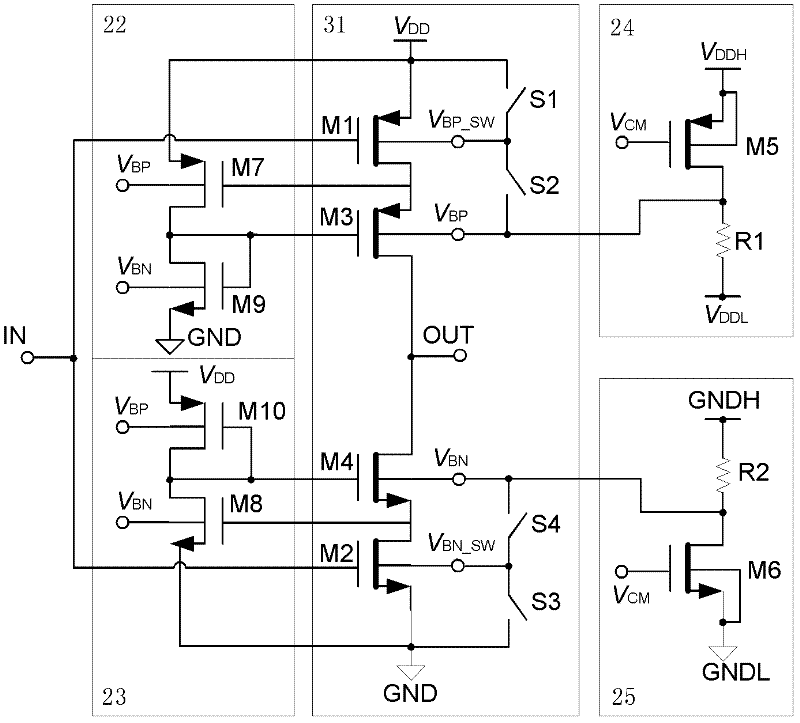
[0025] Embodiment 1 Dynamic Body Bias Type C Inverter
[0026] A dynamic body-bias type C-type inverter, its circuit structure diagram is attached image 3 As shown, it includes a switch body bias type C-type inverter 31 , a first gain bootstrap module 22 , a second gain bootstrap module 23 , a PMOS body potential modulation module 24 and an NMOS body potential modulation module 25 .
[0027] The switching body bias type C-type inverter 31 adopts a cascode structure, and it is composed of a first PMOS transistor M1, a second PMOS transistor M3, a first NMOS transistor M2, a second NMOS transistor M4 and four switches. To realize the operation amplification function.
[0028] Wherein, the first PMOS transistor M1 and the first NMOS transistor M2 are respectively the PMOS and the NMOS input transistors of the above-mentioned dynamic body-bias type C-type inverter, and the gate terminal of the first PMOS transistor M1 is connected to the gate terminal of the first NMOS transisto...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2 Pseudo-differential structure switched capacitor integrator using dynamic body bias type C-type inverter
[0040] A pseudo-differential structure switched capacitor integrator, as attached Figure 4 As shown, it includes two dynamic body-bias type C-type inverters 41 and two common-mode feedback circuits 42 in Embodiment 1, wherein the two dynamic body-bias type C-type inverters 41 are respectively located in the switched capacitor The positive and negative branches of the integrator are differentially symmetrical to form a pseudo-differential structure, and the two common-mode feedback circuits 42 respectively form common-mode feedback in the positive and negative branches of the switched capacitor integrator. The switched capacitor integrator is divided into a sampling phase and an integral phase in actual work, and is controlled by two non-overlapping clocks of p1 and p2.
[0041] During the sampling phase, the input signal IN is sampled to the capacito...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Embodiment 3 A 2-1 cascaded Sigma-Delta analog-to-digital converter using a switched capacitor integrator with a pseudo-differential structure
[0046] A 2-1 cascaded Sigma-Delta analog-to-digital converter, including a 2-1 cascaded analog modulator and a digital decimation filter, wherein the circuit structure diagram of the 2-1 cascaded analog modulator is as attached Figure 6 As shown, it includes a first-level modulator and a second-level modulator, and the second-level modulator is cascaded with the first-level modulator to modulate the quantization error generated by the previous level; the first-level modulator is a second-order It consists of two switched capacitor integrators based on the pseudo-differential structure in Embodiment 2 (i.e. the first integrator 62 and the second integrator 63), the first comparator 67 and the first feedback DAC 65, the first integrator 62 and the second integrator 63 are connected in series to form a second-order single-loop st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com