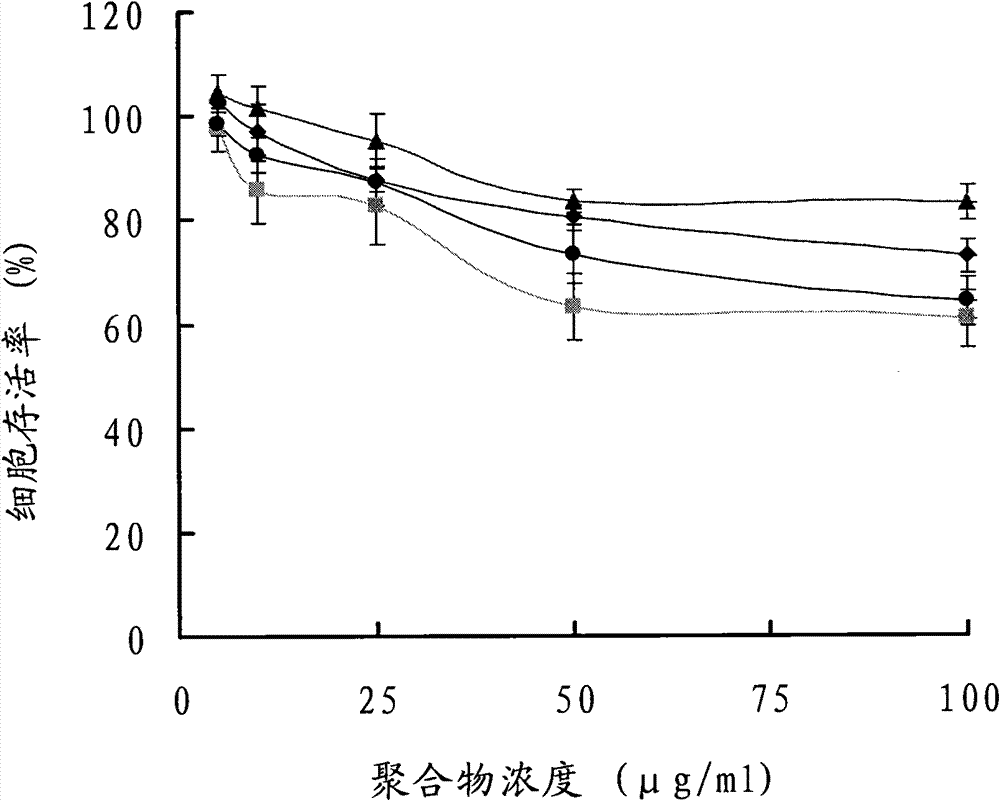
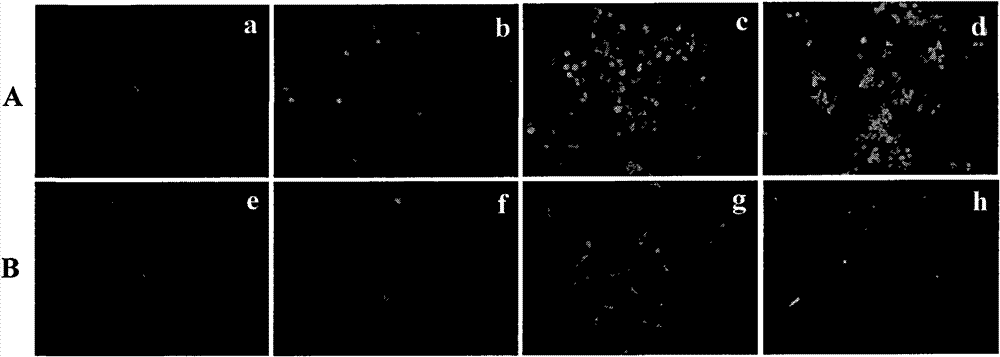
Chitosan derivative used as gene vector, and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of chitosan derivatives and chitosan, which is applied in the direction of introducing foreign genetic material, gene therapy, and pharmaceutical formulations by using a carrier, can solve the problems of unfavorable transfection efficiency, poor water solubility of chitosan, and low transfection efficiency. , to achieve high transfection efficiency, high biocompatibility, and improved water solubility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] The synthetic method of embodiment 1 chitosan derivative
[0044] The raw material of chitosan (Cs) was purchased from Shanghai Boao Biotechnology Co., Ltd., with a molecular weight of 60 kilodaltons and a deacetylation degree of 90%. The specific synthesis method is:
[0045] Step (a): Weigh 2.5 g of Cs and swell overnight in 250 ml of dimethylformamide (DMF). After filtration, the filter cake was redispersed in 100 ml of DMF, 7 g of phthalic anhydride was added, and reacted at 120° C. for 10 hours until the reaction liquid was completely clear. After the reaction was completed, the reaction solution was poured into ice water to separate out a light yellow precipitate, filtered, and the filter cake was rinsed with ether and dried to obtain the product ( 13 C NMR: δ 22.5, 57.8, 61.5, 71.3, 75.9, 83.0, 101.0, 131.4, 168.08 ppm.).
[0046] Step (b): Weigh 1 gram of the product obtained in step (a), dissolve it in 100 milliliters of N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP), add 6.5 gr...
Embodiment 2
[0057] The preparation of embodiment 2 chitosan derivatives / nucleic acid nanocomposite
[0058] The chitosan derivative (prepared by Example 1 (substitution degree 12.5%)) is dissolved with deionized water, and is made into a solution of 0.1~10 mg / ml; plasmid DNA (for the plasmid DNA containing the green fluorescent protein gene, The plasmid number is pEGFP-N1 vector, GenBank Accession #U55762) was dissolved in deionized water to obtain a DNA solution with a concentration of 0.2 mg / ml; Mix for 30 seconds and stand at room temperature for 0.5-1 hour. The chitosan derivative and plasmid DNA self-assemble into a nanocomposite through electrostatic self-assembly.
Embodiment 3
[0059] Embodiment 3 gel retardation experiment
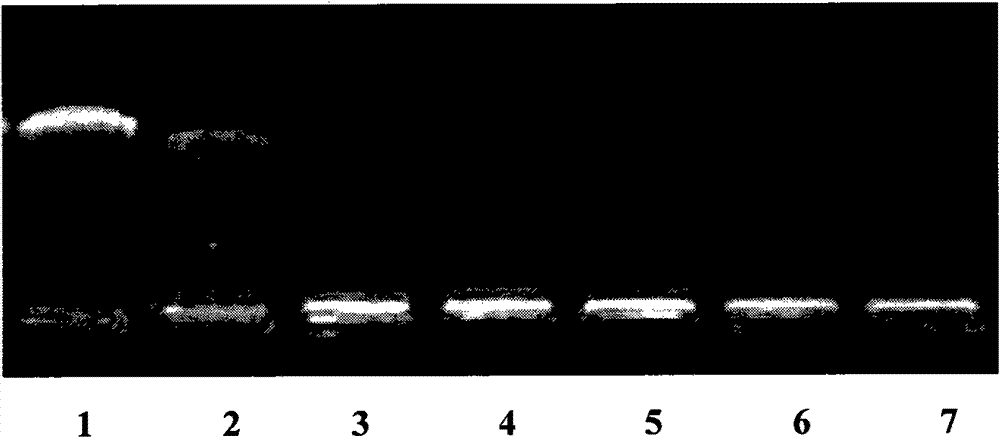
[0060] According to the method of Example 2, a series of chitosan derivatives (substitution degree 12.5%) and plasmid DNA nanocomposites with different N / P ratios were prepared. Take 20 microliters of samples of each ratio respectively, use 10 microliters of pure plasmid as a reference, perform 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, ethidium bromide staining, and photograph through a gel imaging system (UVP Bioimaging Systems). The result is as figure 1 shown.
[0061] figure 1 Among them, the first electrophoresis lane is the pure plasmid control, and the second to seventh lanes are the N / P ratios of chitosan derivatives and plasmid DNA at 0.5, 0.8, 1.2, 5, 10, and 20, respectively. from figure 1 It can be seen that chitosan derivatives can compress DNA very well, and can completely block the migration of DNA when N / P is greater than 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com