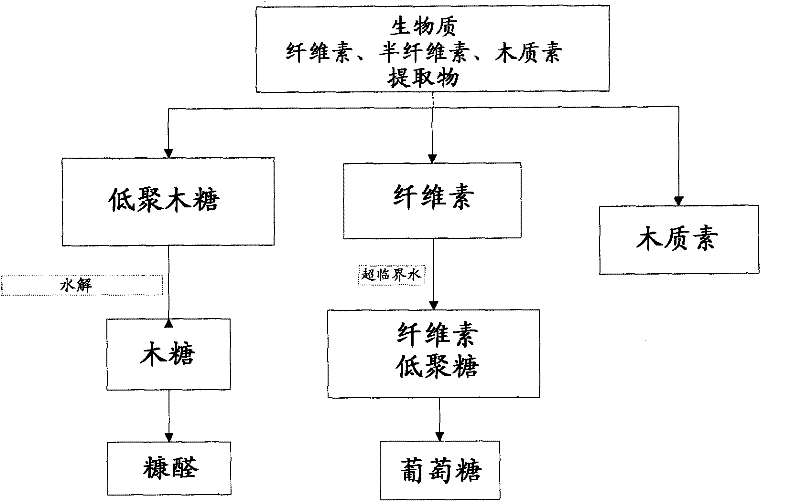
Method of extraction of furfural and glucose from biomass using one or more supercritical fluids
一种生物质、葡萄糖的技术,应用在葡萄糖产生、化学仪器和方法、糖衍生物等方向,能够解决受限生产能力、生物质被处理的速率低等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0176] Example 1 - Semi-batch Process for Biomass Fractionation
[0177] Corn stover was obtained from National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). Corn stover was processed using a grinder to produce 40 mesh corn stover. The 40 mesh particle size was found to be suitable for laboratory scale supercritical fluid extraction processes.
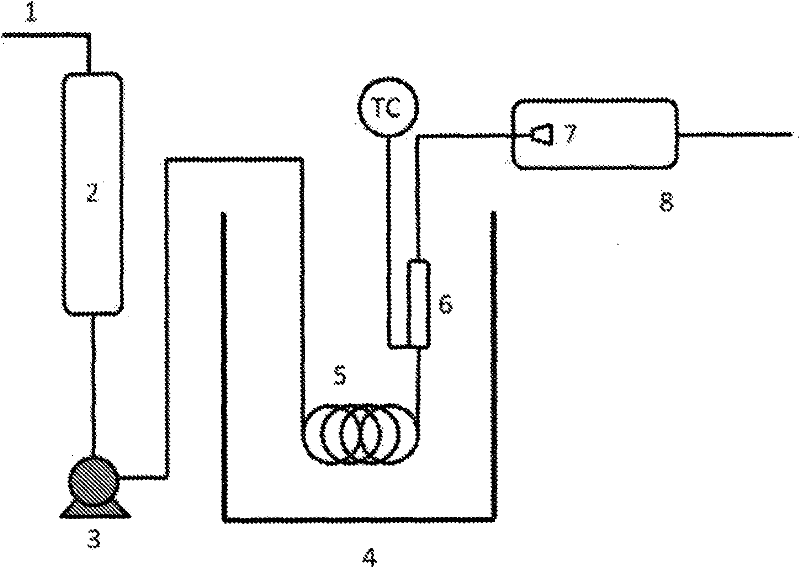
[0178] with supercritical ethanol-CO 2 Treatment of corn stover with the mixture was carried out using a semi-batch reactor (see Figure 2A ). Corn stover was held in bed 6 by a 20 micron sintered metal melt placed at the downstream end of the bed. During sand bath 4 heating, the system was purged with nitrogen. Once the desired temperature is reached, start the ethanol / CO using HPLC pump 3 2 From the reservoir 2 the flow passes first through the preheating coil 5 and then through the corn stover. Solvent temperature was monitored by thermocouples at the bed inlet. After passing through the corn stover, the solvent is expanded to atmosph...
Embodiment 2
[0187] Example 2 - Batch Process for Biomass Fractionation
[0188] One set of experiments was performed using a 1.2 ml batch reactor made of Swagelok stainless steel tubing and a TechneSB-2 fluidized sand bath. Corn stover (40 mesh size) was used for this set of experiments.
[0189] A calculated amount of 40 mesh size corn stover (1 g dry calculated VF), 3 g liquid (50 / 50 wt% mixture of water and ethanol) and 5-20 wt% dry ice (based on liquid weight) was charged to a Swagelok stainless steel tube. The tube was heated in a sand bath at varying temperature (180°C to 320°C) and pressure (75-80 bar) at different time intervals (0.17 min to 15 min). After heat treatment, the reaction was quenched by immersing the tubes in a water bath maintained at 25°C. The reaction product mixture resulting from this workup is filtered to obtain a solid product comprising cellulose. The filtrate was evaporated in an oven maintained at 75°C. The resulting remaining solid was added to water a...
Embodiment 3
[0198] Example 3 - Continuous Fractionation of Biomass - I
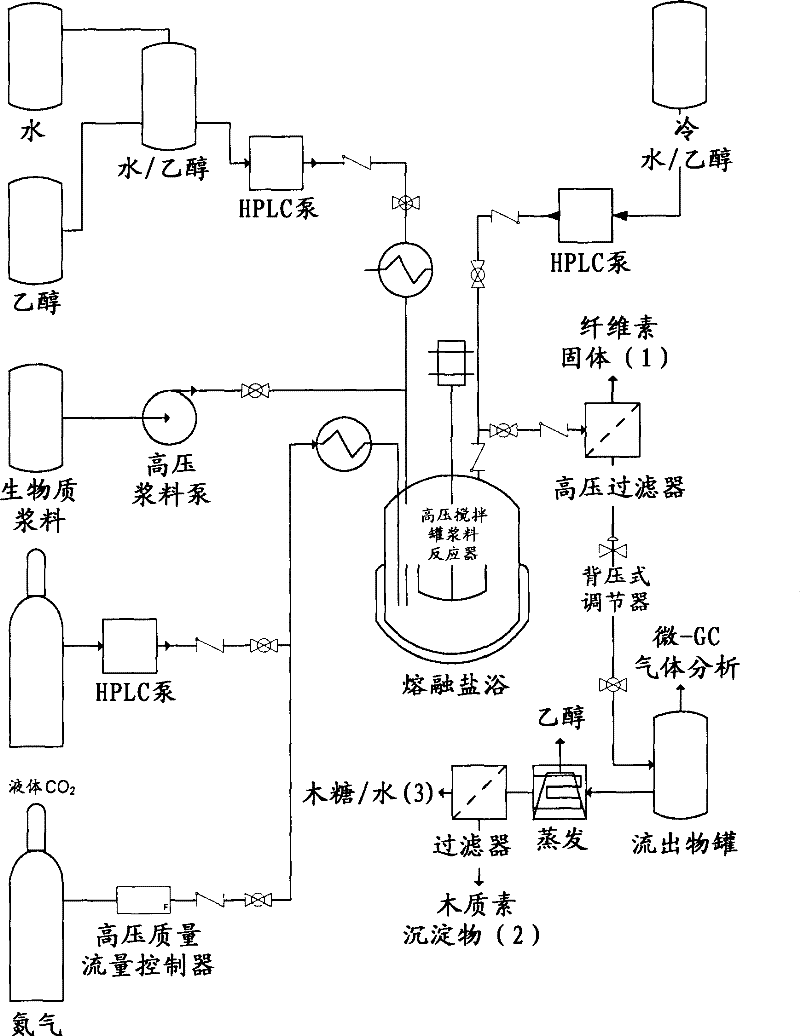
[0199] Continuous fractionation of biomass using a high-pressure, continuously stirred slurry reactor system (participated in Figure 2B ). Slurry reactors have larger volumes (100 ml) and operate at temperatures and pressures up to 350°C and 1,100 psig. The reactor system is equipped with auxiliary systems, including high pressure process gas and liquid feed systems; liquid product collection systems; and data monitoring and collection systems. Samples of liquid and gaseous products were obtained continuously. Similar stirred reactors have been successfully used by other researchers to study the hydrothermal treatment of biomass (Osada M, SatoT, Watanabe M, AdschiriT, AraiK. "Low-Temperature Catalytic Gasification of Lignin and Cellulose with a Ruthenium Catalystin Supercritical Water" Energy Fuels 2004, 18: 327-333).
[0200]In this steady state experimental setup, biomass is first mechanically treated to obtai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com