Identification method for genetic disease-related gene
A technology for hereditary diseases and identification methods, which can be used in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., and can solve the problems of high cost and unfavorable large-scale application of technology.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
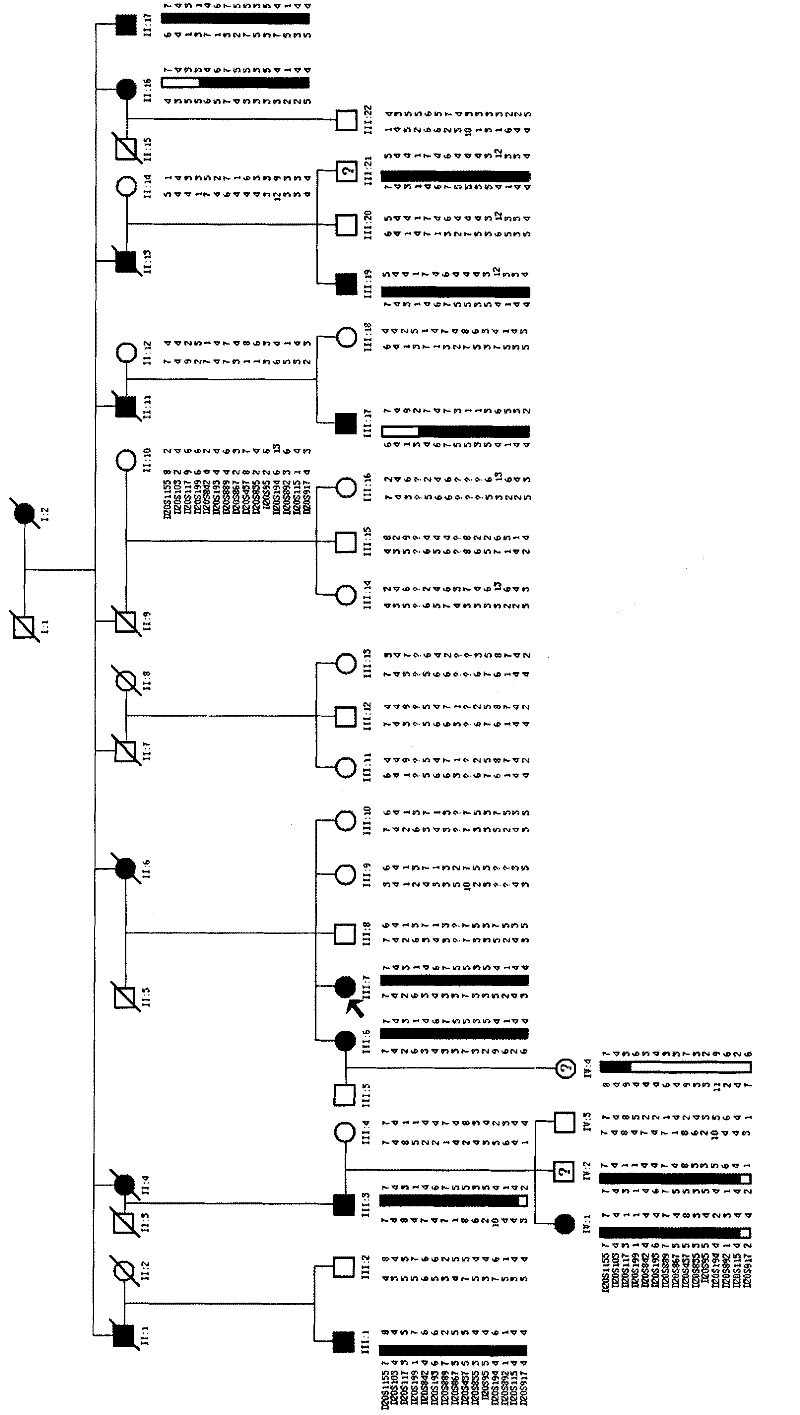
[0058] Example 1 Chromosomal Mapping of SCA Family Related Genes
[0059] Hereditary spinocerebellar ataxias (hereditary spinocerebellar ataxias, SCAs) is a group of neurodegenerative diseases with high clinical and genetic heterogeneity, and its inheritance mode is mostly autosomal dominant (autosomal dominant, AD). Patients are more common in young and middle-aged patients. Clinically, cerebellar ataxia is the main feature, and it can also be accompanied by oculomotor disturbance, slow eye movement, optic atrophy, retinitis pigmentosa, pyramidal tract signs, extrapyramidal system manifestations, and musculoskeletal syndrome. atrophy, peripheral neuropathy, and dementia. The incidence rate is about 5-7 / 100,000. The pathogenesis of the disease is not completely clear, and there is no effective treatment at present.
[0060] With the development of molecular genetics research, a total of 31 positioning sites have been found in SCA, and 19 disease-causing genes have been clone...
Embodiment 2
[0072]Example 2 Using human genome exon capture technology to capture the SCA family-related genes
[0073] On the basis of the mapping, the inventors successfully cloned a new SCA-related gene-transglutaminase 6 (TGM6) gene mutant within the mapping interval by using the human genome exon capture technology. The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0074] 1) Take the genomic DNA of a patient in the SCA family;
[0075] 2) Use ultrasound to randomly interrupt peripheral blood DNA to a fragment size of 200-300bp;
[0076] 3) Add "joints" at both ends of the interrupted DNA fragment;
[0077] 4) Hybridize the adapter-added DNA fragments with Nimblegen's chip HD2.1array for 72 hours (see the instructions for the specific operation method);
[0078] 5) amplifying the DNA fragments eluted after hybridization;
[0079] 6) Purify the amplification product;
[0080] 7) The amplified product was sequenced using the sequencer GA II of Illumina Company.
[0081] The above DNA...
Embodiment 3
[0091] Embodiment 3PCR detects whether the T1550G mutation occurs in the TGM6 gene
[0092] The genes related to hereditary spinocerebellar ataxia were detected in the genomes of 9 SCA patients, 18 normal persons and 3 persons with unclear clinical diagnosis in the family described in Example 1, amplified by PCR, and the products were purified , The sequencing method is used to obtain the sequence of exon 10 of the hereditary spinocerebellar ataxia-related gene. According to the sequence determination result, it belongs to the mutant hereditary spinocerebellar ataxia-related gene or the wild-type hereditary spinocerebellar ataxia Related genes, to verify the correlation between hereditary spinocerebellar ataxia related genes and SCA. The specific method steps are as follows:
[0093] 1) DNA extraction:
[0094] The peripheral venous blood of 9 SCA patients, 18 normal people and 3 patients with unclear clinical diagnosis was collected respectively, 5 mL per person, anticoagul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com