A process for making particles for delivery of drug nanoparticles
A nanoparticle and delivery system technology, applied in the chemical method of liquid-liquid reaction, digestive system, drug combination, etc., can solve the problems of drug instability, high melting point of active ingredients, incompatibility, etc., to improve biological Effect of Utilization, Particle Size Reduction, Increased Dissolution Rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
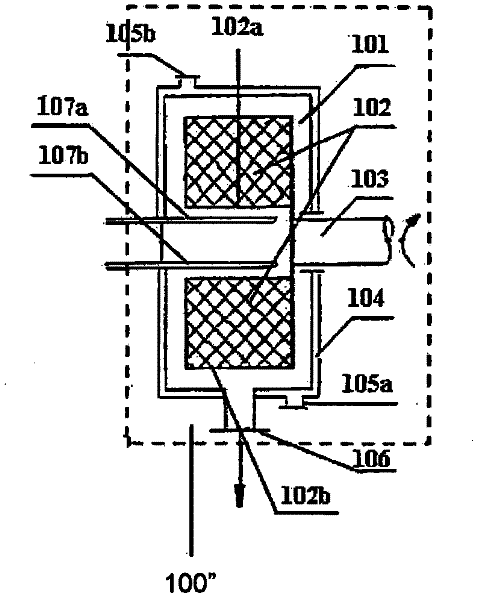
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0311] Embodiment 1---Preparation of Fenofibrate Nanoparticles
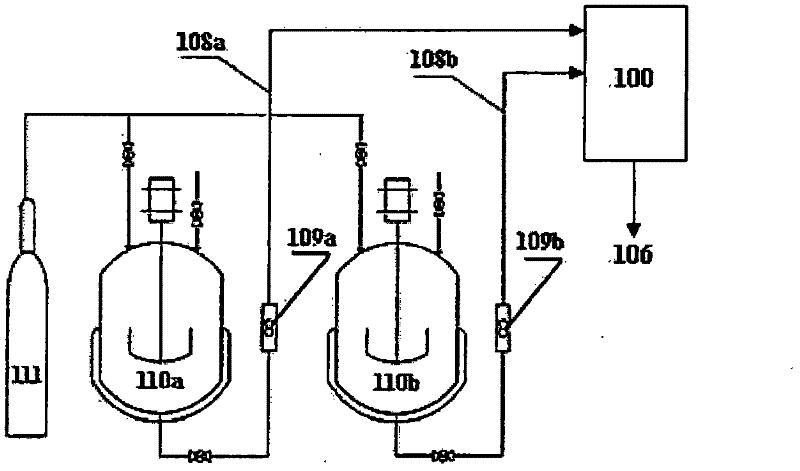
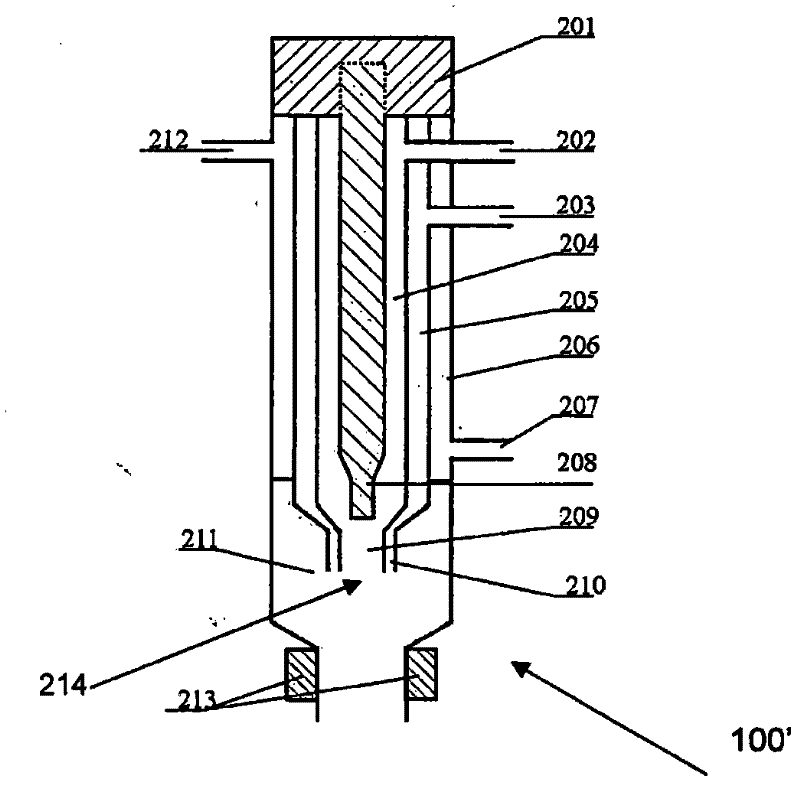
[0312] In this example, fenofibrate nanoparticles are prepared by the process of the present invention and the post-precipitation treatment process shown in Figure 2 as shown in 8a, including precipitating fenofibrate nanoparticles from the precipitant solution and spray drying fenofibrate. Beta nanoparticle process.
[0313] During the drug precipitation process, the solution containing fenofibrate and the anti-solvent form a suspension of fenofibrate nanoparticles and excipients in a micro-mixed environment.
[0314] The solution to be precipitated was prepared by dissolving 20 g of fenofibrate and 0.5 g of sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) in 200 ml of ethanol at 40° C. The solution temperature was maintained at 35°C.
[0315] The anti-solvent solution was prepared by dissolving 76g of lactose and 2g of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC)-E3, 1.5g of SLS in 2000ml of water at 25°C. The temperature of the solution...
Embodiment 2
[0344] Embodiment 2: Preparation of Lopinavir Nanoparticles
[0345] In this example, lopinavir nanoparticles are prepared by the process of the present invention and the precipitation post-treatment process shown in 8a in Fig. 2, which also includes precipitating lopinavir nanoparticles and spray drying from the solution to be precipitated Process of lopinavir rice granules.
[0346] In the precipitation step, the lopinavir-containing solution and the anti-solvent are mixed under conditions of high shear and high gravity to form a suspension of lopinavir and excipients.
[0347] The solution to be precipitated is prepared by dissolving 20 g of lopinavir and 0.5 SLS in 200 ml of ethanol at 40° C. The solution was then cooled and maintained at 20°C.
[0348] The anti-solvent solution was prepared by dissolving 76g of lactose, 2g of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC)-E3 and 1.5g of SLS in 2000ml of water at 25°C. The solution temperature was then maintained at 4°C.
[0349]...
Embodiment 3
[0384] The preparation of embodiment 3-cefuroxim axetil (CFA)
[0385] In this example, CFA nanoparticles are prepared by the process of the present invention and the post-precipitation treatment process shown in Figure 2 8a, which also includes precipitating CFA nanoparticles from the solution to be precipitated, and then preparing by spray drying CFA nanoparticles.
[0386] In the precipitation step, under high shear force and high gravity conditions, the CFA solution is mixed with the antisolvent solution to obtain a cefuroxime axetil suspension containing excipients.
[0387] Take by weighing 20g of CFA raw material drug, 0.5g sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) and dissolve in 100ml ethanol / acetone (proportioning is 1: 3) at 40 ℃, make cefuroxime axetil solution, wherein temperature is cooled gradually And keep it at about 20°C.
[0388] Weigh 76g of lactose, 4g of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC)-E3 and 1.5g of SLS and dissolve them in 1000ml of water at 25°C to prepare an ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com