Mixed type driving and driven magnetic suspension bearing
A magnetic suspension bearing and hybrid technology, applied in the field of magnetic bearings, can solve the problems of large volume, high weight, large temperature rise, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing ampere turns, volume, loss and temperature rise.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
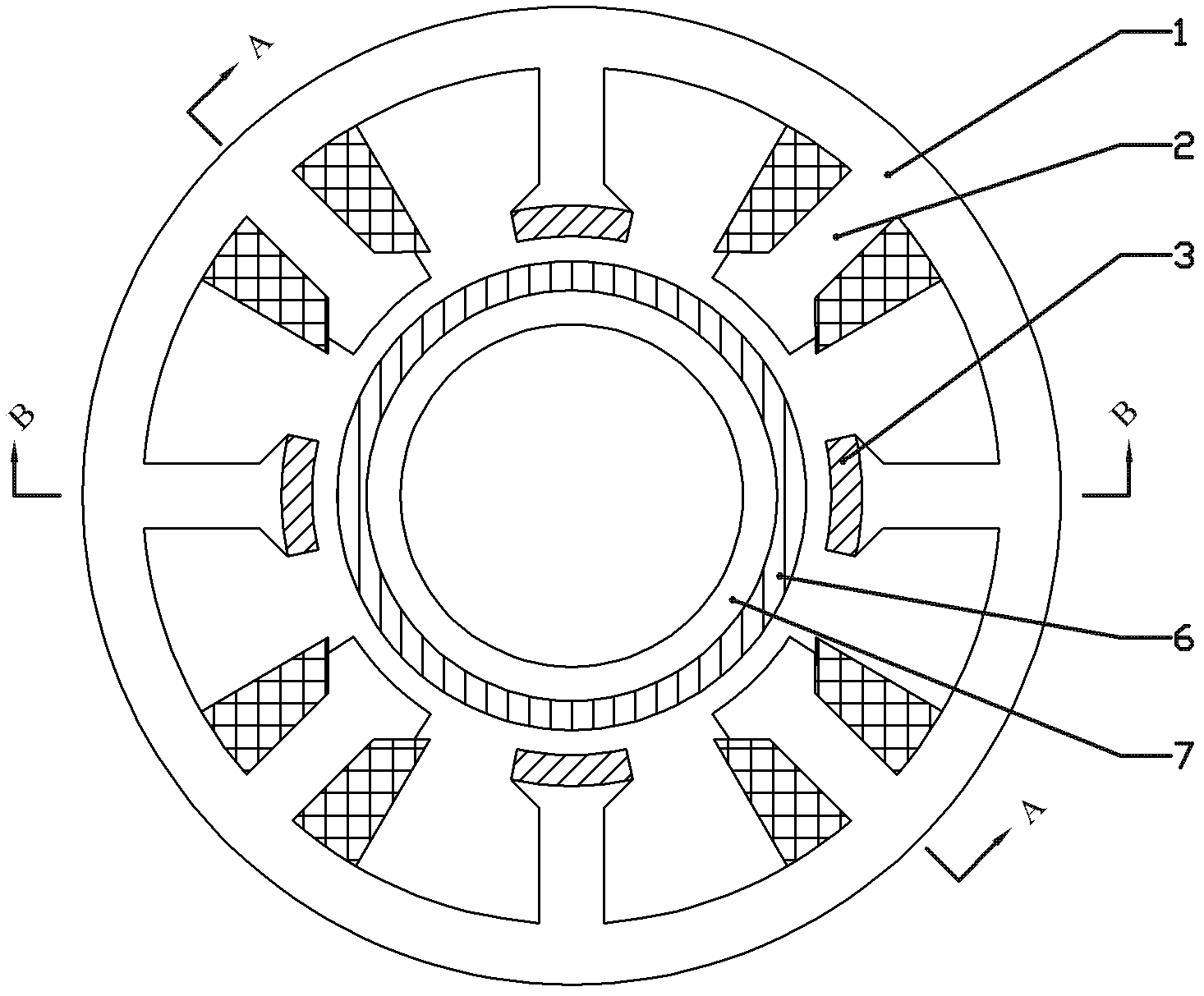
[0009] Specific Embodiments 1. The active and passive hybrid magnetic suspension bearing described in this embodiment includes a stator, a rotor and an air gap.
[0010] The rotor includes a rotor magnetically conducting yoke 7 and a rotor permanent magnet 6. The rotor magnetically conducting yoke 7 is cylindrical, and two annular rotor permanent magnets 6 are axially distributed on the rotor yoke 7. On the outer surface, the magnetization direction of each annular rotor permanent magnet 6 is radial magnetization, and the magnetization directions of the two annular rotor permanent magnets 6 are opposite;
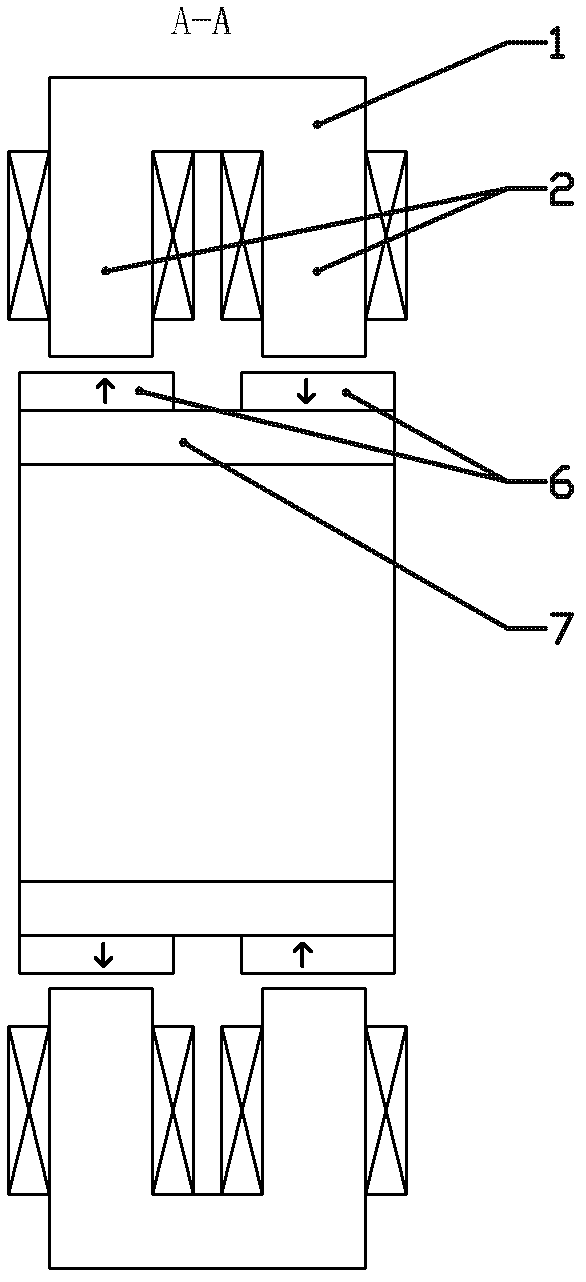
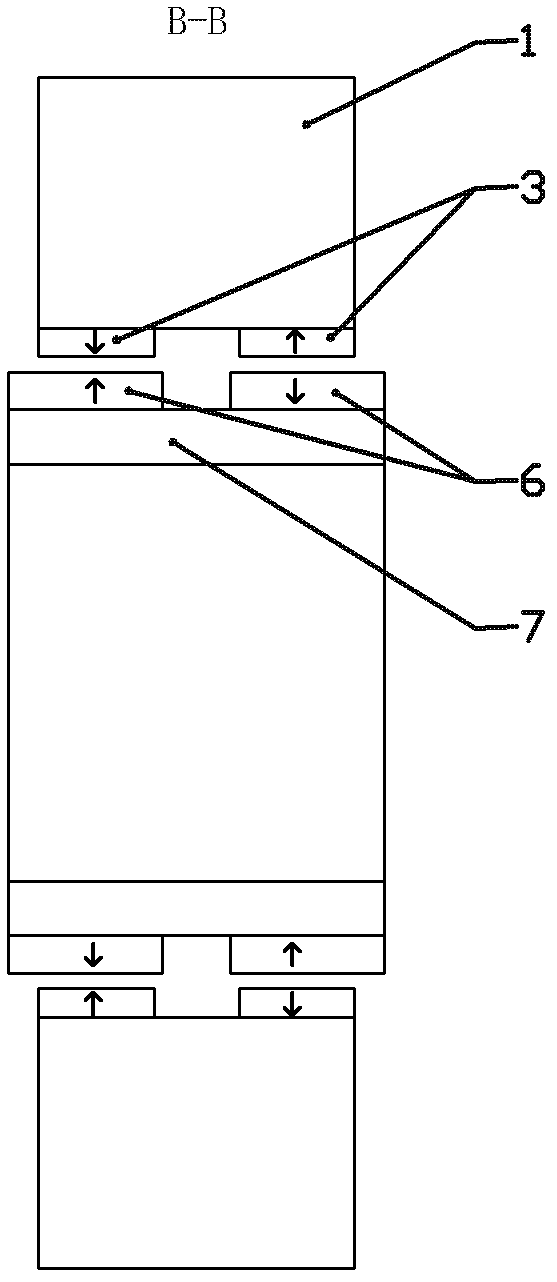
[0011] The stator includes a stator core 1, a radial force control winding and a stator permanent magnet 3. The stator core 1 is cylindrical, and the inner surface of the cylindrical stator core 1 is grooved in the axial direction, and formed on the inner side of the stator core 1. 4n stator teeth, where n is a natural number greater than 1, on the inner surface of the first...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0013] Specific embodiment 2. This embodiment is a further limitation of the active and passive hybrid magnetic suspension bearing described in specific embodiment 1. The rotor in the active and passive hybrid magnetic suspension bearing described in this embodiment also includes a rotor protection sleeve 9 , see Figure 11 As shown, the rotor protective sleeve 9 is cylindrical, and is fixedly sleeved on the outer surface of the rotor permanent magnet 6 .
[0014] The rotor protective sleeve 9 added in this embodiment is made of high-strength material to protect the rotor. The rotor protective sleeve 9 is a thin-walled cylinder, and the wall thickness of the round tube is determined according to the diameter and rotational speed of the rotor, generally 0.5-4mm.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0015] Specific Embodiment Three. This embodiment is a further limitation of the active and passive hybrid magnetic suspension bearing described in specific embodiment one or two. In the rotor of the active and passive hybrid magnetic suspension bearing described in this embodiment, two On the outer surface of the rotor magnetically conducting yoke cylinder 7 between the annular rotor permanent magnets 6, an axially magnetized annular rotor permanent magnet 4 is also fixed, and the axially magnetized annular permanent magnet The direction of magnetization is from the inwardly magnetized annular rotor permanent magnet 6 to the outwardly magnetized annular rotor permanent magnet 6, see Figure 4 and Figure 5 shown.
[0016] In this embodiment, an axially magnetized annular rotor permanent magnet 4 is added in the rotor, and the axially magnetized annular rotor permanent magnet 4 is axially magnetized, which is different from the original Two radially magnetized annular rotor ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com