High-speed low-noise semiconductor device structure and method for forming same
A device structure and semiconductor technology, applied in the fields of semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of increasing device noise coefficient, wasting layout area, reducing circuit operating speed, etc. The effect of increasing speed and improving performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
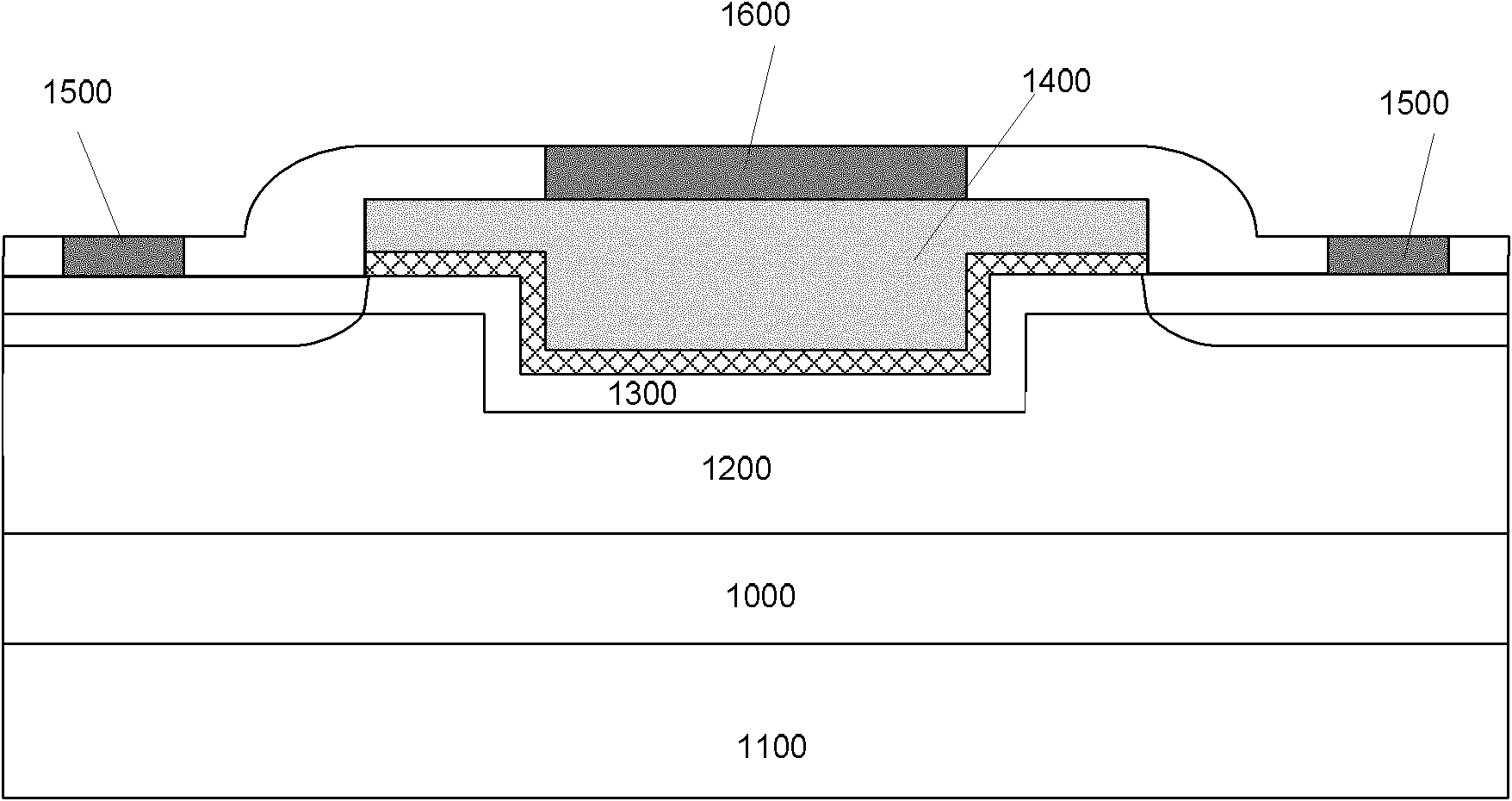
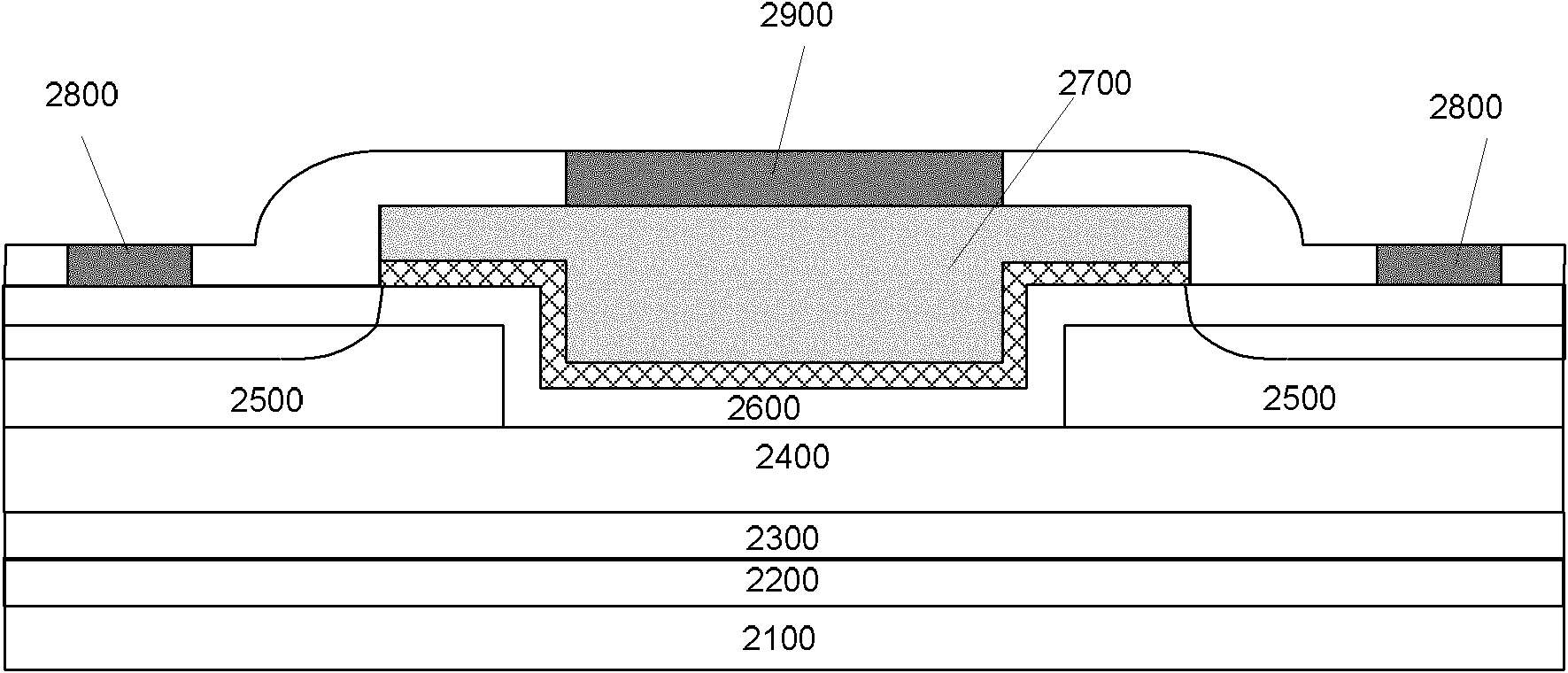
[0030] Embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below, examples of which are shown in the drawings, wherein the same or similar reference numerals designate the same or similar elements or elements having the same or similar functions throughout. The embodiments described below by referring to the figures are exemplary only for explaining the present invention and should not be construed as limiting the present invention.
[0031] The following disclosure provides many different embodiments or examples for implementing different structures of the present invention. To simplify the disclosure of the present invention, components and arrangements of specific examples are described below. Of course, they are only examples and are not intended to limit the invention. Furthermore, the present invention may repeat reference numerals and / or letters in different instances. This repetition is for the purpose of simplicity and clarity and does not in itself indicat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com