Method for preparing nano zinc gallate with blue fluorescence
A technology of blue fluorescence and zinc gallate, applied in the field of nanomaterials, can solve the problems of poor luminescence performance, less luminescent materials, poor dispersion, etc., and achieve the effect of simple operation steps, fast reaction speed and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] ①In a 30mL reaction flask, dissolve 1 part of zinc salt and 2 parts of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate in 1000 parts of water, stir to form zinc complexes and ions, then add 2 parts of gallium chloride, and then add hydrogen The sodium oxide solution was adjusted to pH 10 and stirred vigorously for 2 hours.
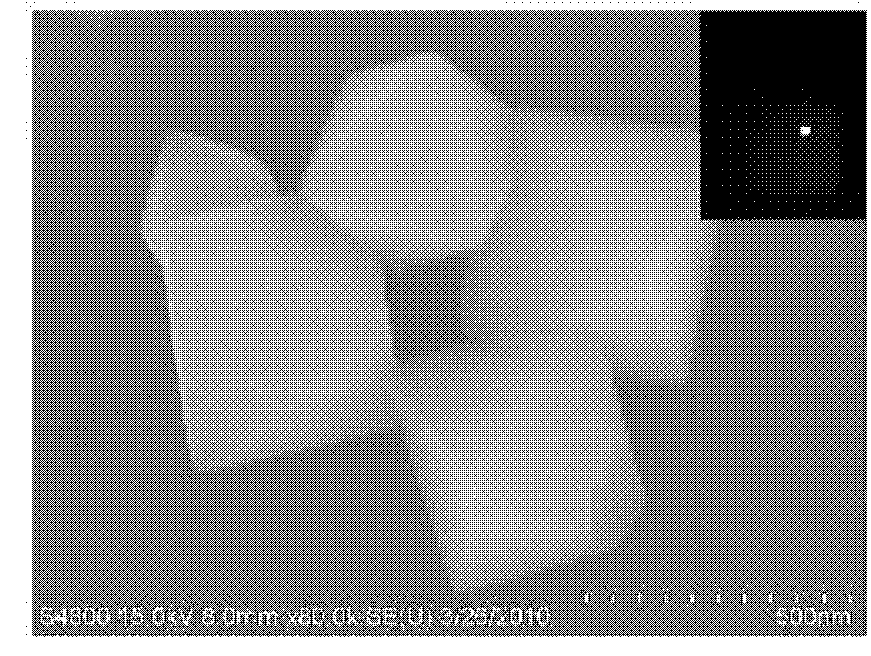
[0021] ②Transfer the reaction solution prepared according to step ① into a 50mL polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, control the reaction temperature to 180°C, and the reaction time to 48 hours. After the reaction, the reaction kettle was naturally cooled to 60° C., the product was filtered, washed with absolute ethanol and water several times, and vacuum-dried to obtain zinc gallate nanomaterials. figure 1 is the scanning electron micrograph of the obtained zinc gallate nanomaterial. It can be seen from the figure that the zinc gallate nanomaterial has a single-crystal regular octahedral structure, which is a pure-phase cubic structure of ZnGa 2 o 4 , the UV-Vis max...
Embodiment 2
[0023] ①In a 30mL reaction flask, dissolve 50 parts of zinc salt and 200 parts of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate in 1000 parts of water, stir to form zinc complexes and ions, then add 100 parts of gallium chloride, and then add hydrogen The sodium oxide solution was adjusted to pH 10 and stirred vigorously for 2 hours.
[0024] ②Transfer the reaction solution prepared according to step ① into a 50mL polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, control the reaction temperature at 200°C, and the reaction time for 6 hours. After the reaction, the reaction kettle was naturally cooled to 60° C., the product was filtered, washed with absolute ethanol and water several times, and vacuum-dried to obtain zinc gallate nanomaterials. The scanning electron micrograph of the obtained zinc gallate nanomaterial is as follows figure 2 shown. It can be seen from the figure that the zinc gallate nanomaterial has a single-crystal regular octahedral structure, which is a pure-phase cubic structure of ZnGa...
Embodiment 3
[0026] ①In a 50mL reaction bottle, dissolve 10 parts of zinc salt and 50 parts of sodium lauryl sulfate in 1000 parts of water, then add concentrated ammonia water to form a clear and transparent zinc complex and ion solution, add 20 parts of gallium sulfate , and then add sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH value to 8, then vigorously stir for 2 hours.
[0027] ②Transfer the reaction liquid prepared according to step ① into a 50mL polytetrafluoroethylene reactor, control the reaction temperature to 160°C, and the reaction time to 96 hours. After the reaction, the reaction kettle was naturally cooled to 60° C., the product was filtered, washed with absolute ethanol and water several times, and vacuum-dried to obtain zinc gallate nanomaterials. The scanning electron micrograph of the obtained zinc gallate nanomaterial is as follows image 3 shown. It can be seen from the figure that the zinc gallate nanomaterials are assembled into small particles to form a cake-like s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com