Method for preparing nano particle enhanced magnesium-based composite material
A composite material and nanoparticle technology, applied in the field of magnesium-based composite material preparation, can solve the problems of limited phase growth of control clusters and particles, affect the performance of composite materials, runaway combustion, etc., achieve flexible operation and production organization, improve Thermodynamics and Kinetics, Effect of Reducing Magnesium Oxidation Burning Loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Implementation example 1: preparation (Al 3 Zr+ZrB 2 ) p / 60%Mg-30%Al composite material
[0033] Raw materials: matrix magnesium metal, pure aluminum; reaction salt: K 2 ZrF 6 -KBF 4 Powder, refining degassing agent and slag removal agent;
[0034] The preparation process is as follows:
[0035] (1) Metal smelting and powder preparation:
[0036] Put 2Kg of pure Al into a crucible, melt it in a 25kW resistance furnace and heat it up to 900°C, degas and remove slag; all the reagents used are fully dried at 250°C, of which K 2 ZrF 6 -KBF 4 , ground into fine powder (particle size less than 100nm), weighed according to 30% of the theoretical weight of the particle-reinforced phase, and then wrapped with aluminum foil for use.
[0037] 4Kg of pure magnesium is melted to 720°C in another crucible melting furnace filled with argon, and at the same time, 0.15% calcium is added to the melt to prevent flames, and NaCl, KCl and MgCl are used to 2 Mix fl...
Embodiment 2
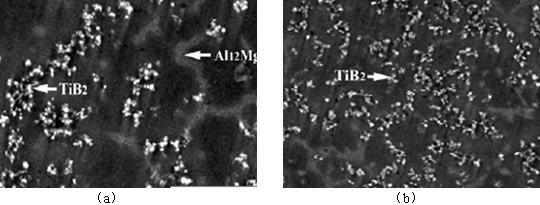
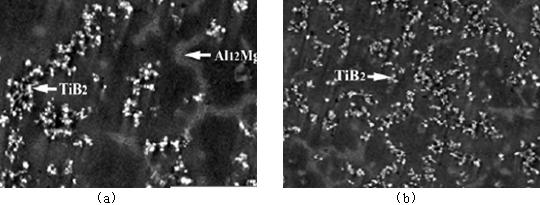
[0043] Implementation Example 2: Preparation of TiB 2 Particle Reinforced Magnesium Alloy Matrix Composites
[0044] Raw material: matrix magnesium alloy (Mg-11%Al-0.5%Zn-0.2%Mn); reaction salt: K 2 TiF 6 -KBF 4 Powder, refining degassing agent and slag removal agent;
[0045] The preparation process is as follows:
[0046] (1) Metal smelting and powder preparation:
[0047] Mixed salt reagents are fully dried at 250°C to 300°C, of which K 2 TiF 6 -KBF 4 , ground into fine powder (particle size less than 100 mesh), weighed according to 10% of the theoretical weight of the particle-reinforced phase, and then wrapped with aluminum foil for use.
[0048] 2Kg of pure magnesium alloy is melted to 750°C in another crucible melting furnace filled with argon, and at the same time, 0.15% calcium is added to the melt to prevent flames, and NaCl, KCl and MgCl are used to 2 Mix flux.
[0049] (2) In situ reaction to prepare aluminum-based alloys containing particle-reinf...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Equivalent diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com