Halomonas strain and application thereof
A technology of Halomonas and hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, applied in bacteria, fermentation and other directions, can solve the problems of uncompetitiveness and high manufacturing cost of PHA manufacturing process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0091] Embodiment 1, isolation and identification of bacterial strain
[0092] 1. Separation
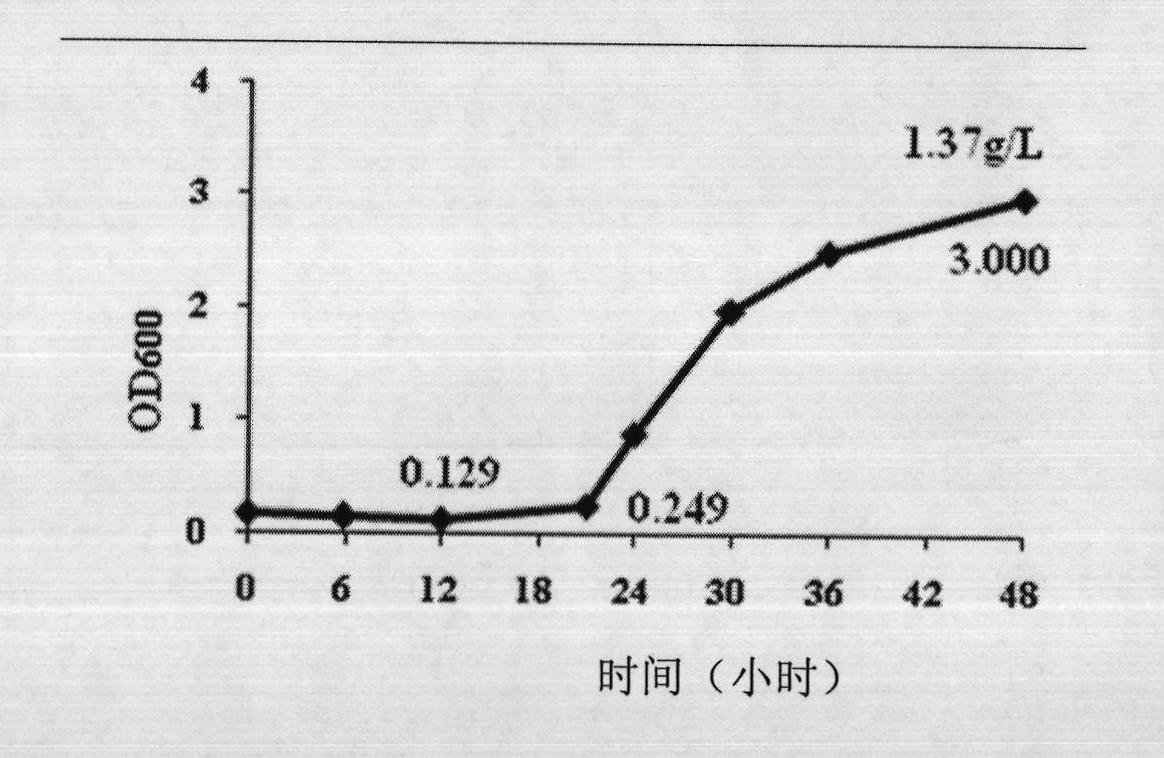
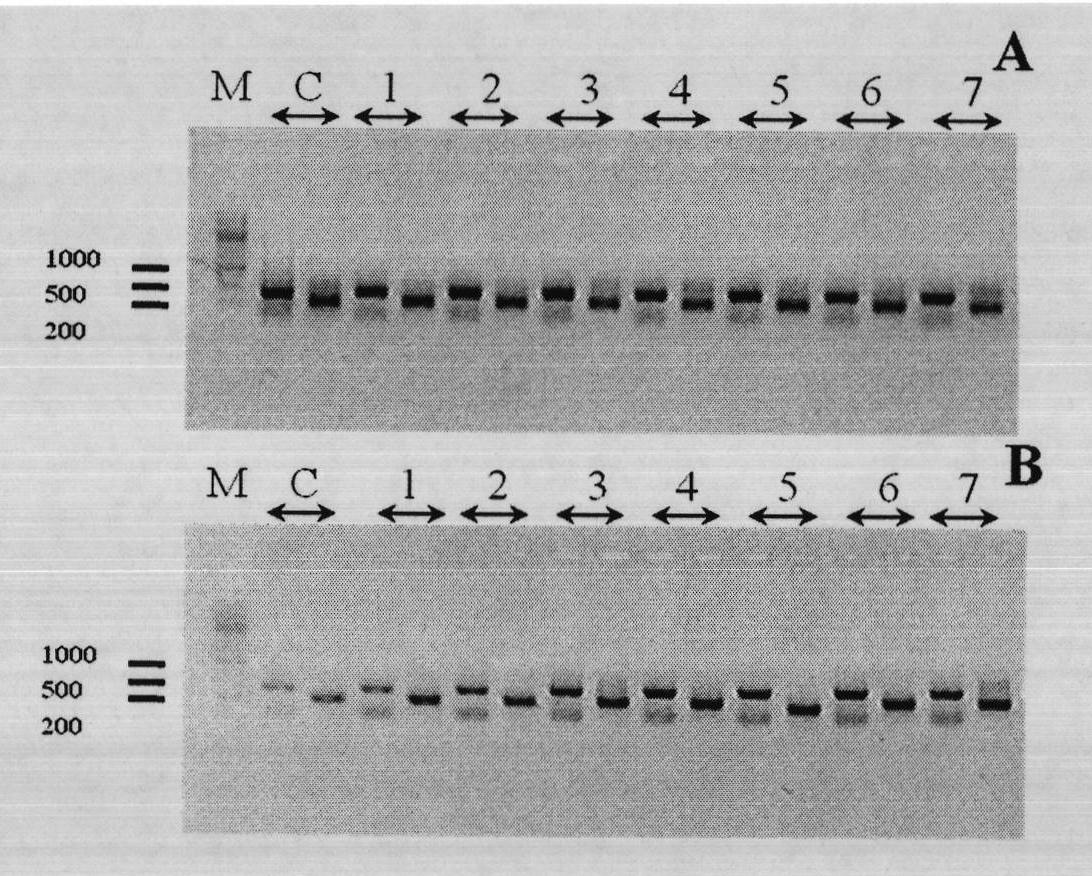
[0093] Soil and water samples were obtained from Aiding Lake, a salt lake in Xinjiang, and strains were isolated from them. Fourier transform infrared (FI-IR) was performed on well-growing colonies to detect whether they accumulated PHA. Ten strains of PHA-producing halophilic bacteria were obtained, and one strain with good growth and high accumulation of PHA was selected and named TD01.
[0094] LB medium for separating and purifying strains: sodium chloride 60g / L, peptone 10g / L, yeast powder 1g / L, the remaining components are water, and the pH value is about 8.0;
[0095] The medium for judging whether PHA can be accumulated was solid glucose mineral (MM-G) medium supplemented with 2% agar. MM-G medium:
[0096] 1 liter of MM-G medium was prepared as follows: 10 g of glucose, 60 g of sodium chloride, 0.5 g of yeast powder, 2 g of ammonium sulfate, 0.2 g of magnesium sulfate, 1...
Embodiment 2
[0113] Example 2, using optimized conditions to cultivate Halomonas TD01 to produce PHB and PHBV
[0114] (1) Production of PHB by Shake Flask Culture with Optimized Medium
[0115] The growth and production conditions of strain TD01 were optimized by combining single factor variable and orthogonal experiment. After optimization, considering the cost of each substrate, the optimal conditions for the growth and production of PHA were obtained.
[0116] The optimal conditions are: temperature 37°C, pH 9.0;
[0117] method 1:
[0118] 1 liter optimized MM-G medium: composed of 30g glucose, 60g sodium chloride, 1g yeast powder, 2g ammonium chloride, 0.2g magnesium sulfate, 1.5g potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 9.65g disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate, 10ml Trace element I, 1ml trace element II and deionized water, deionized water to make up the volume to 1 liter.
[0119] 1 liter of the trace element I is prepared as follows: mix 5 g of ferric ammonium citrate, 2 g of ca...
Embodiment 3
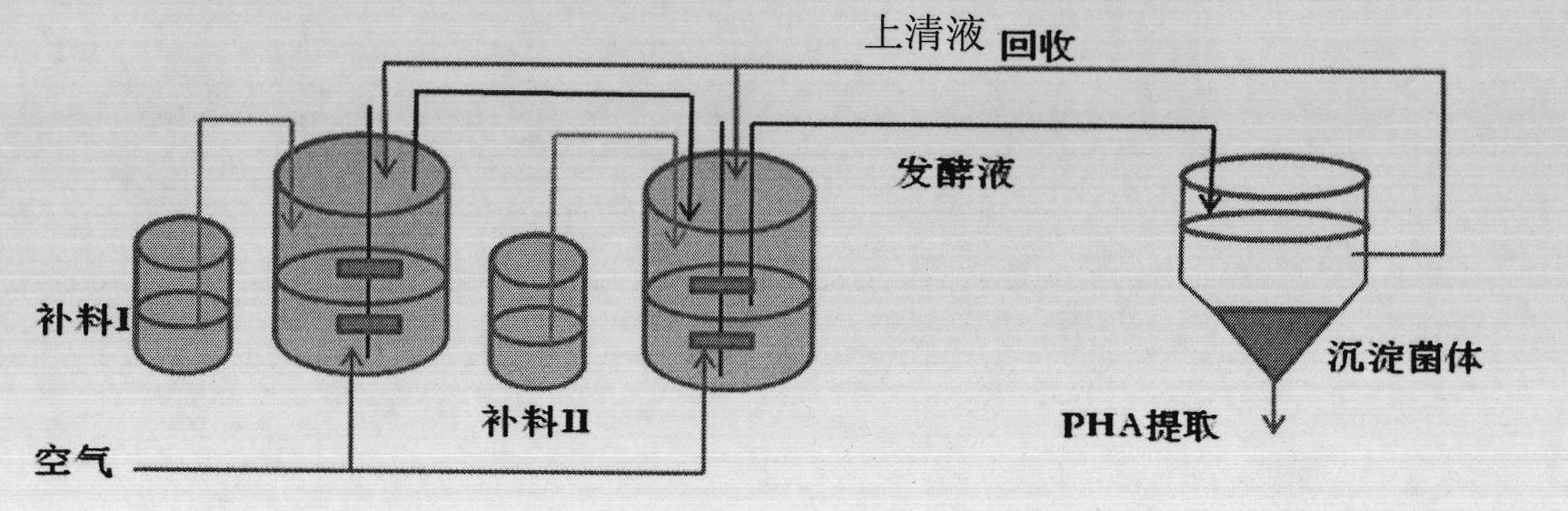
[0196] Embodiment 3, utilize bacterial strain to prepare PHB under non-sterile condition
[0197] (1) Experimental group
[0198] method 1:
[0199] 1. Cultivation of seed solution
[0200] Both primary and secondary seed liquid medium are LB medium, and 1 liter of LB medium is composed of: 60g sodium chloride, 10g peptone, 5g yeast powder, supplemented with distilled water to 1 liter, and sterilized at 121°C for 20 minutes.
[0201] Take 20 μl of Halomonas sp. TD01CGMCC No.4353 stored in a glycerol tube at -80°C and insert it into 20mL of the first-grade seed solution, and culture it overnight at 37°C and 200 rpm to obtain the first-grade seed culture solution . The primary seed culture solution was inserted into a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 100mL of the secondary seed solution according to the inoculation amount of 5%, and 3 bottles of 300mL were connected in total, and cultivated at 37°C and 200 rpm for about 12 hours to obtain the secondary seed culture solution....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com