Cell selection apparatus, and cell selection method using the same
A screening device and screening method technology, applied in the field of cell screening, can solve the problems of unable to screen cells, complicated separation procedures, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
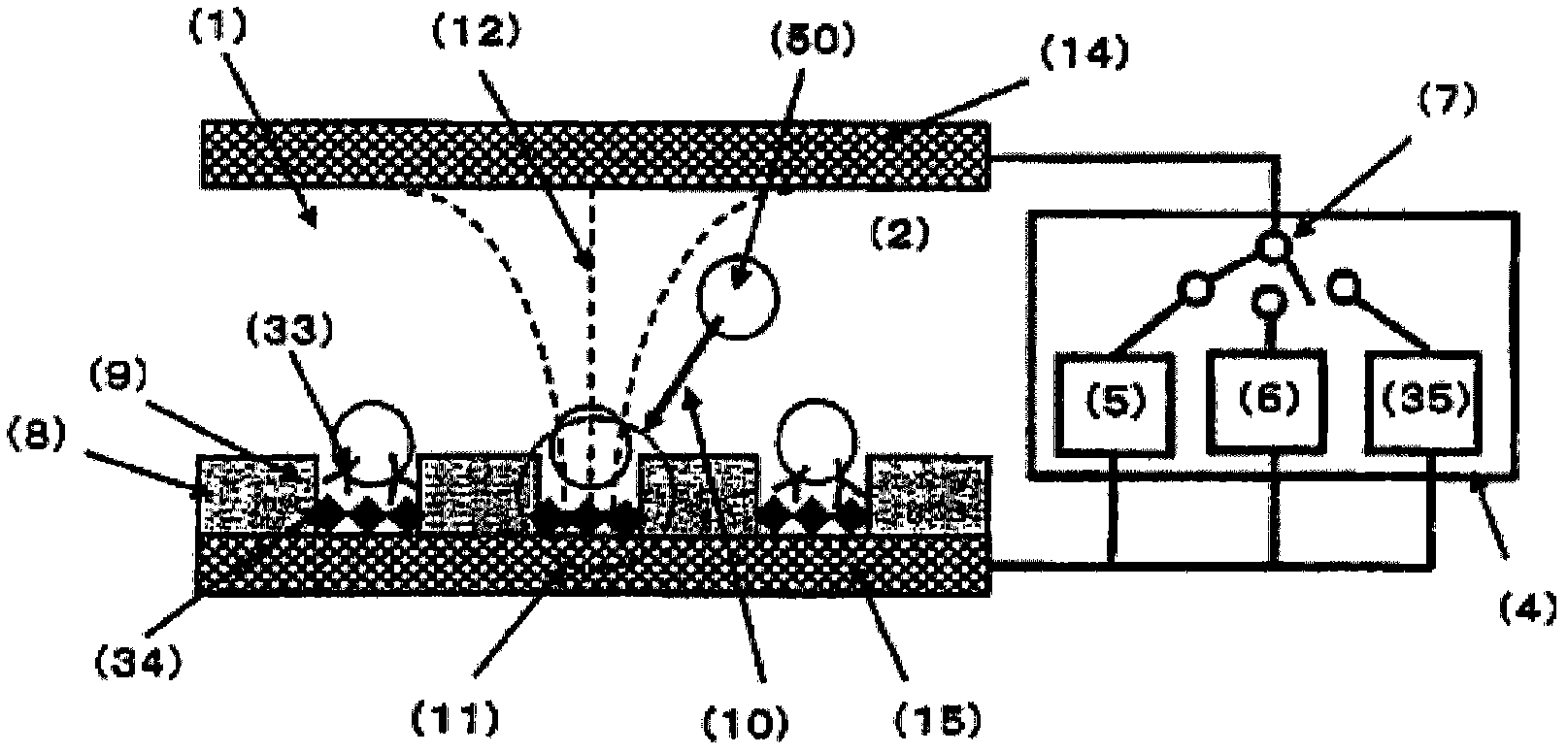
[0237] Figure 4 A schematic diagram of the cell screening device used in Example 1 is shown. Roughly divided, the cell screening device consists of a cell screening container (13) and a power supply (4). Cell screening containers such as Figure 4 The structure shown is as follows: a spacer (16) is arranged between an upper electrode (14) and a lower electrode (15), and an insulator (8) having a plurality of fine holes formed in an array is sandwiched between the spacer and the lower electrode . Also, as will be described later, micropores are formed in the insulator disposed on the lower electrode (15) by general photolithography and etching.
[0238] As the upper electrode and the lower electrode, electrodes formed of ITO (film thickness 150 nm) on a Pyrex (registered trademark) substrate with a length of 70 mm x a width of 40 mm x a thickness of 1 mm were used. A silicone rubber sheet having a shape of 20 mm in length by 20 mm in width and having a shape of 40 mm in le...
Embodiment 2
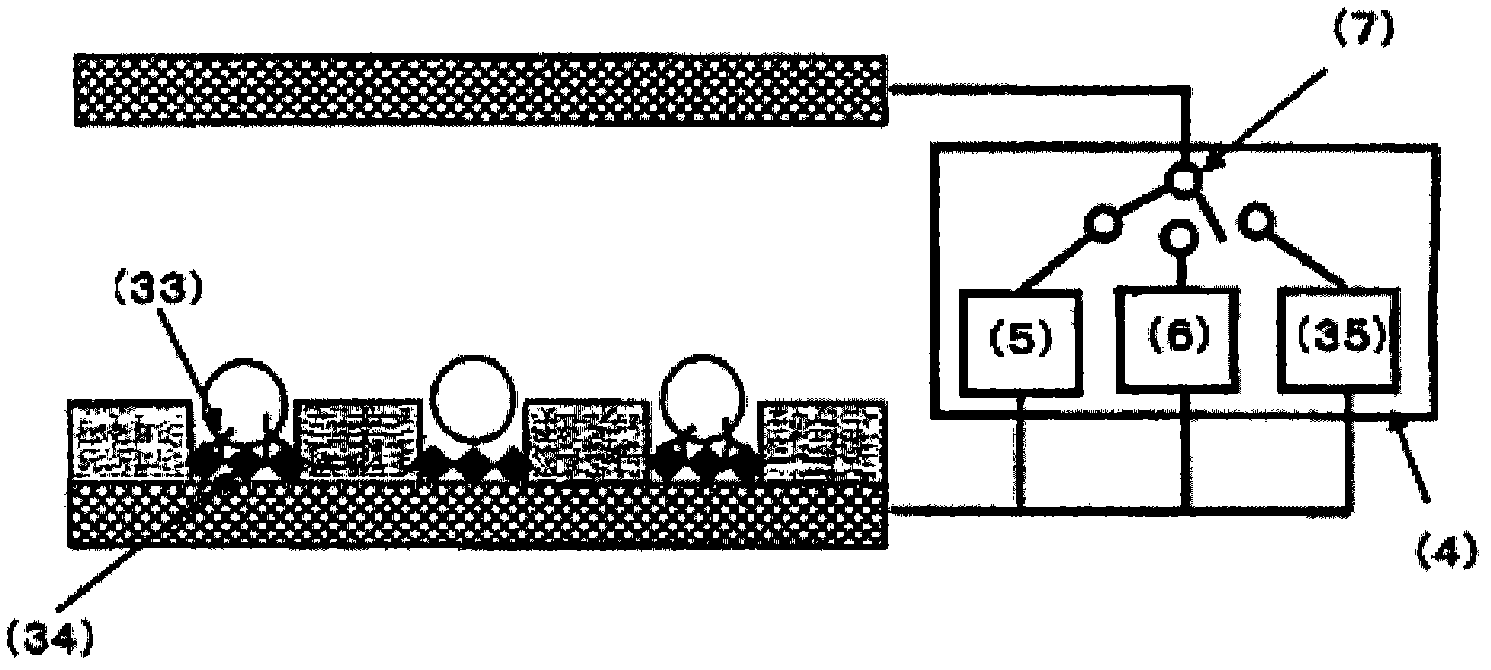
[0255] Antibody-immobilized polystyrene beads used in Example 1 to immobilize the anti-E2 antibody on the surface with the anti-E2-mouse antibody solution at each concentration of 0, 0.1, 0.5, and 2.0 μg / mL were introduced into the spacer. 600 μL of the suspension (bead concentration: about 1.65 x 10 6 cells / mL) were introduced into the cell screening area with a 1mL volume dispenser, and left to stand for about 5 minutes to allow the antibody-immobilized polystyrene beads to settle by gravity, and then left to stand at room temperature for about 40 minutes to allow the beads to enter the micropores. The antibody-immobilized polystyrene beads in the method are in contact with the bottom surface of the micropore, so that the antibody on the surface of the antibody-immobilized polystyrene bead reacts with the antigen immobilized on the bottom surface of the micropore. Next, an AC voltage of 2.5 Vpp and a frequency of 3 MHz was applied between the electrodes by the second AC powe...
Embodiment 3
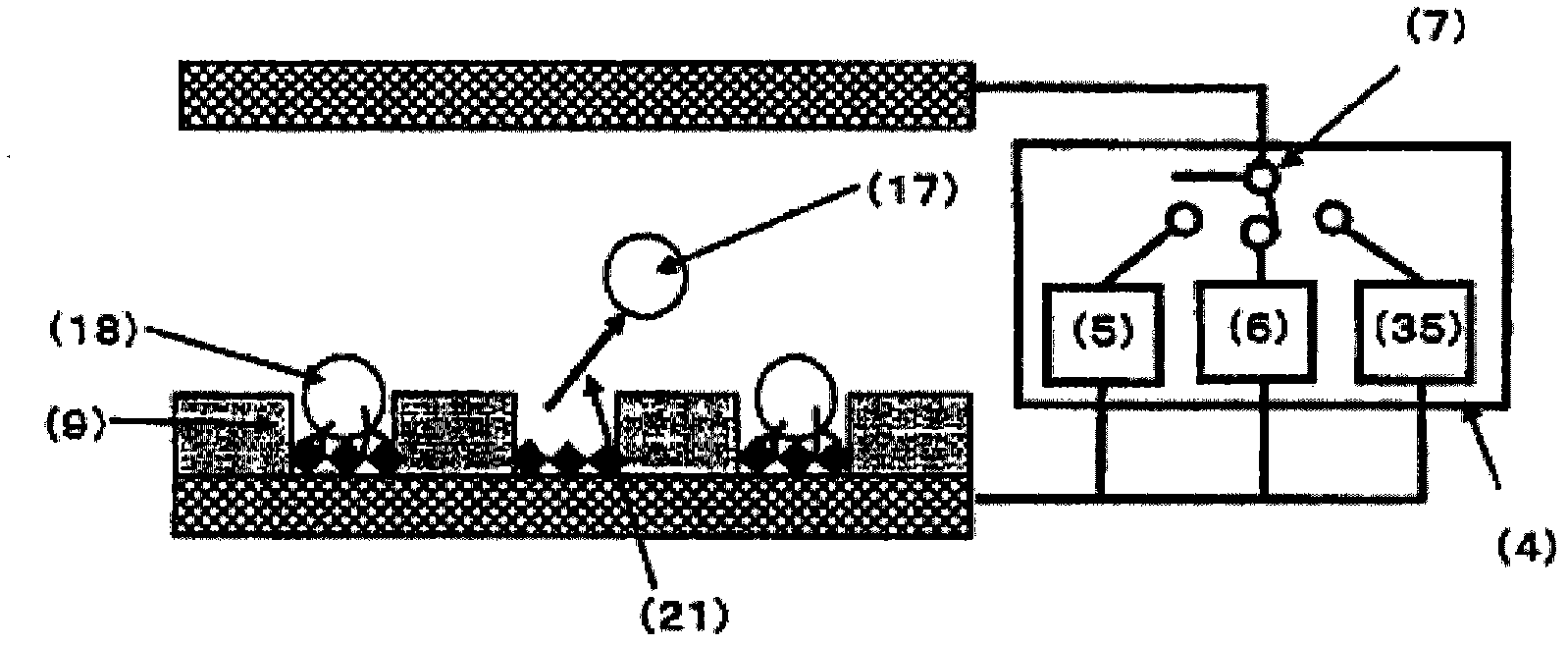
[0261] Using the same cell screening apparatus as in Example 1, spleen cells having specific antibodies present on their surfaces were screened. As the cells, non-immunized mouse spleen cells A and mouse spleen cells B immunized with the E2 antigen were used. In addition, in the spleen cells B of mice immunized with the E2 antigen, there were cells in which the E2 antibody was present on the cell surface (hereinafter referred to as antibody-containing cells). This Example 3 is an example of identifying the antibody present in the cell and the antigen immobilized on the bottom surface of the micropore by the magnitude of the alternating voltage of the second alternating current power supply for determining the magnitude of the negative dielectrophoretic force. The binding force of the antigen-antibody reaction, thereby screening the cells for the presence of antibodies.
[0262] First, mouse spleen cells A and mouse spleen cells B were respectively suspended in 300 mM mannitol...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com