New method for producing active carbon by using biomass wastes
A technology for biomass waste and activated carbon production, which is applied in the removal of solid waste and other directions, can solve problems such as land occupation and atmospheric pollution, and achieve the effects of high conversion rate, good adsorption performance, and increased pore structure.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] 1. Pre-treat raw walnut shells: dry to a moisture content below 15%, mechanically crush, and pass through a 100-mesh sieve.
[0031] 2. Add pyrolusite to the raw walnut shell at a ratio of 5%-10% and mix well.
[0032] 3. Impregnate the product of step 2 with 3mol / L zinc chloride solution for 24 hours (impregnation ratio 1:1).
[0033] 4. The product of step 3 is carbonized and activated in a tube furnace at 500°C for 1 hour (protected by nitrogen).
[0034] 5. After cooling the product of step 4 to room temperature, it is washed with a 3mol / l hydrochloric acid solution, and then rinsed with water at 60°C until it is neutral.
[0035] 6. After drying and grinding the product obtained in step 5, a finished activated carbon product is obtained.
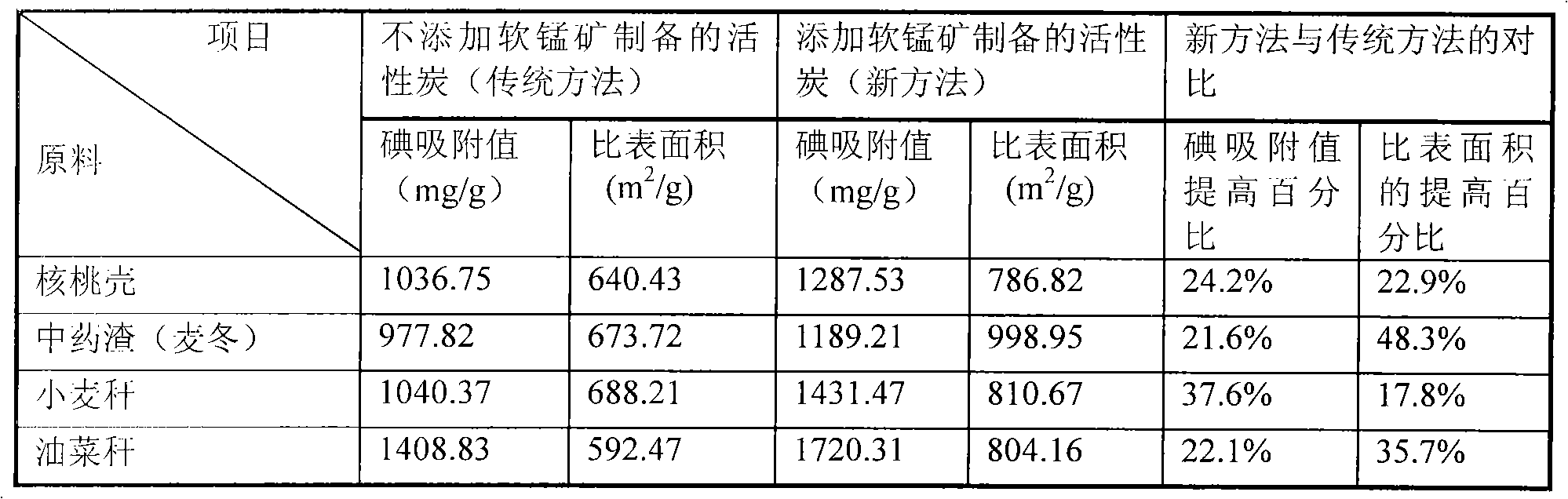
[0036] According to the method specified in GB / T12496.8-1999, the iodine adsorption value of the activated carbon product of this example is measured to be 1287.53 mg / g.
Embodiment 2
[0038] 1. The raw material Chinese medicine residue (Ophiopogon japonicus) is pretreated: dried to a moisture content of less than 15%, mechanically crushed, and passed through a 100-mesh sieve.
[0039] 2. Add pyrolusite to the raw material Chinese medicine residue (Ophiopogon japonicus) at a ratio of 5%-10%, and mix well.
[0040] 3. Impregnate the product of step 2 with 3mol / L zinc chloride solution for 24 hours (impregnation ratio 1:1).
[0041] 4. The product of step 3 is carbonized and activated in a tube furnace at 500°C for 1 hour (protected by nitrogen).
[0042] 5. After cooling the product of step 4 to room temperature, it is washed with a 3mol / l hydrochloric acid solution, and then rinsed with water at 60°C until it is neutral.
[0043] 6. After drying and grinding the product obtained in step 5, a finished activated carbon product is obtained.
[0044] According to the method specified in GB / T12496.8-1999, the iodine adsorption value of the activated carbon product of this e...
Embodiment 3
[0046] 1. Pretreatment of raw wheat stalks: drying to a moisture content of less than 15%, mechanically crushing, and passing through a 100-mesh sieve.
[0047] 2. Add the pyrolusite to the raw wheat stalk at a ratio of 5%-10%, and mix well.
[0048] 3. Impregnate the product of step 2 with 3mol / L zinc chloride solution for 24 hours (impregnation ratio 1:1).
[0049] 4. The product of step 3 is carbonized and activated in a tube furnace at 500°C for 1 hour (protected by nitrogen).
[0050] 5. After cooling the product of step 4 to room temperature, it is washed with 3mol / l hydrochloric acid solution, and then rinsed with water at 60°C until it is neutral.
[0051] 6. After drying and grinding the product obtained in step 5, a finished activated carbon product is obtained.
[0052] According to the method specified in GB / T12496.8-1999, the iodine adsorption value of the activated carbon product of this example is measured to be 1431.47mg / g.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Iodine adsorption value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Iodine adsorption value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Iodine adsorption value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com