Method for producing graphene belts in controllable macroscopic quantity by chemically cutting grapheme
A graphene ribbon and ene macro-quantity technology, which is applied in the field of chemically tailoring graphene macro-controllable graphene ribbons, graphene ribbons with controllable boundaries, macro-preparation layers, and width, can solve the problem of low yield, The number of layers and width of graphene ribbons are difficult to control, etc., to achieve the effects of high product yield, low cost and good controllability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
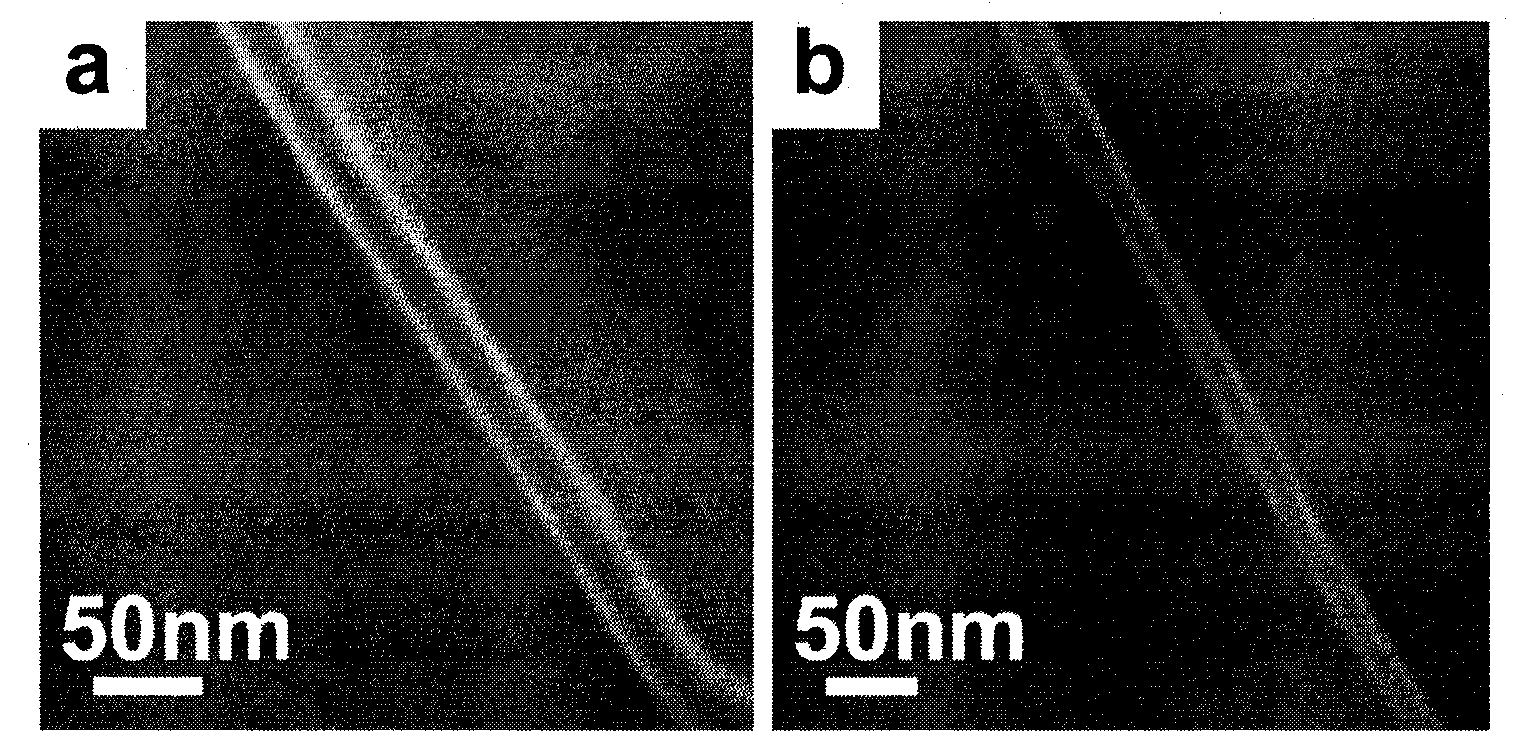
[0027]Adopt Hummers method ["Hummers method " please refer to literature: Hummers W, Offman R.Jumal of The American Chemical Society 1958,80:1339.], take the artificial graphite powder of size<30 μ m as raw material (in this embodiment, be 20 μ m) Graphite oxide was prepared by oxidation at 35°C for 2h; the tube furnace was heated to 1050°C at a heating rate of 35°C / s, and the graphite oxide sample was quickly pushed to the tube under the protection of argon (flow rate 200ml / min) atmosphere. The rapid expansion and peeling was carried out in the high temperature zone of the type furnace, and the holding time was 30s; then, the sample was transferred to the low temperature zone, and reduced for 2 hours in a reducing atmosphere of hydrogen (100 ml / min) + argon (100 ml / min) at 450 ° C; 40 Ultrasonic dispersion in a water bath in N-methylpyrrolidone for 2 hours at ℃, with an ultrasonic power of 300W; use high-speed centrifugation at 10,000 rpm to remove graphite and thick graphite ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Using the Hummers method, the artificial graphite powder with a size of <30 μm is used as a raw material (20 μm in this example), and is oxidized at 30° C. for 5 h to obtain graphite oxide; the tube furnace is heated to 1100° C. at a heating rate of 50° C. / s. Under the protection of a gas (flow rate of 200 ml / min) atmosphere, the graphite oxide sample was quickly moved to the high temperature zone of the tube furnace for rapid heating and expansion stripping, and the holding time was 30s, and then the sample was transferred to the low temperature zone; at 450 ° C, hydrogen (100 ml / min min) + argon (100 ml / min) in a reducing atmosphere for 2 hours; ultrasonically disperse in a water bath in N-methylpyrrolidone for 2 hours at room temperature, with an ultrasonic power of 300W; use 10,000 rpm high-speed centrifugation to remove the incompletely stripped Graphite and thick graphite flakes, obtained graphene after suction filtration; Graphene containing line defect is dispers...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Using the Hummers method, flake graphite powder with a size of <30 μm is used as raw material (20 μm in this example), and oxidized at 40° C. for 10 h to prepare graphite oxide; the tube furnace is heated to 1000° C. at a heating rate of 50° C. / s. (flow velocity 200 milliliters / min) under the protection of atmosphere, the graphite oxide sample is quickly pushed to the high temperature zone of the tube furnace for rapid heating and expansion stripping, and the holding time is 30s, and then the sample is transferred to the low temperature zone; ) + argon (150 ml / min) in a reducing atmosphere for 3 hours; ultrasonically disperse in a water bath in N-methylpyrrolidone for 2 hours at 40°C, with an ultrasonic power of 200W; use 12,000 rpm high-speed centrifugation to remove the incompletely stripped Graphite and thick graphite flakes obtain graphene after suction filtration; Graphene containing line defects is dispersed in polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) containing 0.1wt% and sodiu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com