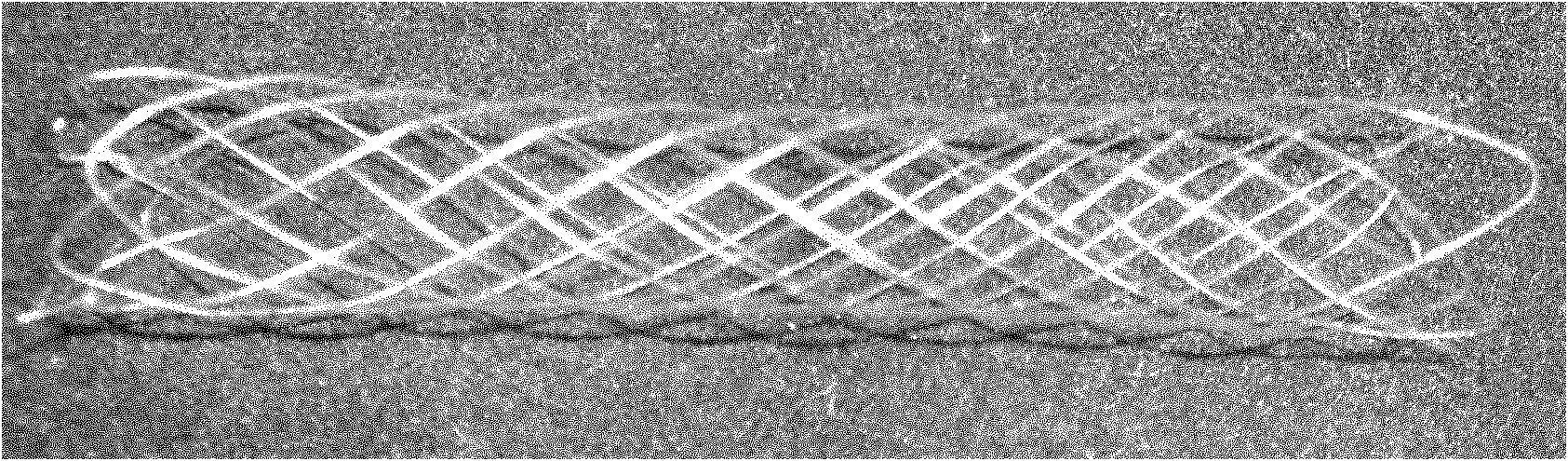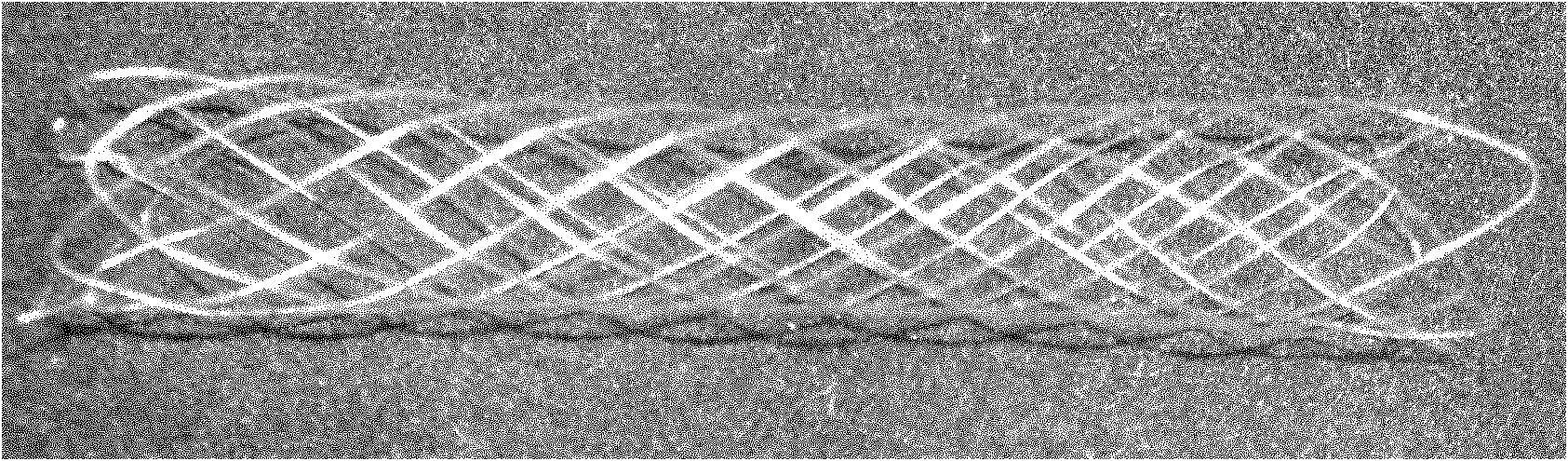Polycaprolactone (PCL) and polylactic acid (PLA) human body absorbable vascular stent and preparation method thereof
A technology for vascular stents and the human body, applied in stents, medical science, surgery, etc., can solve problems such as low mechanical properties of stents, product changes, loss of developing atoms of ion-type developing resins, etc., to achieve easy observation and research, compatibility Good performance and controllable degradation cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029]Weigh 500g samples according to the mass ratio PCL:PLA=1:4, extrude the nascent blended fibers in a twin-screw blending extruder at 190°C, and stretch the nascent blended fibers to obtain a diameter of 0.1mm. Oriented crystalline fiber; weigh barium sulfate and PCL raw materials according to the mass ratio of 1:2, and prepare hollow tubular joints by melt blending method; weave the blended stretched fiber into a network structure blood vessel with a length of 20mm and an inner diameter of 3mm For the stent, use barium sulfate and PCL hollow tubular joints to seal the fibers at both ends of the stent to obtain a mesh-like vascular stent with certain mechanical properties and high elasticity; heat-setting the stent at 95°C for 20 minutes, A blood vessel stent with X-ray display at both ends is obtained.
Embodiment 2
[0031] Weigh 500g samples according to the mass ratio PCL:PLA=2:3, extrude the nascent blended fibers in a twin-screw blending extruder at 170°C, and stretch the nascent blended fibers to obtain a diameter of 0.2mm. Oriented crystalline fiber; weigh barium sulfate and PCL raw materials according to the mass ratio of 1:3, and prepare hollow tubular joints by melt blending method; weave the blended stretched fiber into a network structure blood vessel with a length of 40mm and an inner diameter of 5mm For the stent, use barium sulfate and PCL hollow tubular joints to seal the fibers at both ends of the stent respectively to obtain a mesh-like vascular stent with certain mechanical properties and high elasticity; heat-setting the stent at 115°C for 25 minutes, A blood vessel stent with X-ray display at both ends is obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Weigh 500g samples according to the mass ratio PCL:PLA=1:1, extrude the nascent blended fibers at 200°C in a twin-screw blending extruder, and stretch the nascent blended fibers to obtain a diameter of 0.3mm. Oriented crystalline fiber; weigh barium sulfate and PCL raw materials according to the mass ratio of 1:4, and prepare hollow tubular joints by melt blending method; weave the blended stretched fiber into a network structure blood vessel with a length of 60 mm and an inner diameter of 6 mm For the stent, use barium sulfate and PCL hollow tubular joints to seal the fibers at both ends of the stent respectively to obtain a mesh-like vascular stent with certain mechanical properties and high elasticity; heat-setting the stent at 135°C for 30 minutes, A blood vessel stent with X-ray display at both ends is obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com