Advanced treatment method for Dioscoreazingiberensis C.H.Wright wastewater
A technology for advanced treatment and wastewater, applied in water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of no research reports, achieve high current efficiency, stable performance, and inhibit oxygen evolution The effect of side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
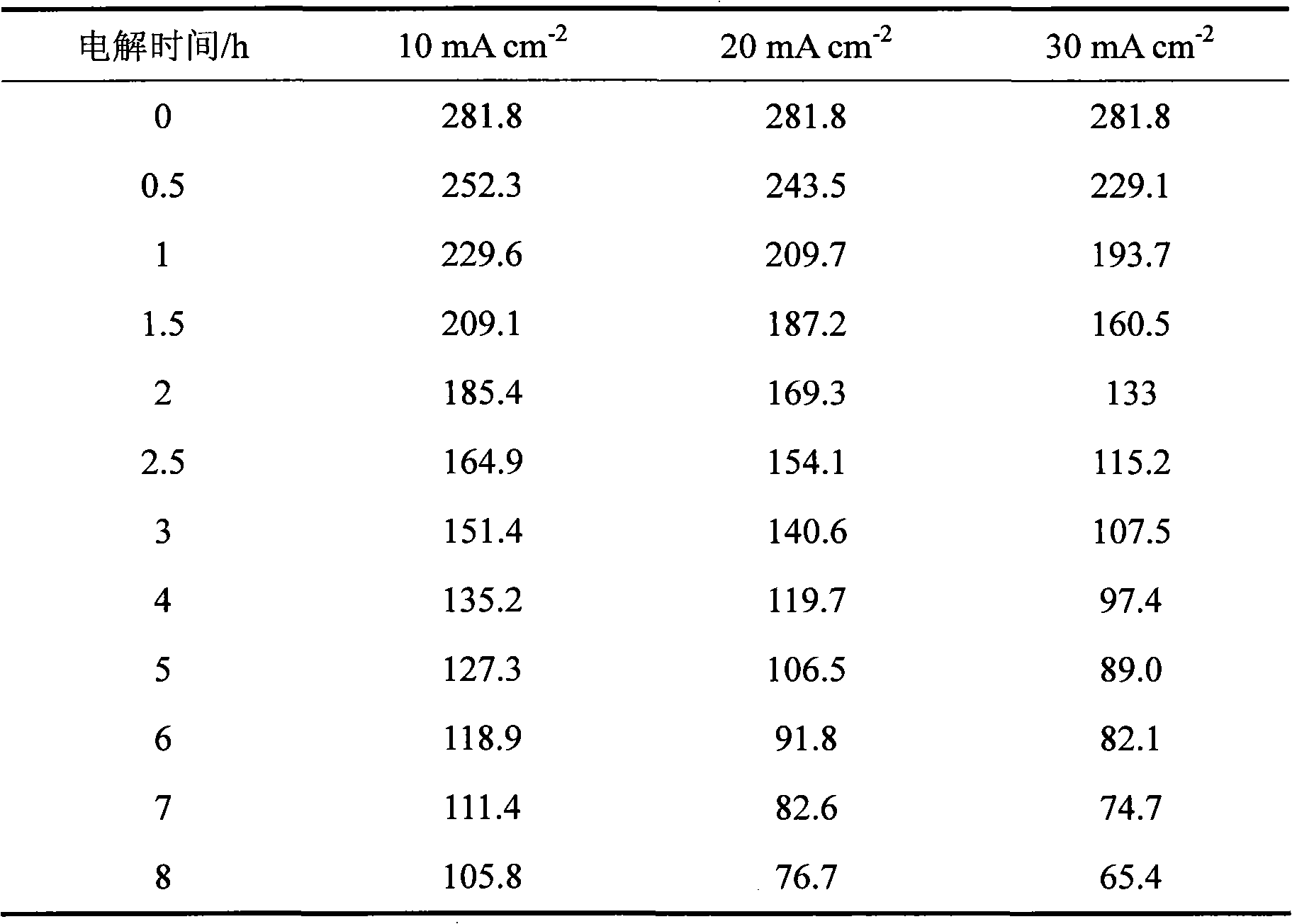
[0029] Using a 20×20mm BDD electrode as the anode, stainless steel of the same size as the cathode, and an electrode spacing of 10mm, electrochemical oxidation advanced treatment of turmeric wastewater biological effluent, COD is 281.8mg L -1 around, pH 7.75, add 0.1M Na 2 SO 4 supporting electrolyte with a current density of 10mA cm -2 、20mA cm -2 and 30mA cm -2 . Samples were taken from the reactor to analyze the COD value at regular intervals, and the experimental results are listed in Table 1. After 8 hours of electrolysis, the COD value of the turmeric wastewater biological effluent dropped to 105.8mg L respectively -1 , 76.7mg L -1 and 65.4mg L -1 . It can be seen that the current density is 30mA cm -2 , the processing effect is best.
[0030] Table 1 The change of COD in biological effluent of turmeric wastewater electrochemically oxidized by BDD electrode under different current densities
[0031]
Embodiment 2
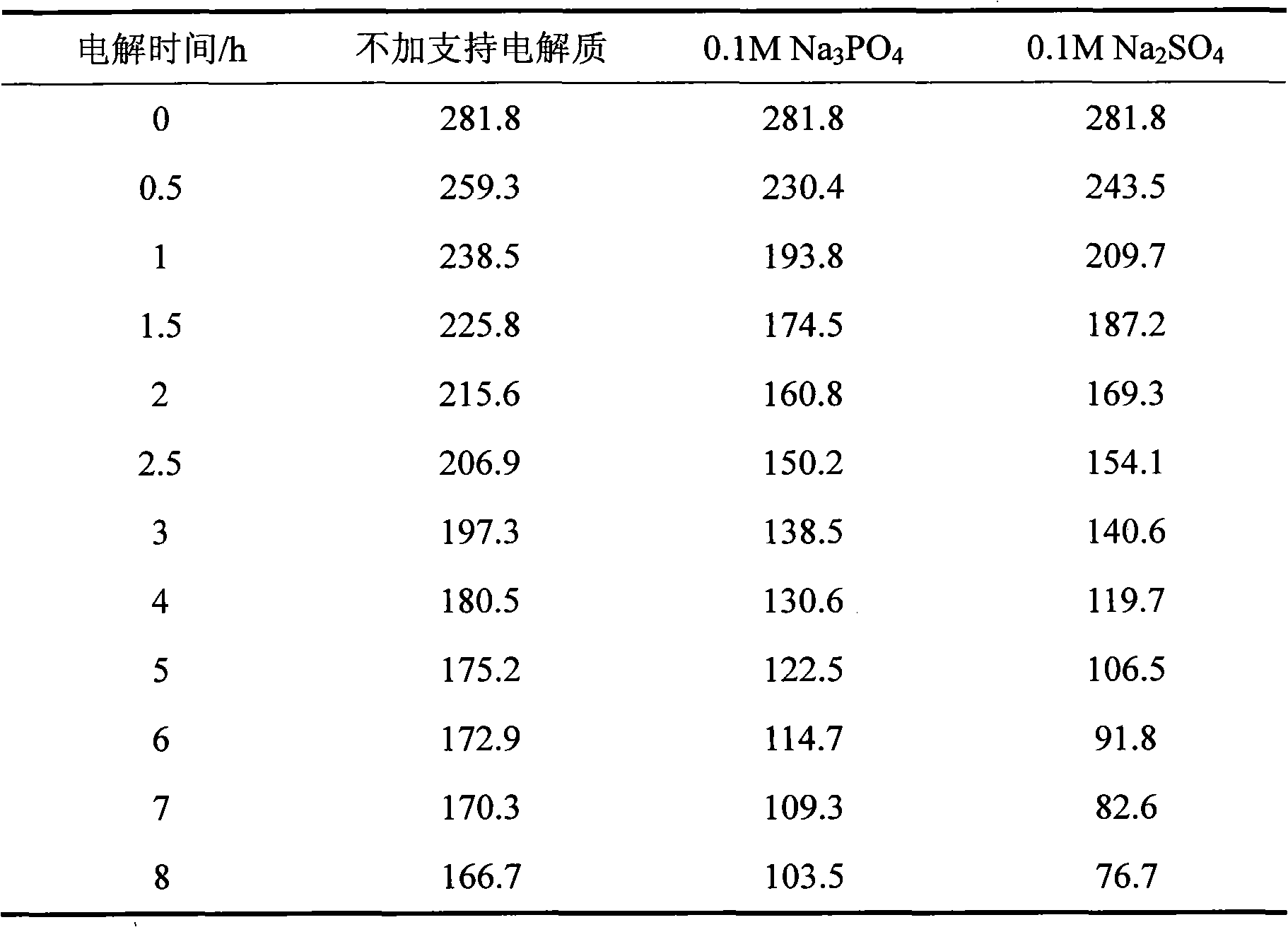
[0033] Using a 20×20mm BDD electrode as the anode, stainless steel of the same size as the cathode, and an electrode spacing of 10mm, electrochemical oxidation advanced treatment of turmeric wastewater biological effluent, COD is 281.8mg L -1 Around, pH is 7.75, no supporting electrolyte or 0.1M Na 2 SO 4 and 0.1M Na 3 PO 4 Supporting electrolyte with a current density of 20mA cm -2 . Samples were taken from the reactor at regular intervals to analyze the COD value, and the experimental results are listed in Table 2. After 8 hours of electrolysis, the COD value of the turmeric wastewater biological effluent dropped to 166.7mg L -1 , 103.5mg L -1 and 76.7mg L -1 . It can be seen that adding 0.1MNa 2 SO 4 Supports electrolytes for best treatment.
[0034] Table 2 Changes of COD in biological effluent of turmeric wastewater electrochemically oxidized by BDD electrode under different supporting electrolytes
[0035]
Embodiment 3
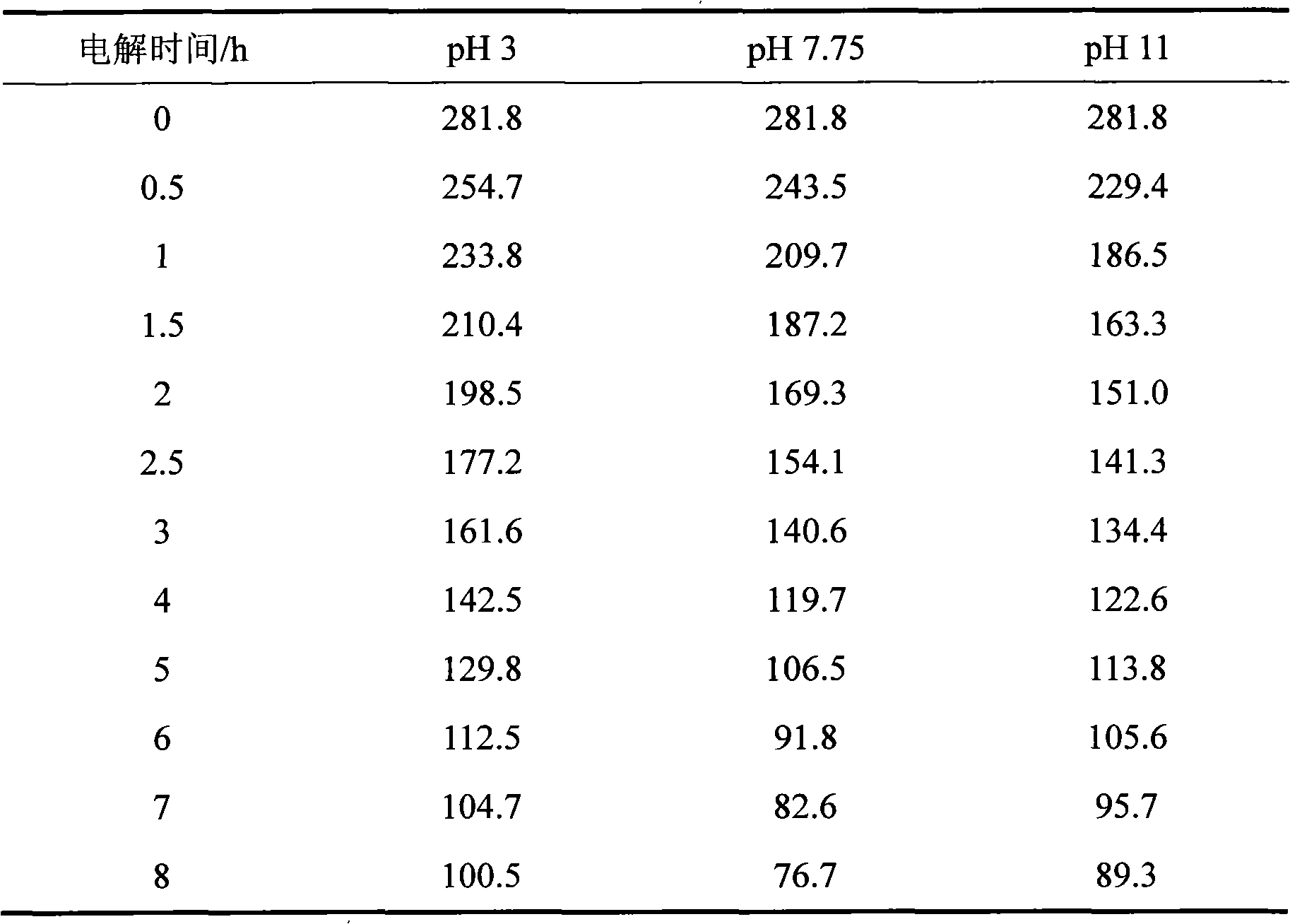
[0037]Using a 20×20mm BDD electrode as the anode, stainless steel of the same size as the cathode, and an electrode spacing of 10mm, electrochemical oxidation advanced treatment of turmeric wastewater biological effluent, the COD is 281.8mg L -1 left and right, pH 3, 7.75 and 11, respectively, adding 0.1M Na 2 SO 4 Supporting electrolyte with a current density of 20mA cm -2 . Samples were taken from the reactor to analyze the COD value at intervals, and the experimental results are listed in Table 3. After 8 hours of electrolysis, the COD value of the turmeric wastewater biological effluent dropped to 100.5mg L respectively -1 , 76.7mg L -1 and 89.3mg L -1 . It can be seen that the treatment works best under neutral conditions.
[0038] Table 3 Changes of COD in biological effluent of turmeric wastewater electrochemically oxidized by BDD electrode at different pH values
[0039]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com