All-fiber current monitoring device based on Faraday effect
A Faraday effect and current monitoring technology, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, using optical devices to transmit sensing components, voltage/current isolation, etc., can solve the problems of high economic cost of two photodetectors, low beam deflection accuracy, and current monitoring results. Inaccurate and other problems, to achieve the effect of small electromagnetic interference, high accuracy, and reduce economic costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
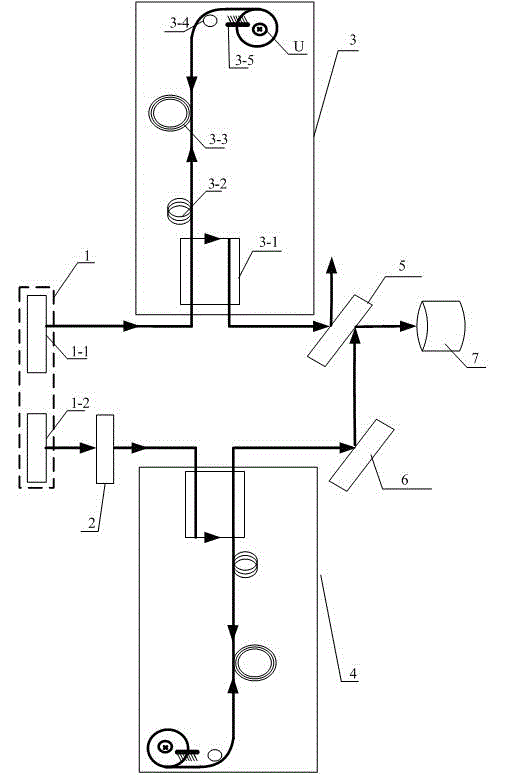
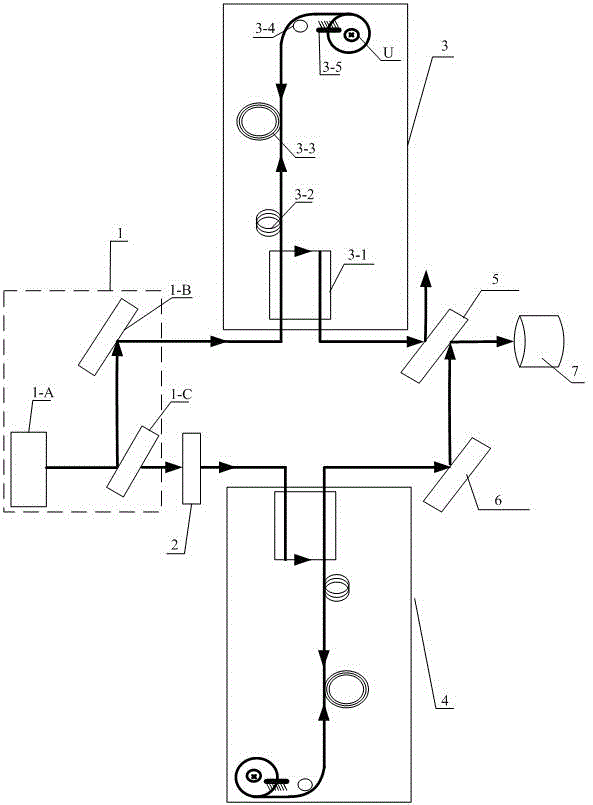
[0008] Specific implementation mode one: according to the instructions attached figure 1 This embodiment is described in detail. The Faraday effect-based all-fiber current monitoring device described in this embodiment includes a light source system 1, a half-wave plate 2, a first fiber optic transformer 3, a second fiber optic transformer 4, a first half-wave The anti-half mirror 5, the second total reflection mirror 6 and the photodetector 7, the second fiber optic transformer 4 have the same structure as the first fiber optic transformer 3, and the light source system 1 emits the first light beam to the signal input of the first fiber optic transformer 3 end, the signal output end of the first optical fiber transformer 3 outputs the first polarized light to the first half mirror 5, and the first half mirror 5 outputs the transmitted light signal to the photodetector 7; the light source system 1 Also send the second light beam to the half-wave plate 2, the second light beam ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0009] Embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further description of Embodiment 1. The first fiber optic transformer 3 and the second fiber optic transformer 4 described in Embodiment 1 are two identical optically active crystals.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0010] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is a further description of Embodiment 1. The first fiber optic transformer 3 described in Embodiment 1 includes a single-mode fiber coupler 3-1 and a fiber optic polarizer 3-2. , polarization-maintaining optical fiber 3-3, λ / 4 wave plate 3-4 and the first total reflection mirror 3-5, the signal input end of the single-mode optical fiber coupler 3-1 is the signal input end of the first optical fiber transformer 3, The first light beam emitted by the light source system 1 is input to the signal input end of the fiber polarizer 3-2 through the single-mode fiber coupler 3-1, and the fiber polarizer 3-2 outputs linearly polarized light to the polarization maintaining fiber 3- 3, the polarization maintaining fiber 3-3 outputs a bundle of linearly polarized light to the signal input end of the λ / 4 wave plate 3-4, and the λ / 4 wave plate 3-4 outputs left-handed circularly polarized light or The right-handed circularly polarized light is sent to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com