Preparation method of monodisperse lithium iron phosphate nanometer material and lithium-ion secondary battery
A lithium iron phosphate and nanomaterial technology, applied in secondary batteries, battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of poor conductivity and slow diffusion of lithium ions, and achieve small size, easy in-situ doping and carbon encapsulation, Stable dispersion effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
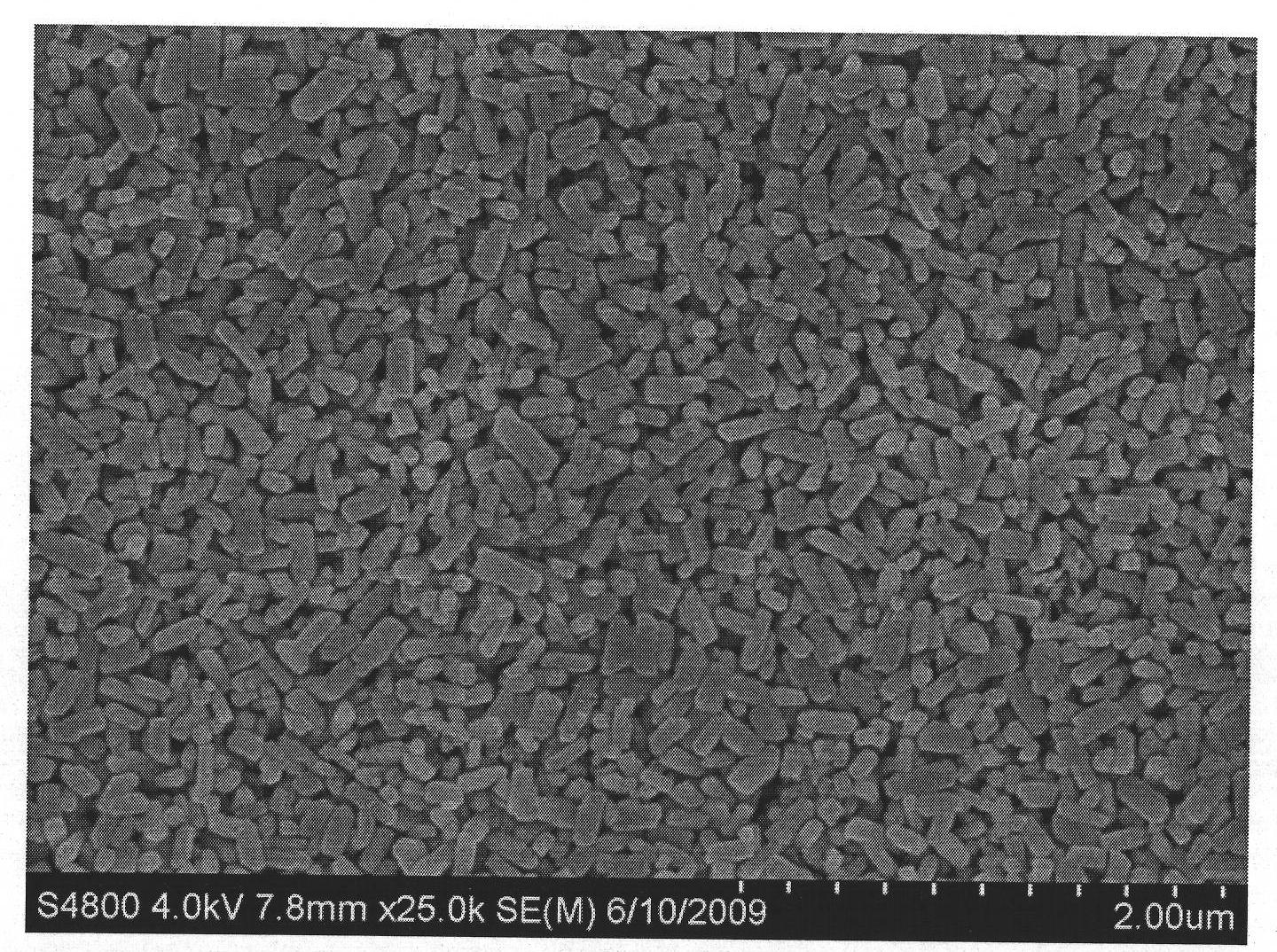
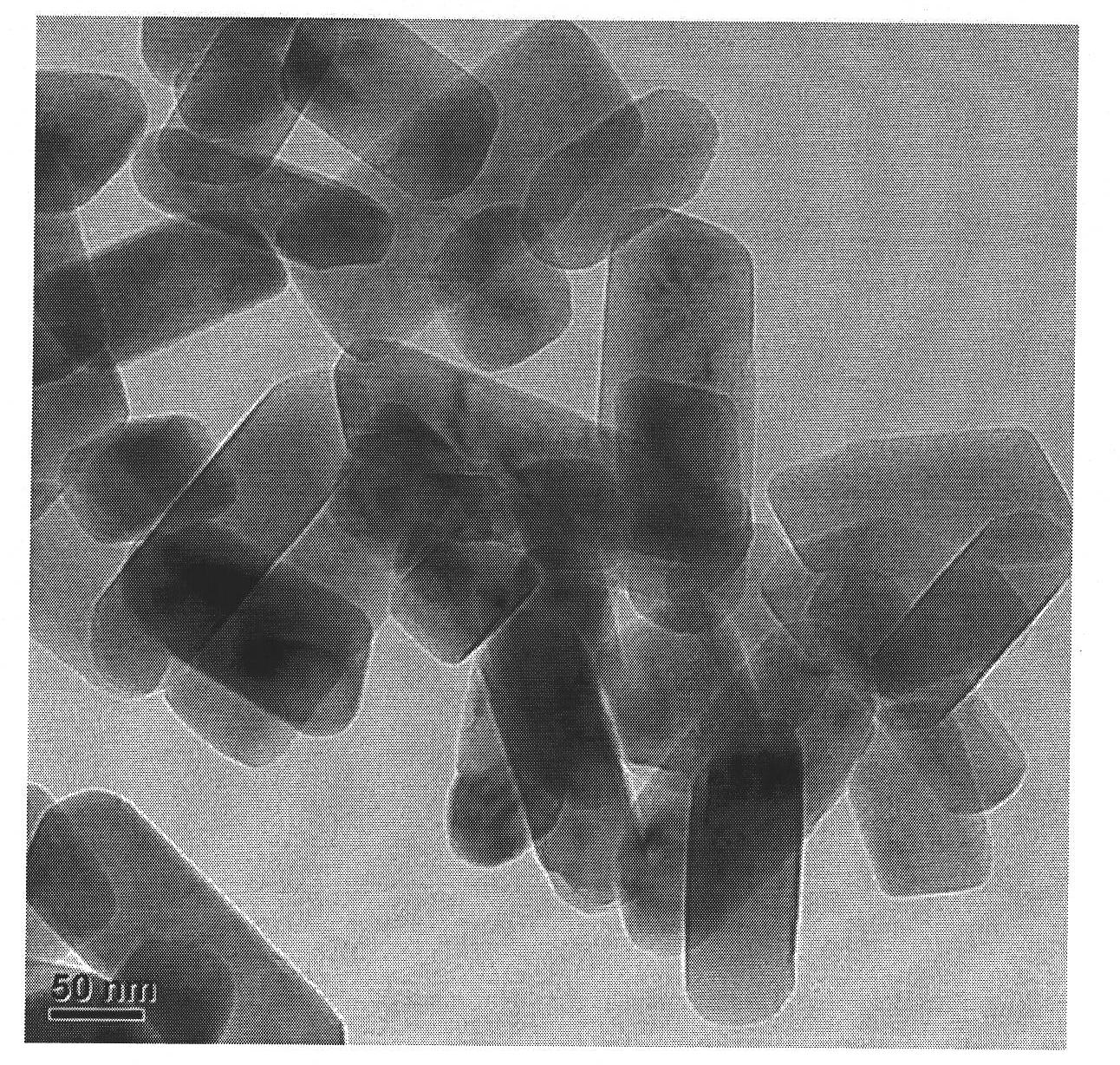
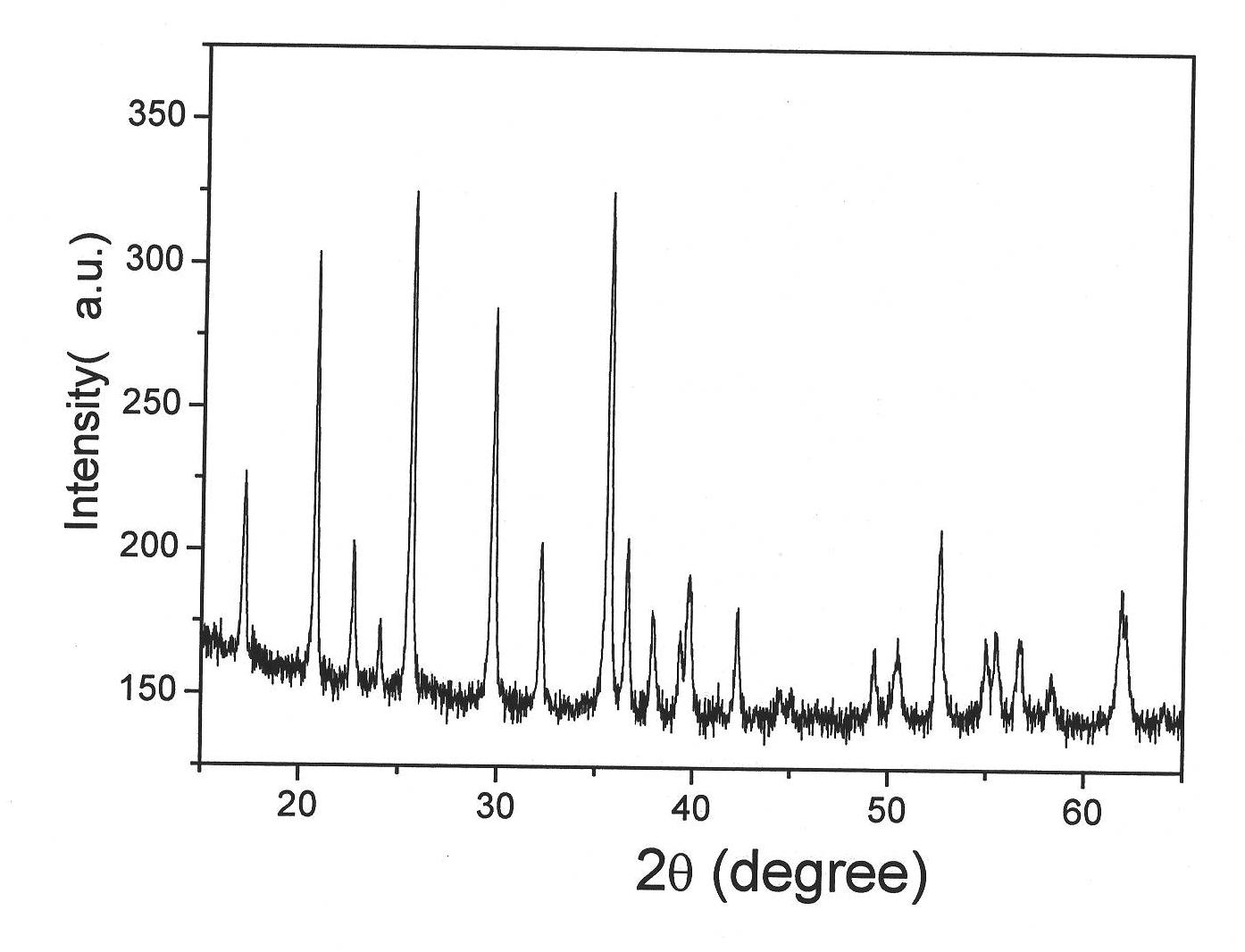
[0026] The first step, preparation of lithium iron phosphate nanomaterials
[0027] Dissolve soluble lithium source compounds, ferrous source compounds, and phosphorus source compounds in water, add them to the organic solvent in sequence according to the specific molar ratio of materials and the order of addition, stir and mix, and control the volume ratio of the organic solvent to water in the mixed solution at 1 : between 3 and 3: 1, the concentration of each substance is controlled between 0.1 mol / L and 0.5 mol / L, the mixture is transferred to an autoclave, and reacted at 120°C to 230°C for 2 to 24 hours. The product undergoes processes such as washing and drying to obtain lithium iron phosphate nanomaterials.
[0028] The second step, preparation of lithium iron phosphate@carbon nanocomposite cathode active material
[0029] The carbon encapsulation process of lithium iron phosphate nanomaterials adopts the conventional carbon encapsulation process: in-situ encapsulation...
Embodiment 1
[0037] The first step, weigh 10.3ml of concentrated phosphoric acid with a mass fraction of 85%, add 150ml of water to make a 1M phosphoric acid solution, weigh 19.6g of lithium hydroxide and dissolve it in 450ml of water to make a 1M lithium hydroxide solution, weigh 41.7 g ferrous sulfate heptahydrate was dissolved in 300ml water to make 0.5M ferrous sulfate solution, first pour the phosphoric acid solution into 600ml polyethylene glycol 400 solvent, stir and mix well, then slowly add lithium hydroxide solution under stirring , Let it react for a period of time, then add the ferrous sulfate solution quickly, and continue to stir for a few minutes. Pour the mixed solution into a 2L magnetically driven stirred reactor with a lithium iron phosphate concentration of about 0.1M. Bubble argon or nitrogen for 5 minutes while stirring, then seal the reaction vessel, and react at 180° C. for 9 hours. After the reaction is completed and cooled, the collected product is washed and dri...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The first step, weigh 19.8g diammonium hydrogen phosphate, add 300ml water to make 0.5M diammonium hydrogen phosphate solution, weigh 6.6g lithium hydroxide and dissolve in 300ml water to make 0.5M lithium hydroxide solution, weigh Dissolve 29.81g of ferrous chloride tetrahydrate in 300ml of water to form a 0.5M ferrous sulfate solution. First, pour the diammonium hydrogen phosphate solution into 600ml of polyethylene glycol 400 solvent, stir and mix evenly, and slowly Add lithium hydroxide solution, let it react for a period of time, then add ferrous chloride solution quickly, and continue to stir for several minutes. The mixed solution was poured into a 2L magnetically driven stirred reactor, and argon or nitrogen gas was blown for 5 minutes while stirring, and then the reactor was sealed and reacted at a temperature of 180°C for 9 hours. After the reaction is completed and cooled, the collected product is washed and dried to obtain a lithium iron phosphate nanomateri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com