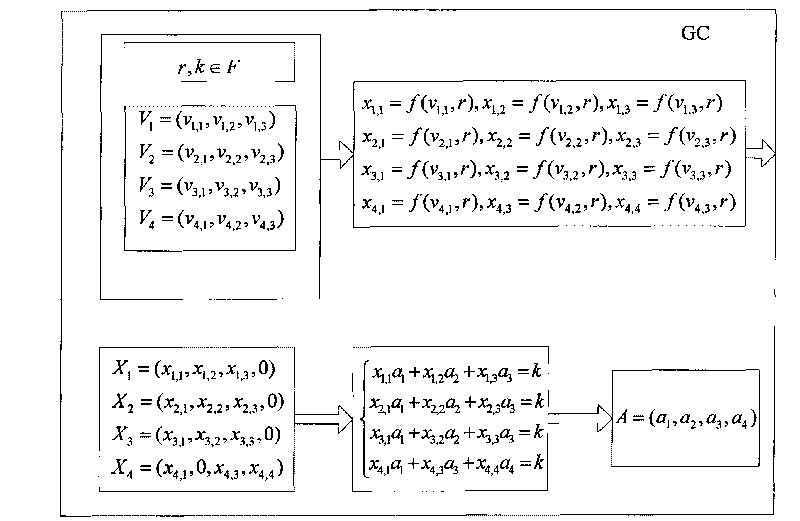Group key management method based on linear geometry
A group key and management method technology, applied in the field of group key management, can solve the problem of increasing the total cost of updating keys
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
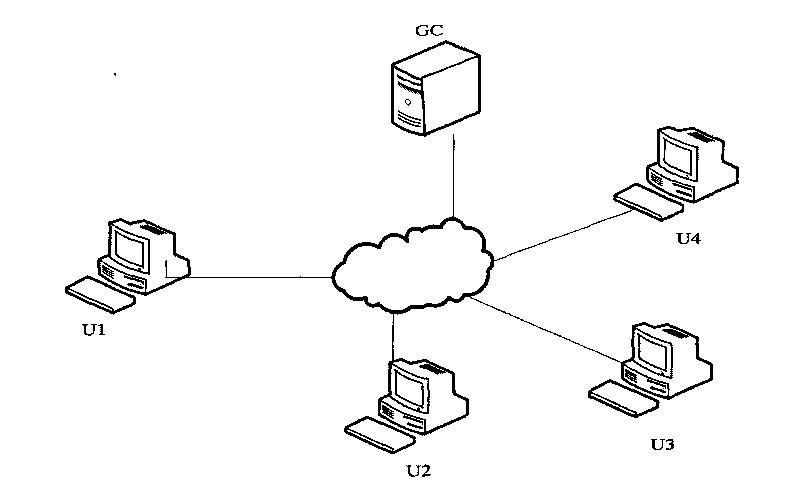
[0171] A typical secure group communication system architecture is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the system includes a group controller (GroupControl, GC), and four group users U1, U2, U3 and U4. The Group Controller (GC) and individual users are connected via the Internet.
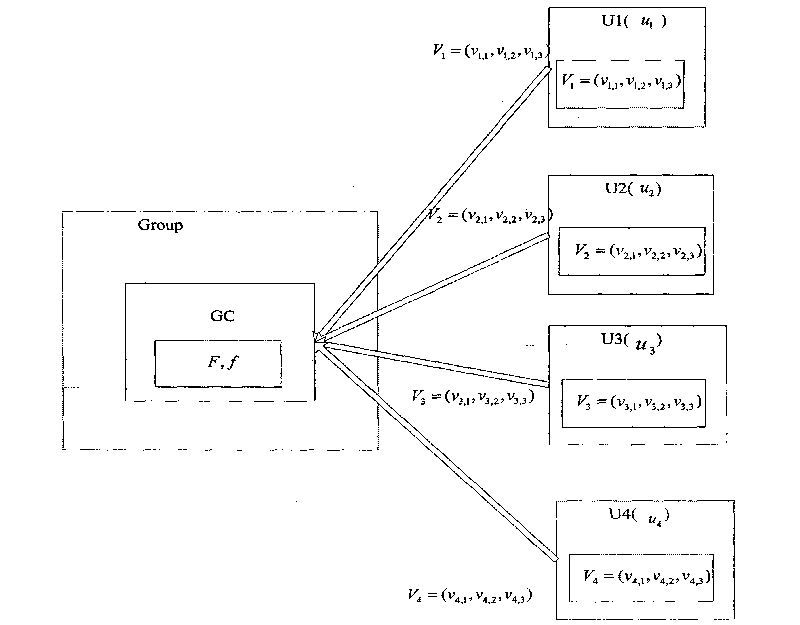
[0172] Such as figure 2 As shown, when the group is initialized, the group controller (GC) selects the finite field F and the mapping f used by the group, all operations in the group are established on the finite field F, and the mapping f is generated using pseudo-random numbers device.
[0173] Step 1, group members U1, U2, U3, and U4 want to join the group, and U1 selects three secret random numbers v in the finite field F 1,1 , v 1,2 , v 1,3 ∈F, forming a three-dimensional secret vector V 1 =(v 1,1 , v 1,2 , v 1,3 ), U2 also selects three secret random numbers v 2,1 , v 2,2 , v 2,3 ∈F, forming a three-dimensional secret vector V 2 =(v 2,1 , v 2,2 , v 2,3 ), U3 also selects three secr...
Embodiment 2
[0222] Assume that the secure group communication system includes a group controller (GC) and five group users U1, U2, U3, U4 and U5, and the group controller (GC) and each user are connected through the Internet. When the group is initialized, the group controller (GC) selects the finite field F and the mapping f used by the group. All operations in the group are established on the finite field F, and the mapping f uses a pseudo-random number generator.
[0223] Step 1, group member U4 applies to the group controller (GC) to leave the group;
[0224] The group controller (GC) deletes the secret vector V of the exiting group member 4 , and reassign the number u of the remaining group members according to the order of the subscripts of the current members i , where i=1, 2, 3, 4; the group controller (GC) broadcasts the numbers of all members to all members through the open channel, and the secret vector of group members saved by the group controller (GC) is V 1 , V 2 , V 3 ...
Embodiment 3
[0227] Assume that the secure group communication system includes a group controller (GC) and two group users U1 and U2, the group controller (GC) and each user are connected through the Internet. When the group is initialized, the group controller (GC) selects the finite field F and the mapping f used by the group. All operations in the group are established on the finite field F, and the mapping f uses a pseudo-random number generator.
[0228] Step 1, group members U3 and U4 want to join the group, new member U3 selects three secret random numbers v 3,1 , v 3,2 , v 3,3 ∈F, forming a three-dimensional secret vector V 3 =(v 3,1 , v 3,2 , v 3,3 ) and sent to the group controller (GC) through a secure channel; U4 also selects three secret random numbers v 4,1 , v 4,2 , v 4,3 ∈F, forming a three-dimensional secret vector V 4 =(v 4,1 , v 4,2 , v 4,3 ) and sent to the group controller (GC) through a secure channel.
[0229] The group controller (GC) assigns the number...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com