N-arylation method taking substituted adipic dihydrazide as ligand in aqueous phase system
A dihydrazide and arylation technology, applied in the field of chemistry, can solve the problems of inability to popularize and use, cost defects, and high ligand dosage, and achieve the effects of wide application range of substrates, improved environmental friendliness, and broad application prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
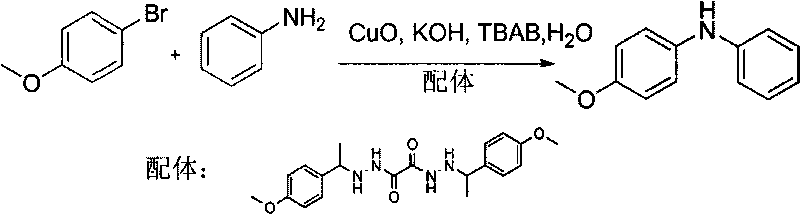
[0026] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of N-p-methoxyphenylaniline
[0027]
[0028] 2mg (0.025mmol) CuO, 48mg (0.125mmol) ligand, 96mg (0.5mmol) p-methoxybromobenzene, 279mg (2.0mmol) aniline, 0.28mg (0.5mmol) KOH, 32mg (0.1mmol) TBAB, 5.0ml H 2 O was added to a 50ml round bottom flask, and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 96h. After the reaction stopped, it was extracted with ethyl acetate, washed with water, washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered, and the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure, and the obtained reaction mixture was separated and purified by silica gel column chromatography [eluent: petroleum ether / ethyl acetate (20:1)] to obtain 83 mg of N-p-methoxyphenylaniline, with a yield of 83%.
[0029] N-p-methoxyphenylaniline: 1 H NMR (300MHz, CDCl 3 )δ: 7.26-7.19 (m, 2H), 7.10 (d, J=8.7, 2H), 6.93-6.81 (m, 5H), 5.62 (br s, 1H), 3.81 (s, 3H); MS (ESI , m / z): 200[M+H] +
[0030] Ligand:1 H NMR (30...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Embodiment 2: the synthesis of N-phenylbenzylamine
[0032]
[0033] 1.1mg (0.0125mmol) CuCl, 48mg (0.125mmol) ligand, 96mg (0.5mmol) p-methoxybromobenzene, 214mg (2.0mmol) benzylamine, 0.56mg (1mmol) KOH, 32mg (0.1mmol) TBAB , 2mlH 2 O, 78mg (0.5mmol) of bromobenzene was added to a 50ml round bottom flask, and the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 24h. After the reaction stopped, it was extracted with ethyl acetate, washed with water, washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered, and the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure, and the obtained reaction mixture was separated and purified by silica gel column chromatography [eluent: petroleum ether / ethyl acetate (20:1)] to obtain 46 mg of N-phenylbenzylamine with a yield of 50%.
[0034] N-Phenylbenzylamine: 1 H NMR (300MHz, CDCl 3 )δ: 7.42-7.41 (m, 7H), 6.81-6.68 (m, 3H), 4.38 (s, 2H), 4.07 (br s, 1H). MS (ESI, m / z): 184 [M+H ] +
[0035] Ligand: 1 H NMR (...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3: the synthesis of N-paraacetylphenylbenzylamine
[0037]
[0038] 47.5mg (0.25mmol) CuI, 104mg (0.25mmol) ligand, 0.1mg (0.5mmol) p-acetyl bromide, 214mg (2.0mmol) benzylamine, 212mg (1.0mmol) K 3 PO 4 , 94mg (0.25mmol) tetraphenyl phosphorus chloride, 5.0ml H 2 O was added to a 50ml round bottom flask, and the reaction was stirred at 90°C for 24h. After the reaction stopped, it was extracted with ethyl acetate, washed with water, washed with saturated brine, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, filtered, and the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure, and the obtained reaction mixture was separated and purified by silica gel column chromatography [eluent: petroleum ether / ethyl acetate (10:1)] to obtain 56 mg of N-p-acetylphenylaniline, with a yield of 50%.
[0039] N-P-Acetaminophen: 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ: 7.83 (d, J=8.8, 2H), 7.36-7.30 (m, 5H), 6.61-6.59 (d, J=8.8, 2H), 4.41 (s, 2H), 2.49 (s, 3H). ESI-MS: m / z=226[M+H] +
[004...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com