Temperature compensation for shape-induced in-plane stresses in glass substrates
A glass, flat technology used in the manufacture of glass sheets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
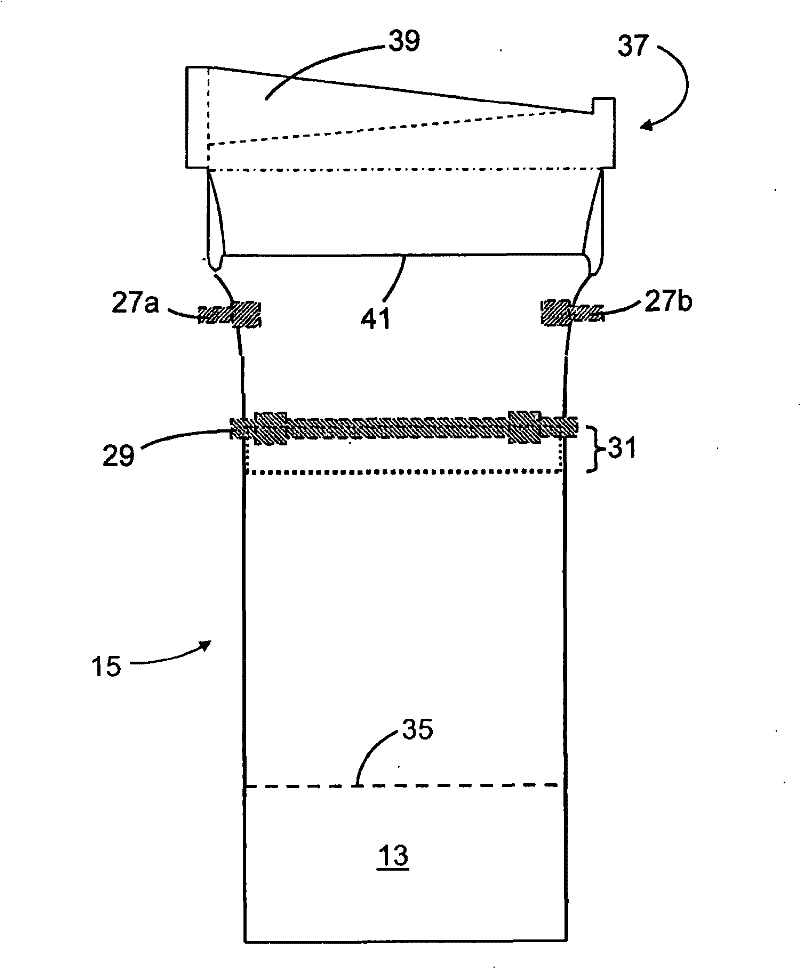
[0234] Compensation for the temperature distribution of a spherical glass sheet
[0235] This embodiment illustrates the principle of the present invention by taking a spherical glass sheet as an example. Generally speaking, the method adopted in this embodiment and embodiment 2 is to simulate the stress generated when the selected forming body is pressed onto the plane by vacuum, and then use the calculated stress value to select the thermal distribution to obtain the calculated thermal stress distribution , this distribution can at least partially eliminate the stress distribution caused by the vacuum.
[0236] image 3 A spherical sheet of glass is shown with a width of 1100 mm and a length of 1300 mm, and a ball with a dome height δ of 1 mm. Figure 4 The calculated edge stress levels along the width and length of the glass sheet when the glass sheet is pressed onto a flat surface are shown (curves 43 and 45, respectively).
[0237] Figure 5 and 6 shows the geometric...
Embodiment 2
[0256] Compensation for the temperature distribution of an ellipsoidal glass sheet
[0257] This example extends the analysis of Example 1 to ellipsoid shaped glass slides.
[0258] Figure 12 A representative ellipsoid shaped glass sheet is shown, wherein the ratio (F) of the curvature in the width direction of the glass sheet to the curvature in the length direction of the glass sheet is 2.0.
[0259] Figure 14A shown Figure 12 The edge stress produced when the shown ellipsoid is flattened (curve 59 along the width direction of the glass sheet; curve 61 along its length direction), Figure 14B shows the pass Figure 13 Compensating thermal stress applied along the width of the glass ribbon produced by the medium heat profile. specifically, Figure 14B Middle curves 63 and 65 show compensating thermal stresses along the width and length of the glass sheet, respectively. Compare Figure 14A and 14B It can be seen that Figure 13 The thermal profile shown can be use...
Embodiment 3
[0263] Decomposition into Components: Edge Stress Decomposition
[0264] This example shows how to decompose the edge stress distribution into long-scale and short-scale variables.
[0265] Figure 17 Shown are representative in-plane stress measurements taken along one edge of a glass sheet under vacuum flattening conditions, the plane thickness being averaged (curve 67). The figure also shows the decomposition of the stress distribution into long-scale components (low spatial frequency components) and short-scale components (high spatial frequency components). In particular, curve 69 shows the length component, which is determined by fitting a parabola to curve 67, for example. Curve 71 shows the short metric component, which is determined by subtracting curve 69 from curve 67 . Alternatively, the decomposition can also be performed as a Fourier series expansion.
[0266] This decomposition can be applied in a variety of ways. For example, the temperature profile across...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com