Method for separating chromosomes in plant cells by using fluorescence in-situ hybridization
A fluorescent in situ hybridization and plant cell technology, applied in DNA preparation, chemical library, combinatorial chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of application limitations, immature plant chromosome banding technology, etc., to broaden the range, avoid chemical treatment, and ensure integrity sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
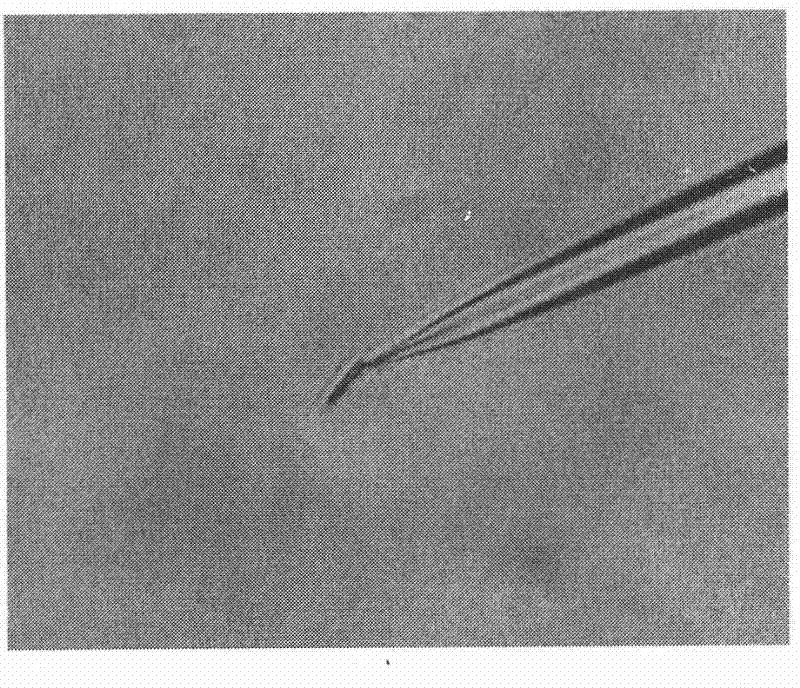
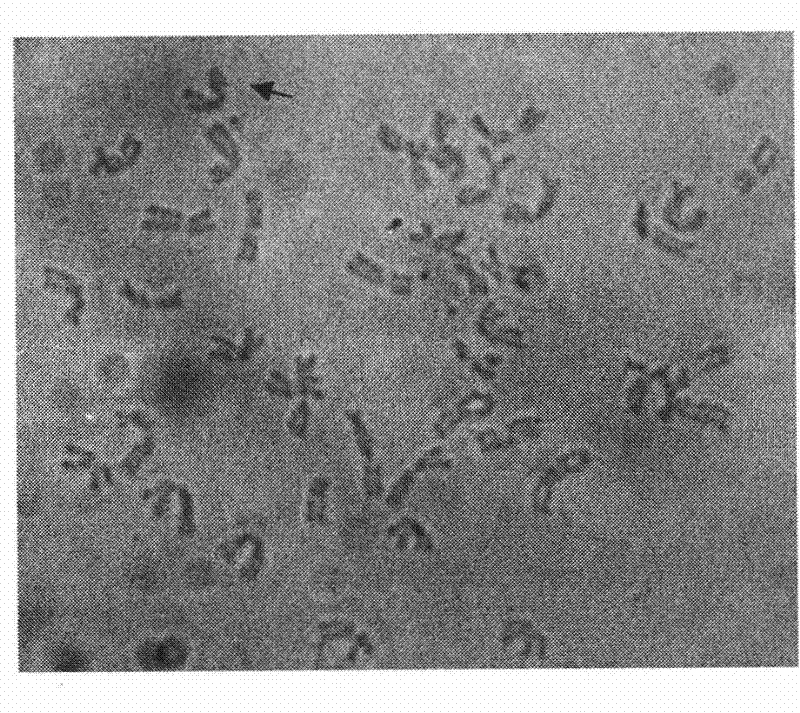
[0019] Embodiment 1, the microseparation technique of wheat chromosome
[0020] 1. Chromosome production
[0021] Wheat seeds germinated on a petri dish with double-layer filter paper at 23°C, and treated at 4°C for 24 hours after dew blanching, then transferred to 23°C for constant temperature cultivation for 24 hours, cut the roots of germinated seeds, and treated them under ice water at 0°C for 36 hours. Hours, after absorbing the water on the surface of the root tip, place it in fresh Carnoy's fixative solution (absolute ethanol: glacial acetic acid = 3: 1) and fix it for 10 minutes, then transfer it to 70% ethanol (volume percentage), Store at 4°C until use. Take the fixed root tip, rinse it with sterile water, cut the root tip under sterile conditions and place it in a 1:1 configuration of 2% cellulase (R-10Yakult.) and 2% pectinase (Y-23Yakult.) in the mixed solution of 37°C for 3 hours, gently rinsed twice with sterile water, stained with 1% acetic acid magenta and p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com