Fermentation technique for producing red yeast with high color value
A fermentation process and production process technology, which is applied in the field of fermentation process for producing high-color red yeast rice, can solve the problems of darker color tone of the product, adverse effects, and expand the application field of red yeast rice pigment, and achieve a short culture period and bright color tone. , the effect of high color price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Production of red yeast rice with yellowish color and higher color price
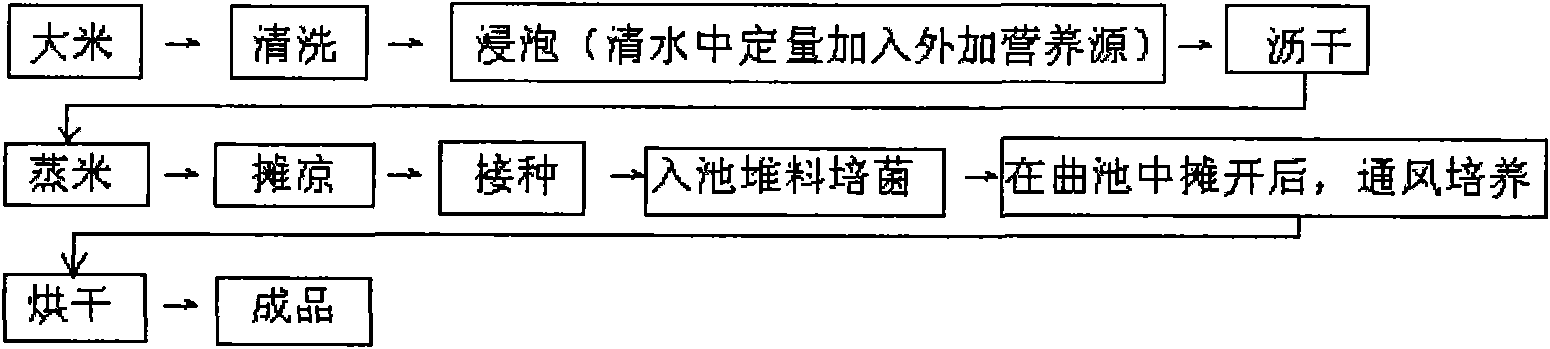
[0044] (1) Cleaning and soaking the rice for 12 hours, adding an additional nutrient source during soaking; the additional nutrient source is a mixture of inorganic salts and vitamins, the added amount is 0.8% of the soaking liquid quality, and the proportion of the additional nutrient source is in parts by weight The number is 1 part of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 1 part of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 5 parts of zinc sulfate, 5 parts of magnesium sulfate, 5 parts of sodium nitrate, 5 parts of ammonium bicarbonate, vitamin B 6 0.1 part; the pH value of the soaking solution is adjusted to 5.2 with acetic acid;
[0045] (2) Drain and steam rice at 100°C for 6 minutes;
[0046] (3) cooling, adopting 116-R bacterial strain to inoculate, the inoculum size is 10% of rice dry weight;
[0047] (4) Bacteria cultivation for 48 hours in the pool, the temperature of the cultivation temperature is 3...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Production of red yeast rice with yellowish color and higher color price
[0053] Washing and soaking the rice for 8 hours, and adding an external nutrient source during soaking; the external nutrient source is a mixture of inorganic salts and vitamins, the added amount is 0.3% of the soaking liquid mass, and the proportion of the external nutrient source is according to parts by weight: 0.5 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.5 parts of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 4 parts of zinc sulfate, 4 parts of magnesium sulfate, 3 parts of sodium nitrate, 3 parts of ammonium bicarbonate, vitamin B 6 0.05 part; adjust the pH value of soaking liquid with acetic acid to be 4.6;
[0054] (1) Drain and steam rice at 100°C for 8 minutes;
[0055] (2) spread cool, adopt 116-L bacterial strain to inoculate, inoculum size is 8% of rice dry weight;
[0056] (3) Bacteria cultivation for 40 hours in the pool, with a temperature of 33-35°C and a humidity of 85% or more;
[0057]...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Production of red yeast rice with yellowish color and higher color price
[0062] (1) Washing and soaking the rice for 14 hours, adding an additional nutrient source during soaking; the additional nutrient source is a mixture of inorganic salts and vitamins, and the added amount is 1.3% of the soaking liquid quality, and the proportioning of the additional nutrient source is in parts by weight The quantity is: 1 part of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 2 parts of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 8 parts of zinc sulfate, 8 parts of magnesium sulfate, 5 parts of sodium nitrate, 8 parts of ammonium bicarbonate, vitamin B 1 0.1 parts, Vitamin B 6 0.3 part; adjust the pH value of soaking solution with acetic acid to be 5.8;
[0063] (2) Drain and steam rice at 100°C for 15 minutes;
[0064] (3) spread cool, adopt Z6 bacterial strain to inoculate, inoculum size is 13% of rice dry weight;
[0065] (4) Bacteria cultivation for 36 hours in the pool, with the cultivation tempera...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com