Process for coproduction of normal butanol and isobutyraldehyde
A technology of isobutyraldehyde and n-butanol, which is applied in the field of co-production of n-butanol and isobutyraldehyde, can solve the problems of increased manufacturing costs, low selectivity of straight-chain alcohols, and high manufacturing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
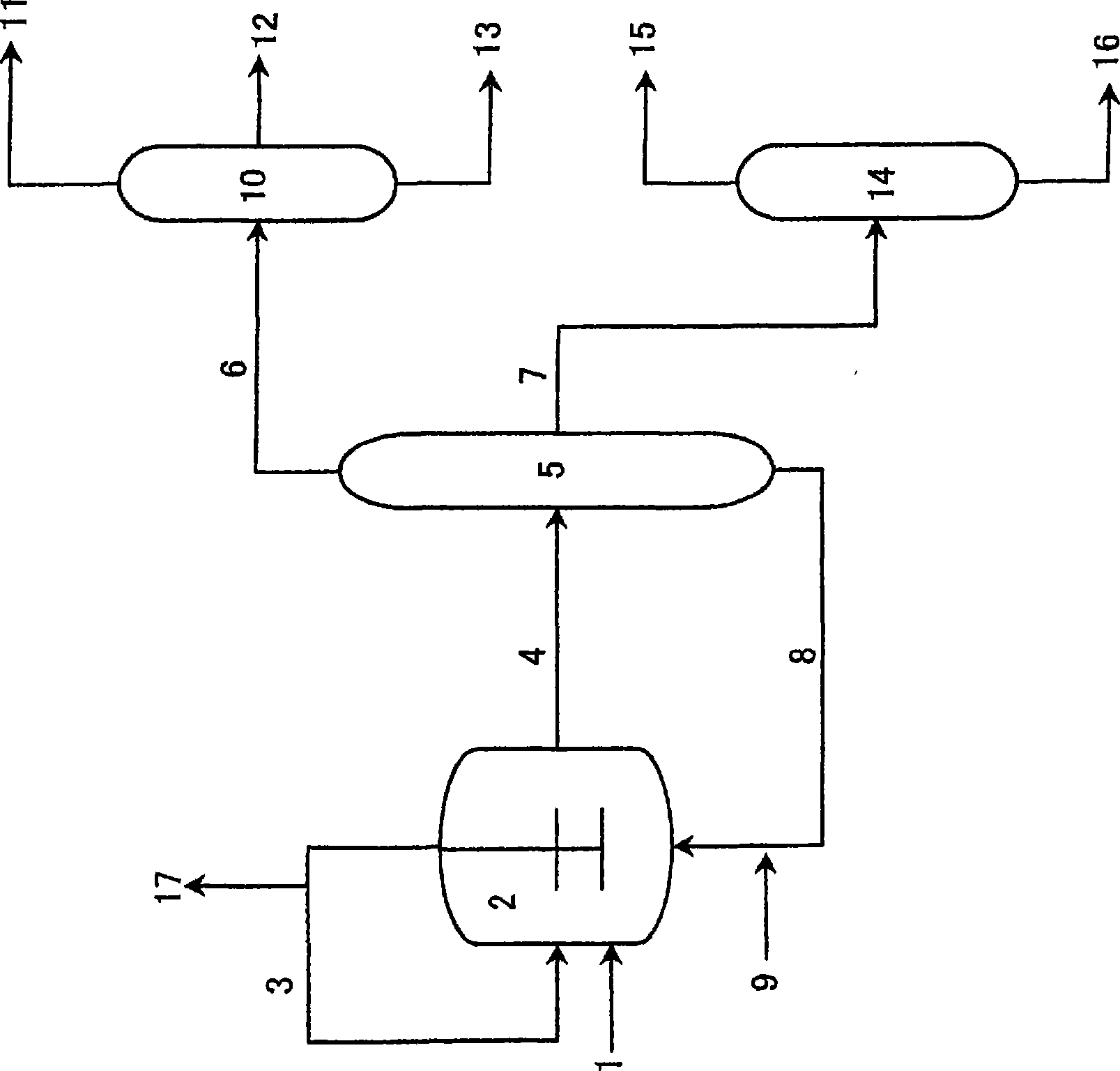
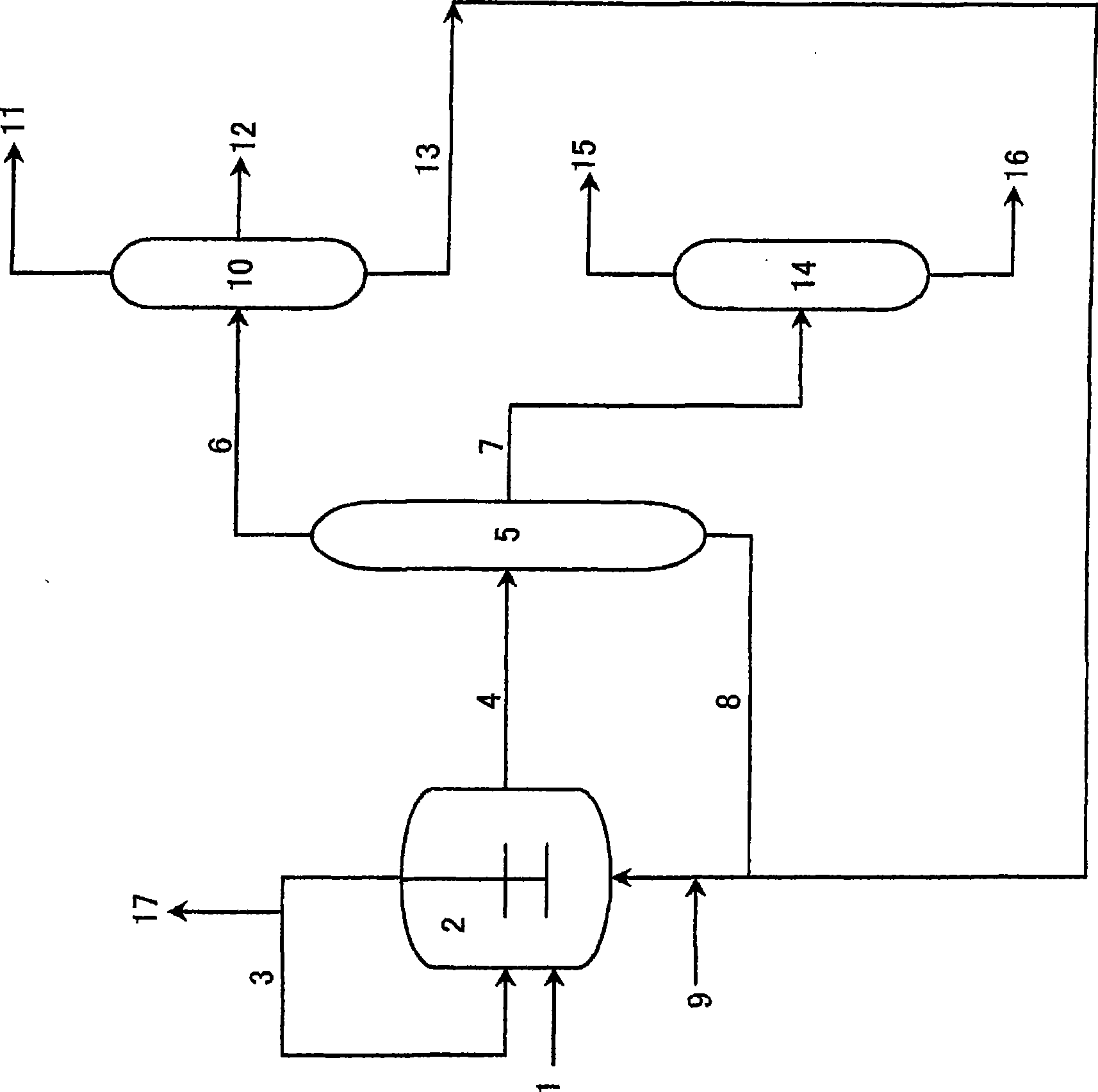
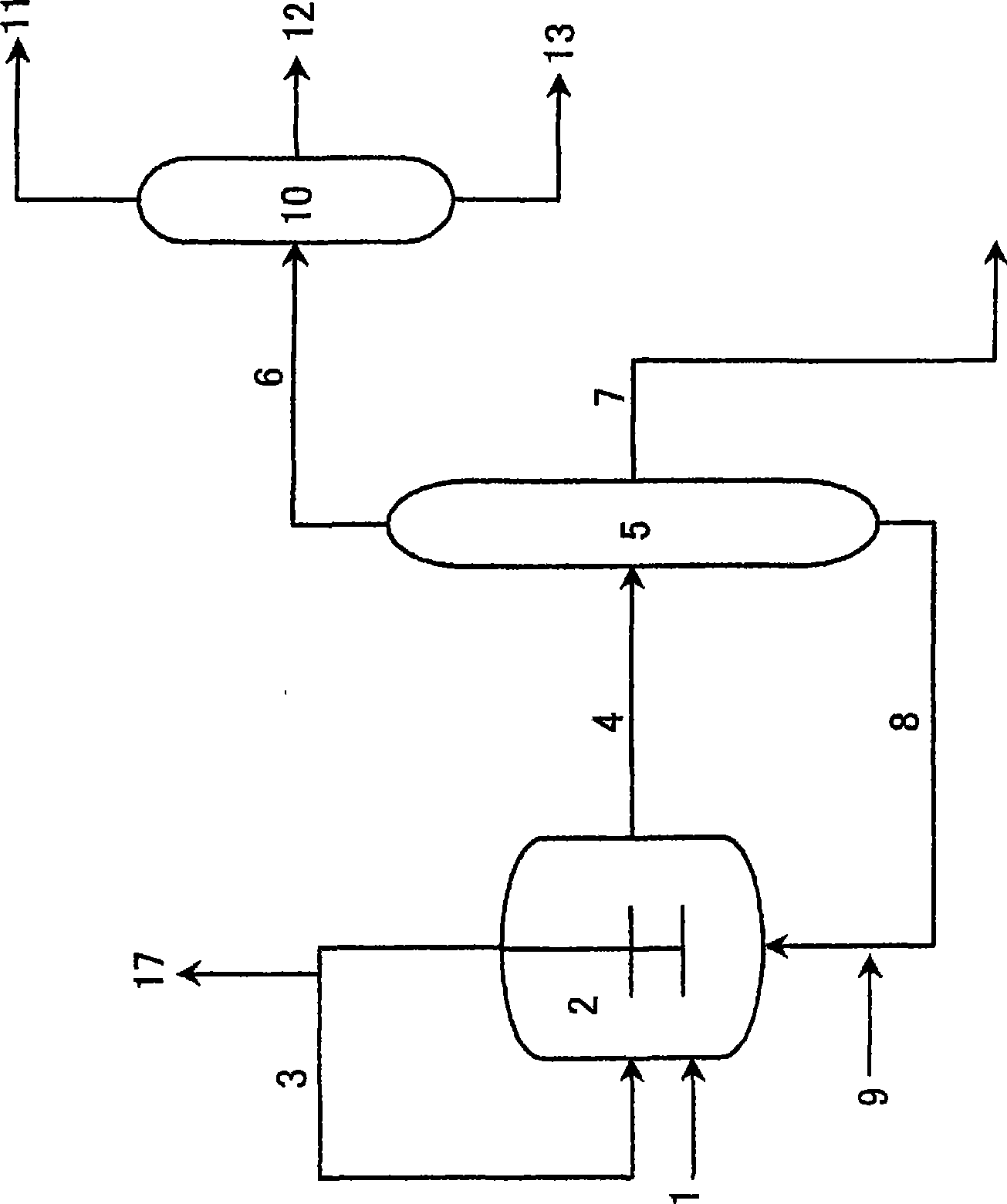
[0116] Next, a method for preparing the catalyst will be described.
[0117] The catalyst used in this embodiment can be added to the reaction zone after pre-preparation in an additional catalyst preparation zone, or can be added to the reaction zone separately, and the catalyst is prepared in the reaction zone.
[0118] As a preferred embodiment of the preparation method of the catalyst, after the co-production reaction of n-butanol and isobutyraldehyde, the product system and the catalyst system are separated, and the catalyst is recycled to the reaction zone. In this case, It is preferable to appropriately add a metal compound or an organophosphorus compound for supplementation according to the degree of deterioration and disappearance of the catalyst.
[0119] In a specific catalyst preparation method, each metal compound and each organophosphorus compound may be directly mixed to prepare the catalyst, or each component may be dissolved in an organic solvent or the like be...
Embodiment 1
[0169] Under nitrogen atmosphere, add Rh(acac)(CO) into the glass container for catalyst preparation 2 (11.2mg, 0.0434mmol), trioctylphosphine (64.3mg, 0.174mmol, relative to 1 mole Rh(acac)(CO) 24 moles), add ethanol (11.4ml, 83.6% by weight of the total weight of the reaction medium) and n-heptane (0.8ml) used as an internal standard for gas chromatograph analysis, and make it dissolve. Under nitrogen atmosphere, the solution Add it into a stainless steel autoclave with an inner volume of 50 ml prepared separately. After further pressing in propylene (1.15 g, 27.33 mmol), the autoclave was closed. After raising the temperature of the autoclave to 120° C., a mixed gas of hydrogen and carbon monoxide (mixing ratio: hydrogen / carbon monoxide=1 / 1) was injected so that the pressure in the system was 2.0 MPa, and the reaction was started. In addition, a mixed gas was introduced while bubbling into the reaction liquid through a feed pipe installed in the autoclave. Regarding stir...
Embodiment 2
[0173] In Example 1, the addition amount of trioctylphosphine was changed to 160.9 mg (0.434 mmol, relative to 1 mole of Rh(acac)(CO) 2 10 mol), except that, it reacted and analyzed similarly to Example 1. Furthermore, ethanol was 82.8% by weight of the total weight of the reaction medium.
[0174] Its result is as follows: n-butanol yield is 57.3%, isobutyraldehyde yield is 12.8%; The ratio of generation rate is as follows respectively: F NBA / F NBD =8.1, F NBA / F IBA =3.0, F IBD / F IBA =0.7. In addition, the ratio of the generation rate to the feed amount of raw material propylene to the reactor is as follows: F PPY / F IBD =7.8, F PPY / F NBA = 1.7.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com