Modified polyacrylonitrile fiber (fabric) with flame retardant or noncombustible performance and a preparation method thereof
A technology of modified fiber and polyacrylonitrile, applied in the direction of fiber type, fiber treatment, textile and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of easy combustion, limited use range, easy to generate static electricity, etc., and achieve high flame resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
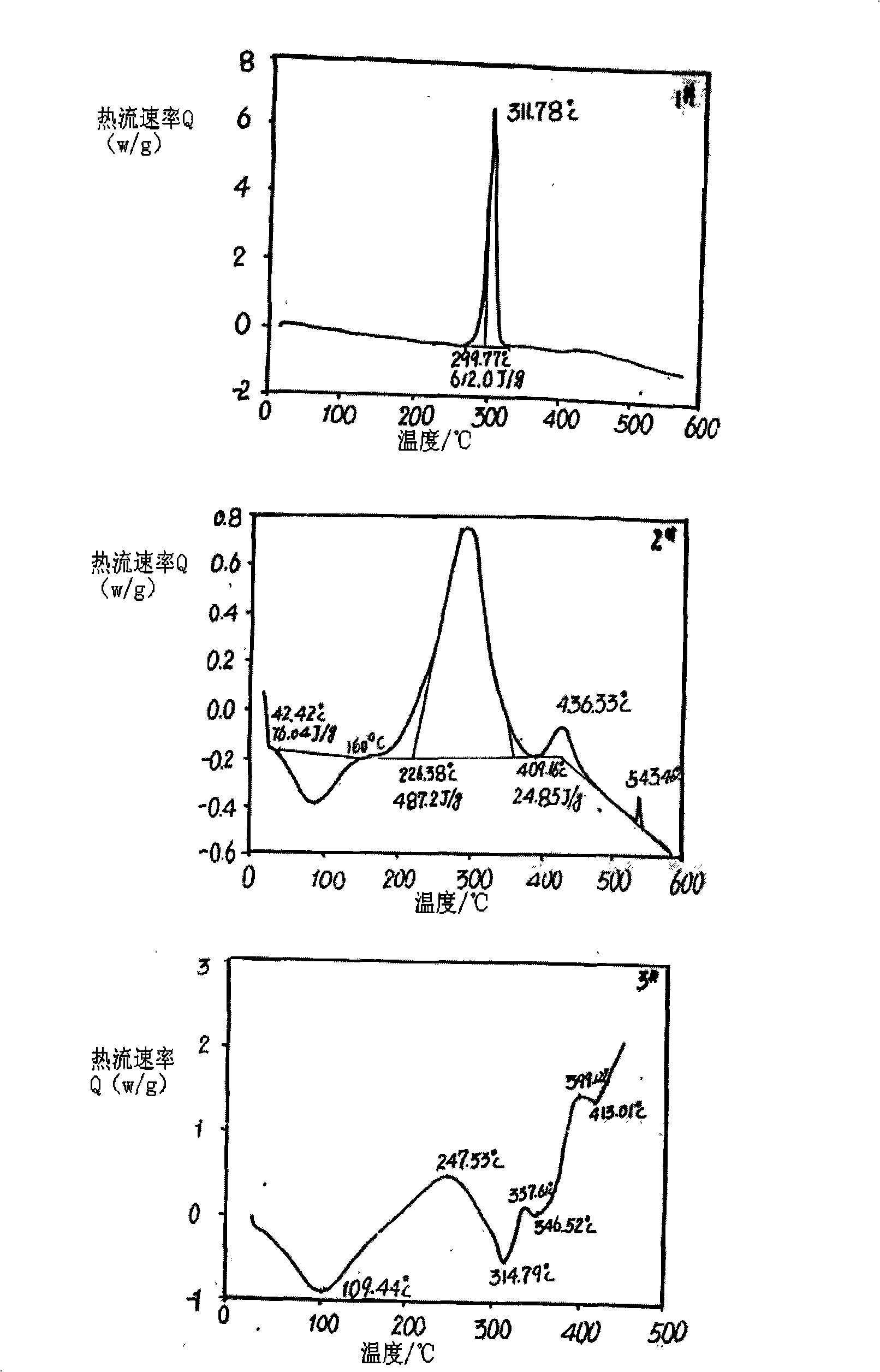
[0036] Use 15-28% hydrazine hydrate as a catalyst, add it to the reactor, heat it to 90°C, add soap to wash the oil-free acrylic fiber with a bath ratio of 1:15-25; keep the temperature in the range of 95-100°C. After stirring for 38-45 minutes, take it out, wash it with water, and dry it. Add zinc sulfate solution to the above-mentioned modified fiber at a bath ratio of 1:15-25, heat to 95-100°C, and process for 38-45 minutes under stirring, and keep the pH value at 1-5 during the reaction acidic range. That is, the flame-resistant fiber whose color is light purple is obtained. The LoI value of this flame-resistant fiber is 35. And it fully complies with ASTM D 1230 of the United States, BS 5722 of the United Kingdom (Western Europe), JIS L1091 of Japan, and GB / T17591-2006 and GB / T5455-1997 of China. When burning, after the fire source is removed (ignited), the flame-resistant fabric will not continue to burn or smolder. After the combustion is terminated or the fire sourc...
Embodiment 2
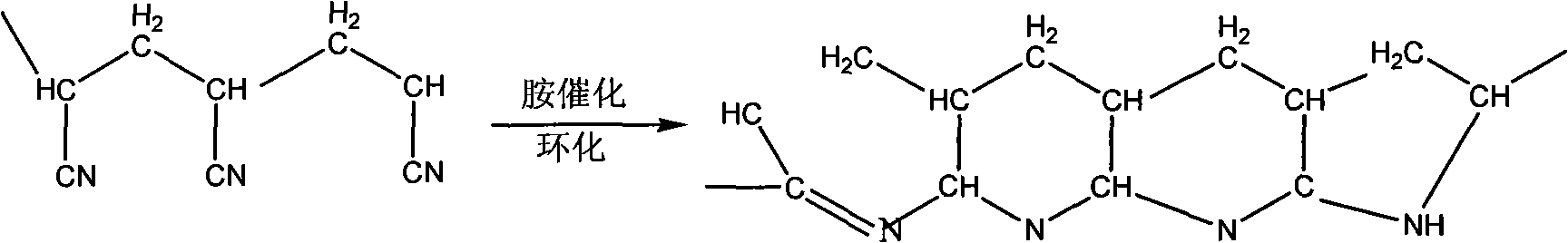
[0038] Before the flame-resistant process, wash the fabric or fiber to be treated with washing powder to remove the oil on the fabric or fiber, and then use 20-30% amine aqueous solution to catalyze the cyclization of acrylic fiber at 80-95 ° C, then wash with water, drying to obtain partially cyclized fiber (I); then hydrolyzing the fiber (I) with 10-25% NaOH aqueous solution, washing with water, and drying to obtain fiber (II); then neutralizing the alkali with 10-25% HCl aqueous solution and Further hydrolysis, washing and drying to obtain fiber (III); and then treating with calcium (Ca) salt solution to bond or chelate with fiber (III), washing and drying to obtain fiber (IV). Drying is carried out after each step of the above treatment, so that the samples of each step of treatment must be analyzed and tested. However, in actual mass production, it is not necessary to dry each product obtained. It is only necessary to wash the treatment solution of the previous step on th...
example 3
[0043] The acrylic fibers or fabrics of ternary copolymerization are used as samples, and the original acrylic samples are washed with washing powder or detergent to remove the original fibers obtained from the oil agent on the surface of the original samples (I # ). Treat the fibrils with 18-25% amine aqueous solution and add oxygen at 85-98°C for 30 minutes to make them cyclized, then wash with water and dry to obtain the modified fiber (II # ). Neutralize the alkali with 10-25% hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, and further hydrolyze, make flame-resistant fiber (III # ). Then treat modified fiber II with copper salt solution (25% aqueous solution) at 80-90°C # 30min, cleaning, drying, made non-combustible fiber (IV # ). In continuous and large-scale production, the above two-step treatment does not need to be dried. The properties of modified acrylic fibers or fabrics after the above steps are shown in Table 2
[0044] Table 2, performance indicators after each step...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com