Method for making flash memory
A memory and flash technology, applied in the field of flash memory production, can solve problems such as uneconomical, low adhesion of metal silicide layer 22, abnormal oxidation, etc., and achieve improved silicon/tungsten distribution ratio and improved word line sheet resistance. Problems, the effect of avoiding abnormal oxidation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
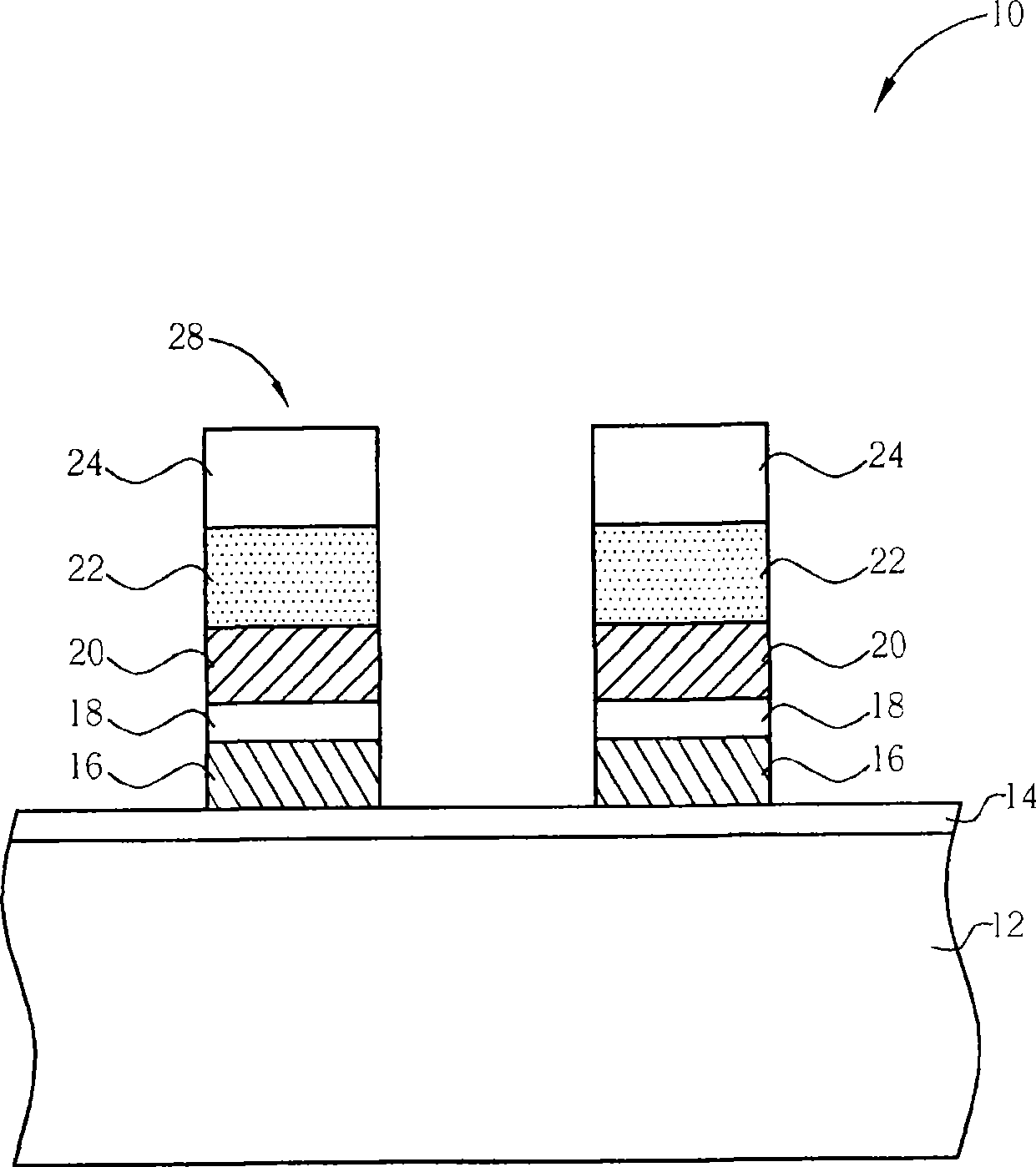
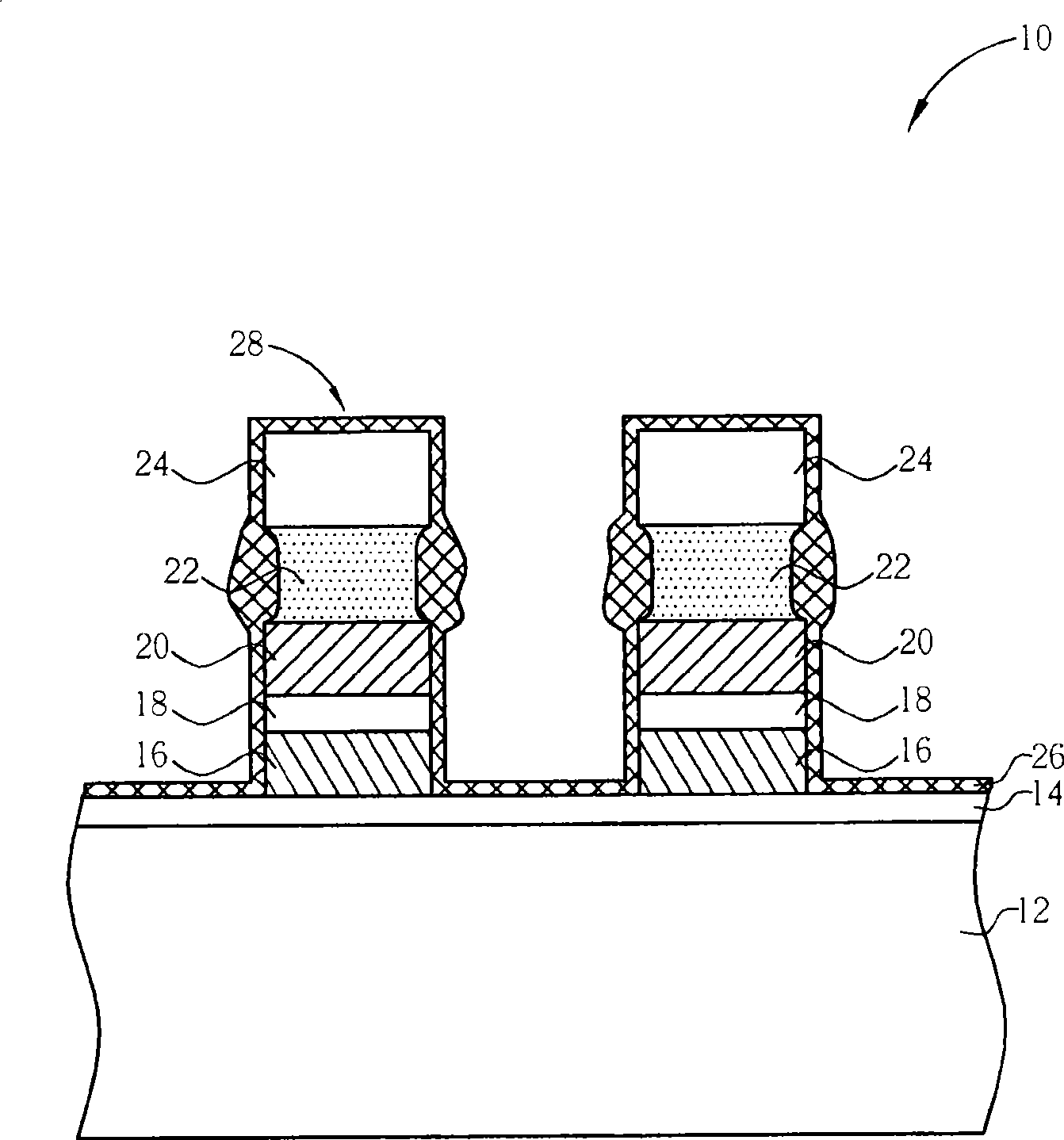
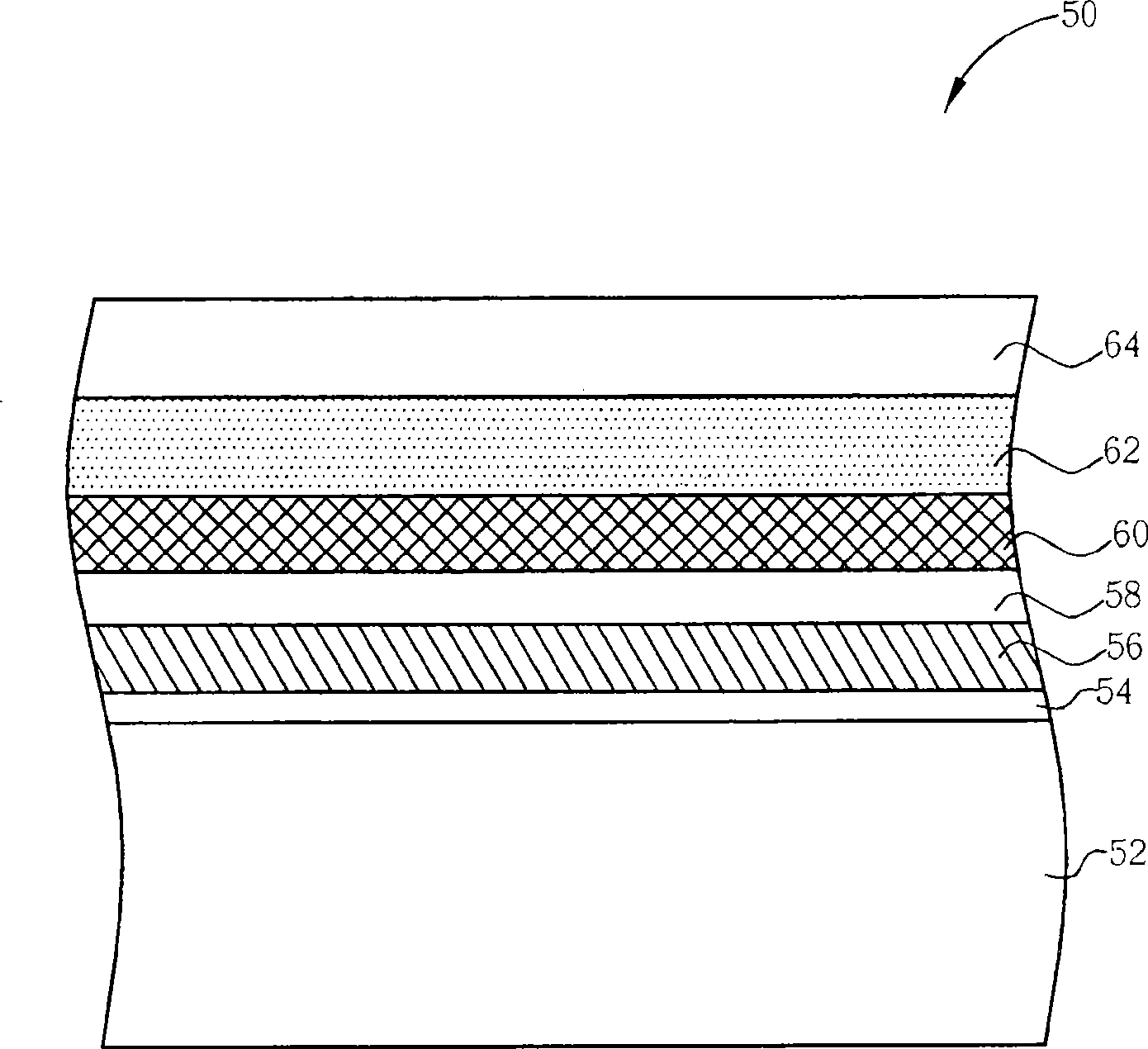
[0031] Please refer to Figure 3 to Figure 8 , Figure 3 to Figure 8 It is a process schematic diagram of the first embodiment of the method for manufacturing a flash memory 50 of the present invention. The flash memory 50 of the present invention is a split-gate flash memory. First, if image 3 As shown, a semiconductor substrate 52 is provided, which may be a silicon substrate. An oxidation process is then performed to form an oxide layer on the surface of the semiconductor substrate 52 as the floating gate dielectric layer 54 . Next, a floating gate material layer 56, a dielectric layer 58, a control gate material layer 60, a metal silicide layer 62, and a hard mask layer 64 are sequentially formed on the surface of the semiconductor substrate 52, wherein the floating The gate material layer 56 and the control gate material layer 60 preferably comprise a polysilicon material layer, the metal silicide layer 62 may comprise a tungsten silicide material, the hard mask laye...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com