Conductive filament of titanium molybdenum alloy
A titanium-molybdenum alloy, guide wire technology, applied in catheters, guide wires, medical science and other directions, can solve the problem of difficult to reach the vascular system of patients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] A large number of medical procedures require the use of guide wires within the patient's passageway. Many of these procedures involve the use of a guide as a guidewire within the patient's vasculature to insert a catheter or other device. Guide wires have been manufactured from stainless steel, which is somewhat rigid but does not bend easily within the patient's canal. Nickel-titanium alloy is also often used to make guide wires. Its softness and elasticity are better than stainless steel, and it also has a better memory, but its rigidity is not enough, so its propulsion is not as good as stainless steel. In addition, nitinol does not bend easily, so its distal tip is not easy to shape.
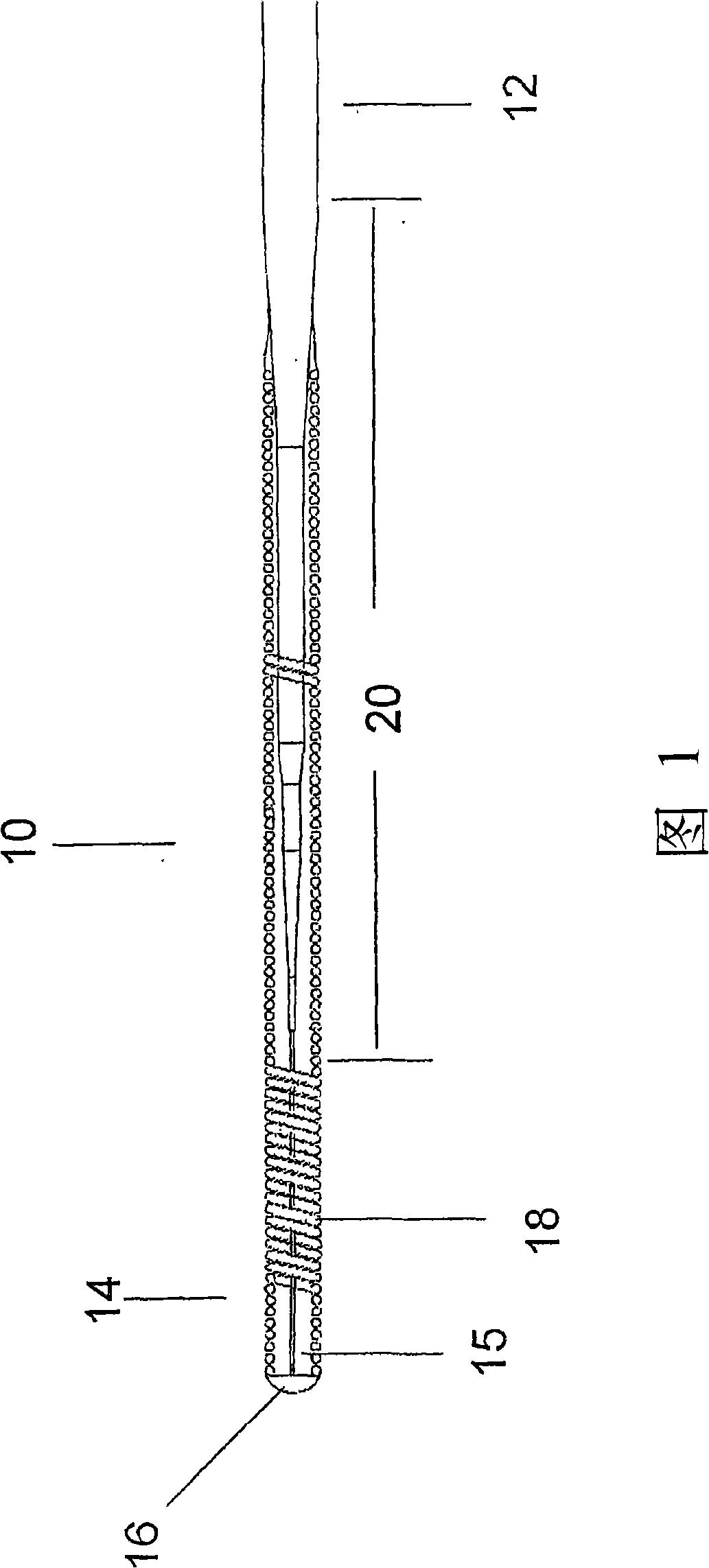
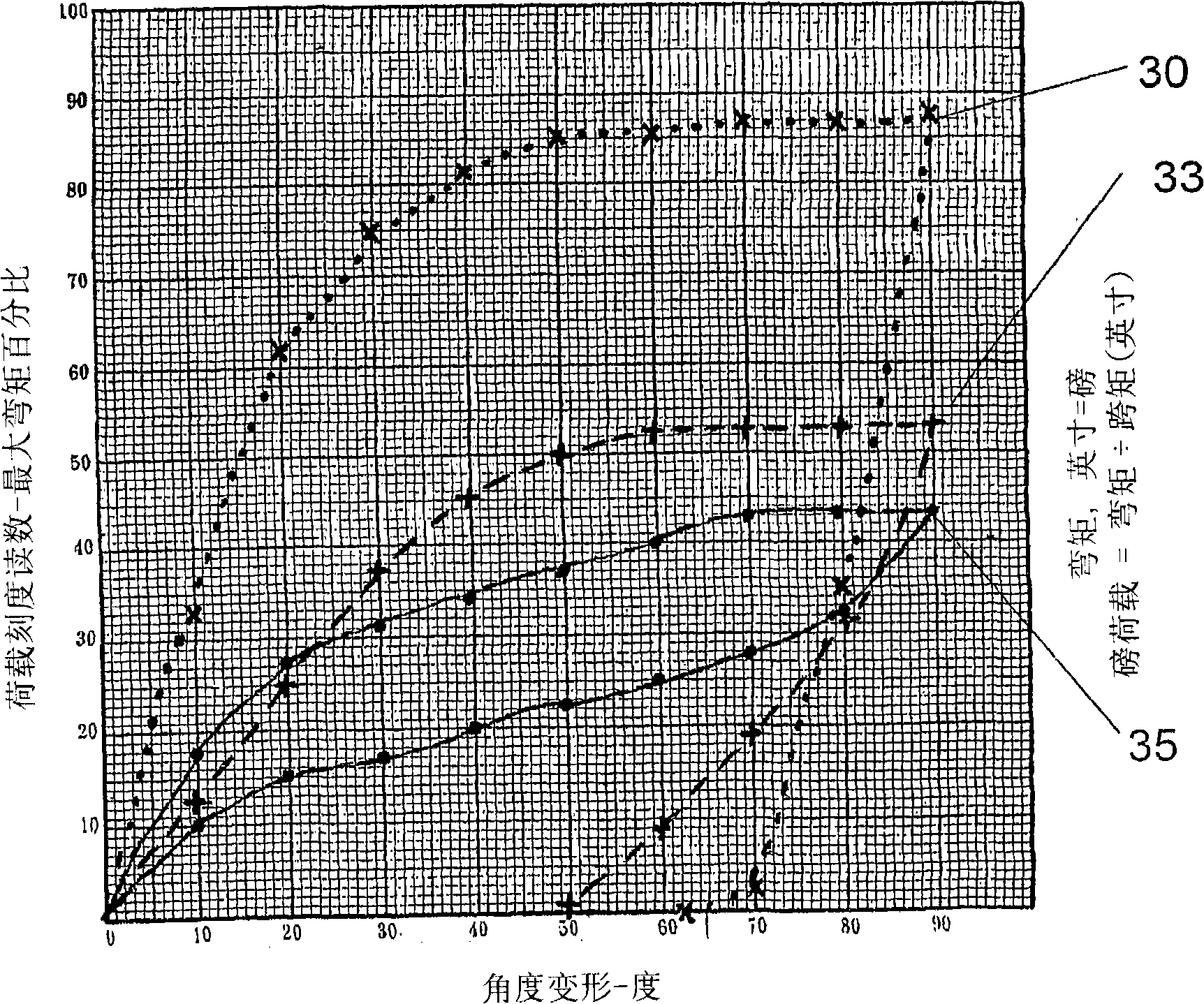
[0031] The guide wire shown in Figure 1 is made of titanium-molybdenum alloy, and its performance is between stainless steel and nickel-titanium alloy. Compared to guidewires made of other materials, titanium molybdenum alloys are easier to use, with better torsion, flexibility and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com