Purification process for piasmid DNA
一种质粒、溶胞产物的技术,应用在DNA制备、重组DNA技术、生物化学设备和方法等方向,能够解决可能性没被到认识到等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0099] Flocculation of host cell debris with PEG
[0100] Analytical Methods - Analytical methods used included: (i) anion-exchange ("AEX") HPLC assay; (ii) gel electrophoresis with E-gel (Invitrogen; 0.8% agarose with ethidium bromide) and (iii) qPCR using Taq man PCR assay. The E-gel was run at 60 volts for 50 minutes with a loading volume of 20 [mu]L per well. Samples were pretreated with ethanol precipitation (2 equal volumes) and centrifuged for 5 minutes in an Eppendorf microcentrifuge before performing the E-gel assay. The supernatant was decanted and the pellet was allowed to dry for 5 min before resuspending in 10 mM Tris buffer pH 8.0. The pretreated samples were then diluted in IX TAE buffer before loading onto the E-gel. The same pretreatment was performed for the samples used for qPCR analysis.
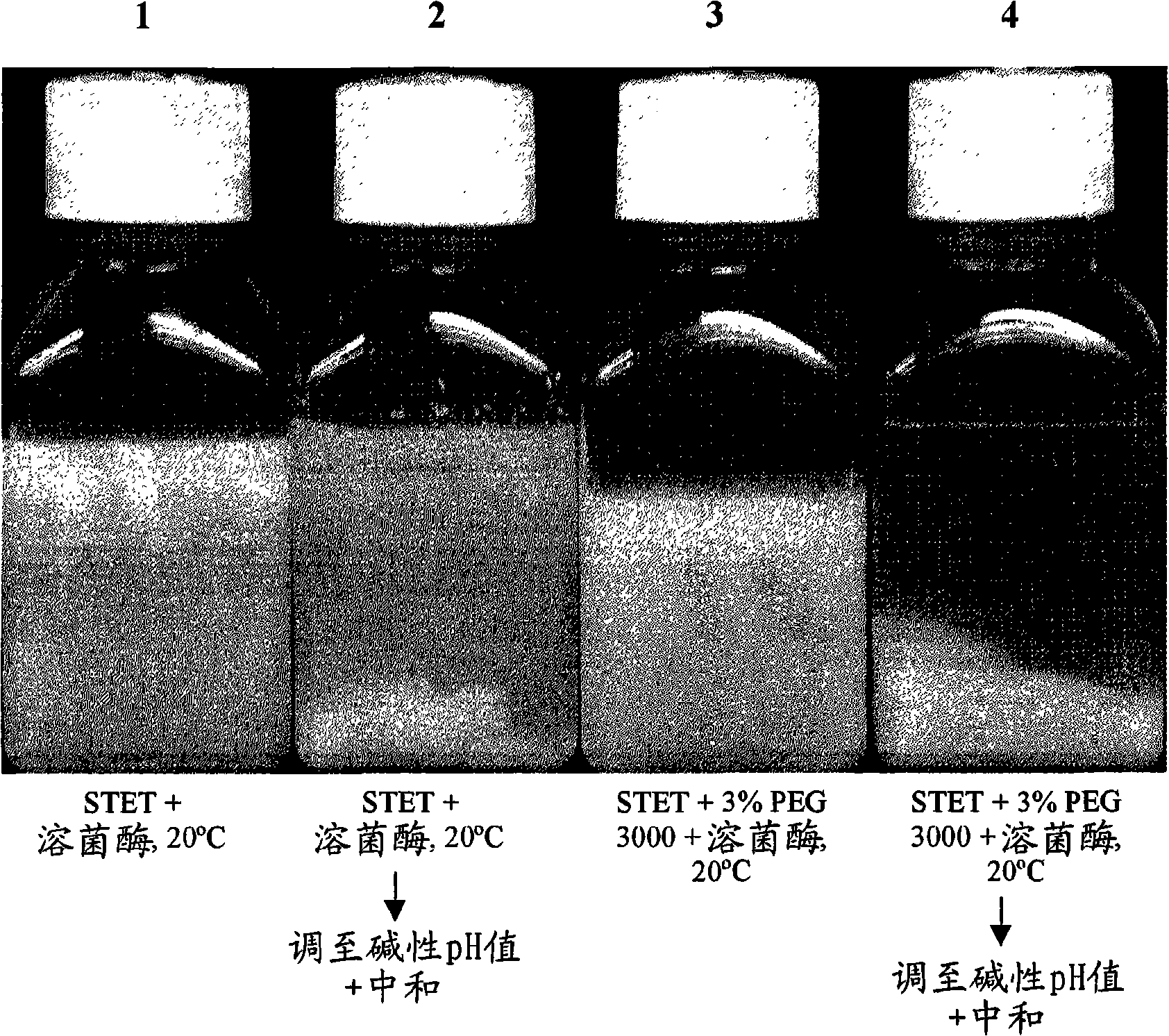
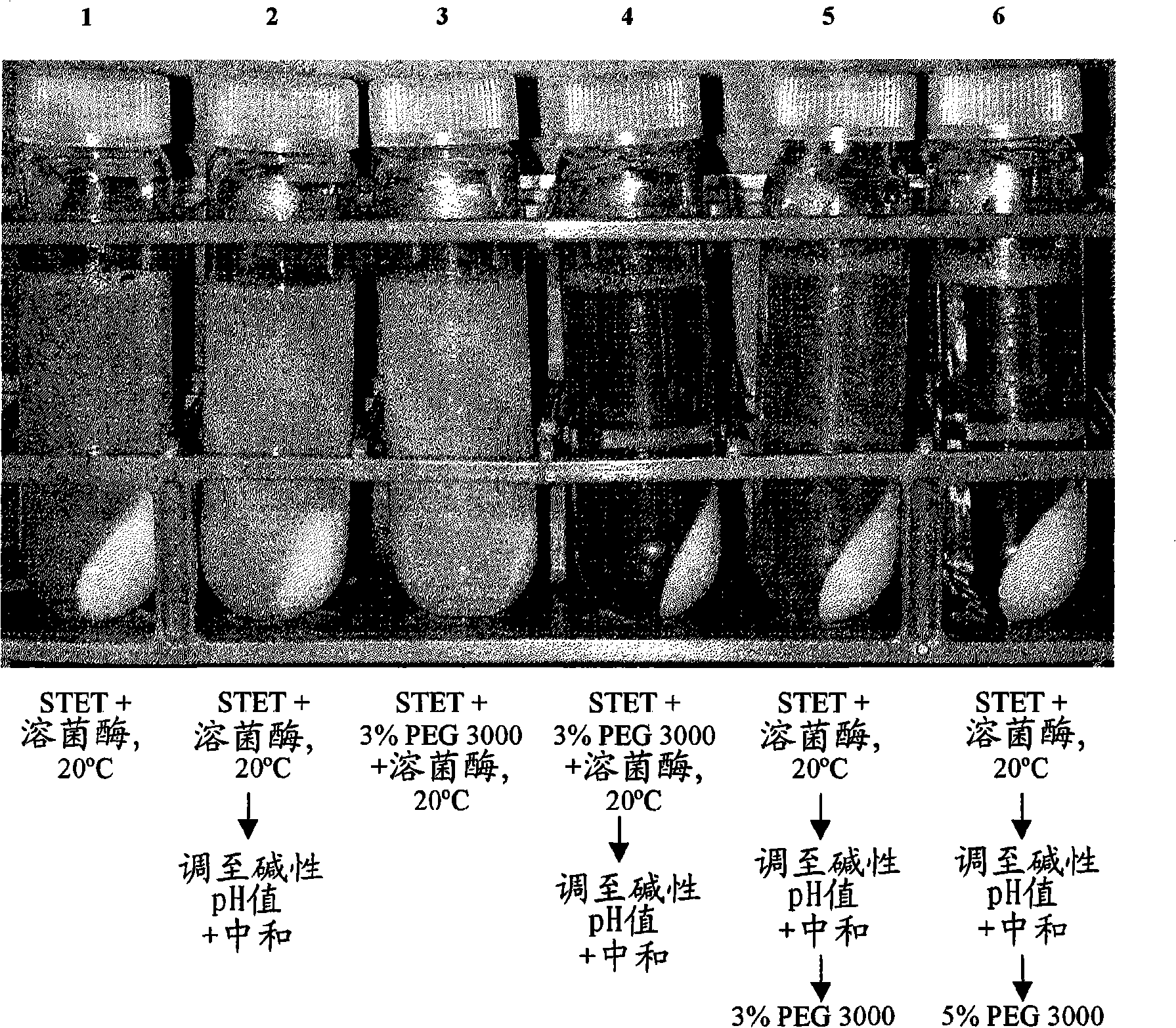
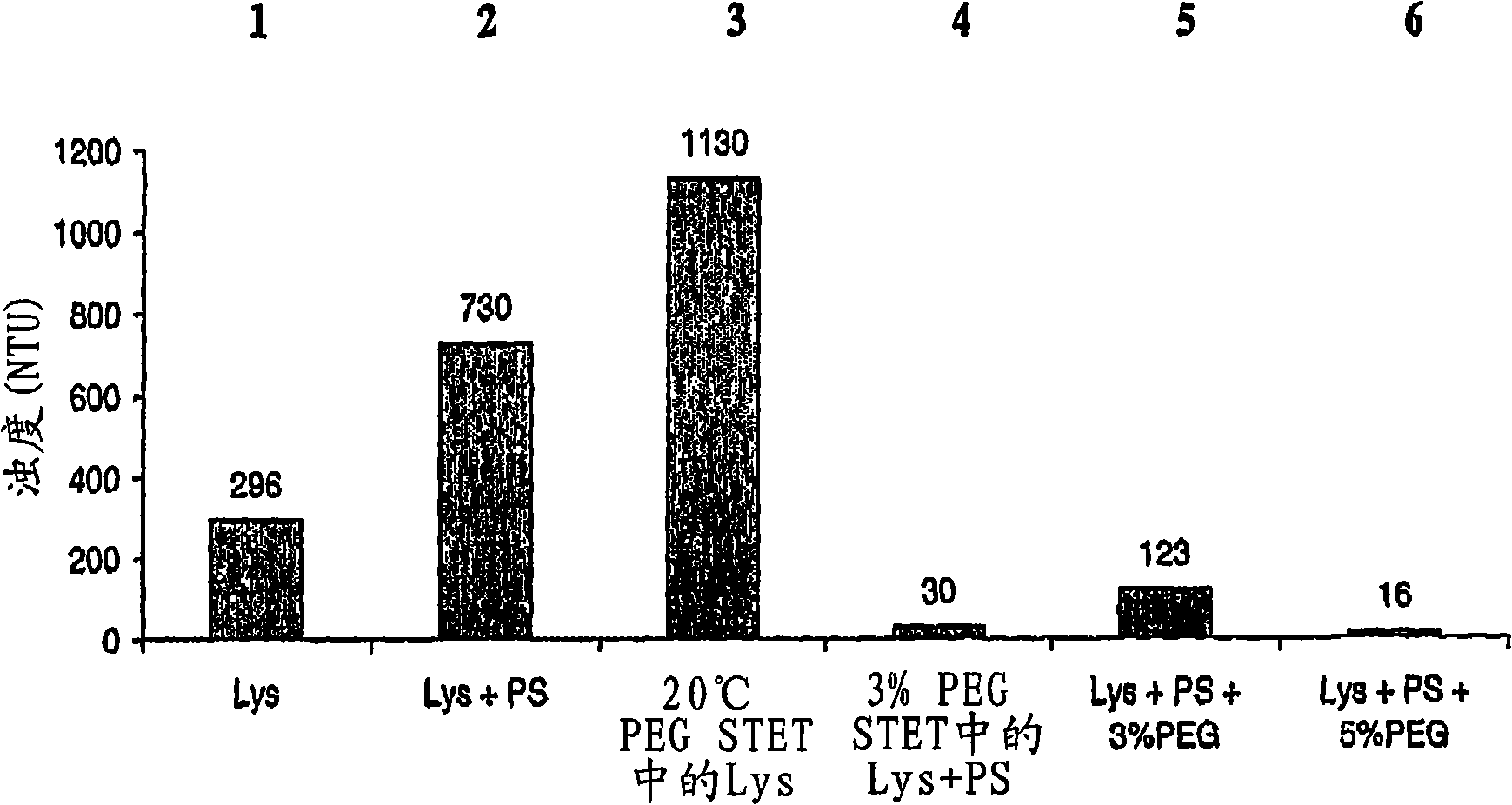
[0101] Lysis with Lysozyme - An initial E. coli lysis study was performed to assess the effect of lysozyme, base / acid treatment (addition of base to pH 12-13 followed...
Embodiment 2
[0111] Plasmid DNA purification after lysozyme incubation, alkali / acid treatment and PEG flocculation
[0112] Analytical Methods - See Example 1 for methods.
[0113] 30 L Lysis: Frozen cells containing supercoiled DNA collected from a 2,000 L E. coli fermentation were thawed in a warm (approximately 35 °C) water bath and processed in a 50 L Lee tank with a 5-inch A310 impeller using STET buffer ( 50mM Tris HCl, 100mM EDTA, 2% v / v X-100, 8% w / v sucrose, pH 8.2) diluted to OD 600 70. A resuspension volume of 30 L was obtained. Add Ready-Lyse TM Lysozyme (500 U / mL, Epicentre), and the resulting cell slurry was incubated at 37°C for ca. 2 hours. The cell slurry was then cooled to 20°C and 5M NaOH was slowly added subsurface over 60 minutes to raise the pH of the lysozyme lysate to ca. 12. After a 30-minute rest period, then over 60 minutes 2.5M acetic acid was added to lower the pH to 8-9. PEG 3000 (50% w / v) in RCM 6 (saline, 150 mM NaCl) was then slowly added to a final...
Embodiment 3
[0125] Final DNA polishing treatments: PEG-precipitation and microfiltration of PEG precipitate
[0126] One prior DNA purification method described in U.S. Patent Application No. 09 / 875,379 (U.S. Publication No. US2002 / 0012990) utilized an ultrafiltration ("UF") step at the end of the method to separate calcium silicate (e.g., LRA ) filtrate was concentrated to ~7+ mg / mL DNA, followed by 10X diafiltration for buffer exchange into formulation buffer, PBS (see Figure 6 A), said patent application number is incorporated herein by reference. This final finishing step is satisfactory for volumes of about 100 L or less, but larger production scale purification processes show pump sizes and flow rates starting to reach the limits of the technology. To avoid these scale-up problems, the final UF step of the plasmid DNA method was replaced with a PEG precipitation step, followed by two separate filtration / diafiltration steps (see Figure 6 B). The first filtration / diafiltration st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com