Method for extracting proanthocyanidins from cranberry
A technology of proanthocyanidins and cranberry, applied in the direction of organic chemistry and the like, can solve the problems of high cost and complicated process, and achieve the effects of low production cost, easy industrialization and simple process flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
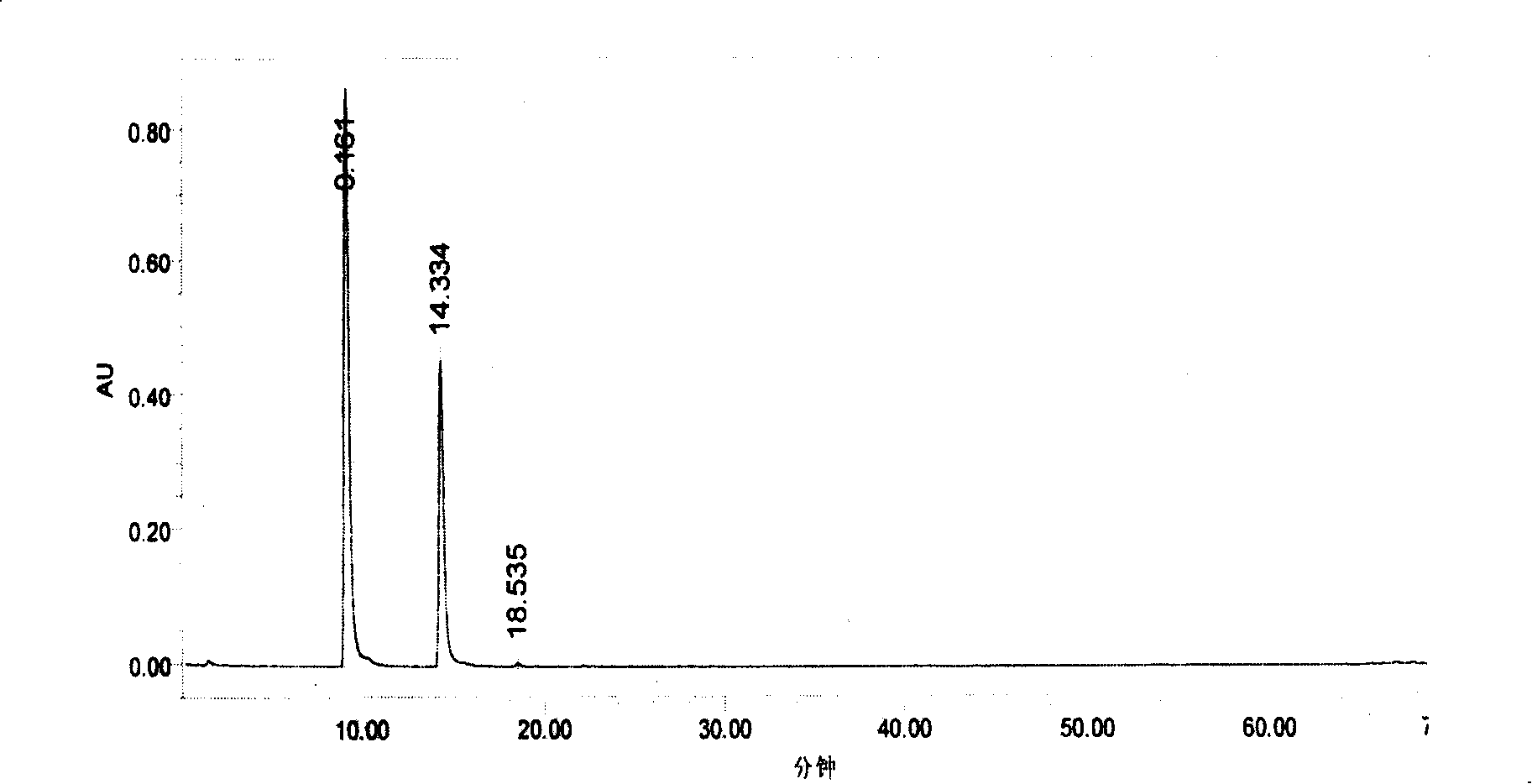
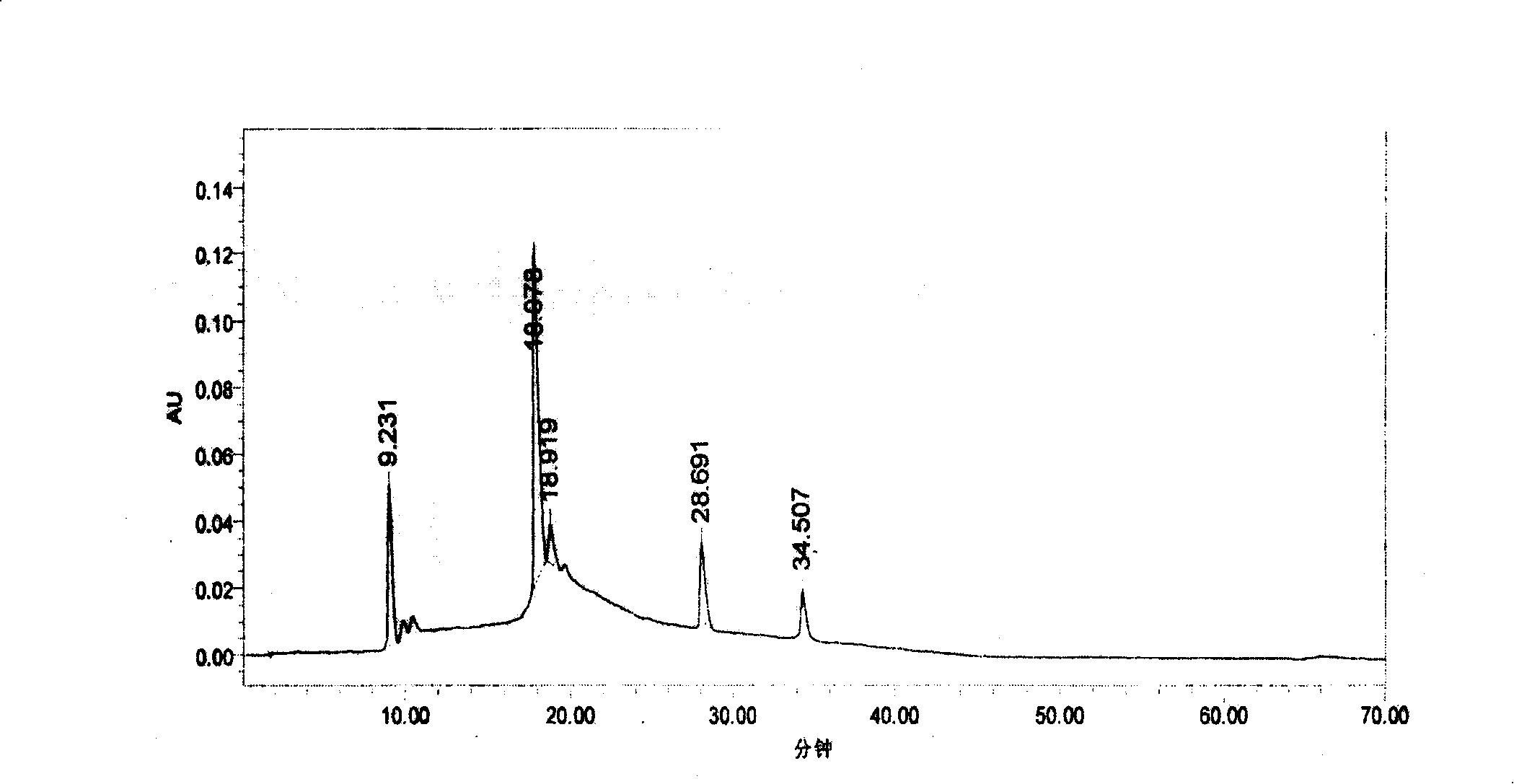
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1 The method for extracting proanthocyanidins from cranberries
[0033] 1. Raw material processing:
[0034] Grind 200 grams of cranberries in 50 ml of solvent at 4°C for 5 minutes (solvent is: 70% acetone by volume, 30% methanol by volume, 0.1g / 100ml citric acid), get the supernatant after centrifugation, and remove the pulp , and then the solvent was evaporated to dryness, and the extract was dissolved in water to obtain a cranberry extract.
[0035] 2. Solvent degreasing:
[0036] Add an equal volume of petroleum ether to the cranberry extract for degreasing treatment, repeat once for 3 hours each time. Evaporate and dry the degreased cranberry extract under reduced pressure to obtain cranberry extract.
[0037] 3. Sephadex LH-20 gel column chromatography separation and purification:
[0038] The LH-20 column (purchased from Pharmacia Company) was equilibrated overnight with 50% ethanol aqueous solution by volume percentage; the cranberry extract was d...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Embodiment 2 The method for extracting proanthocyanidins from cranberries
[0051] 1. Raw material processing:
[0052] 200 grams of cranberries were ground for 5 minutes at 25°C in 100ml of solvent (solvent: 70% acetone by volume, 30% methanol by volume, 0.1g / 100ml citric acid), and the pulp was removed by sieve filtration, and then the solvent Evaporate to dryness, and dissolve the extract in water to obtain a cranberry extract.
[0053] 2. Solvent degreasing:
[0054] Add an equal volume of petroleum ether to the cranberry extract for degreasing treatment, and repeat twice for 1 hour each time. Evaporate and dry the degreased cranberry extract under reduced pressure to obtain cranberry extract.
[0055] 3. Sephadex LH-20 gel chromatography:
[0056] The LH-20 column (purchased from Pharmacia Company) was equilibrated overnight with 50% ethanol by volume percentage, and the cranberry extract was dissolved in 10ml volume percentage 50% ethanol and loaded immediately ...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Embodiment 3 The method for extracting proanthocyanidins from cranberries
[0058] 1. Raw material processing:
[0059] Dilute 10 ml of cranberry juice concentrate (commercially available) to 25 ml with water to obtain a cranberry extract.
[0060] 2. Solvent degreasing:
[0061] Add an equal volume of petroleum ether to the cranberry extract for degreasing treatment, repeat once, 1 hour each time. Evaporate and dry the degreased cranberry extract under reduced pressure to obtain cranberry extract.
[0062] 3. Sephadex LH-20 gel chromatography:
[0063] The LH-20 column (purchased from Pharmacia Company) was equilibrated overnight with 50% ethanol by volume, and the cranberry extract was dissolved in 10ml 50% ethanol by volume, and loaded immediately after vortexing (10 grams of LH-20 gel, The column volume is 40ml); wash the column with 50% ethanol by volume, and the flow rate is 2.5ml / min, until the eluate that flows out becomes colorless, discard the washing solu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com